Trino架构
架构
如下:
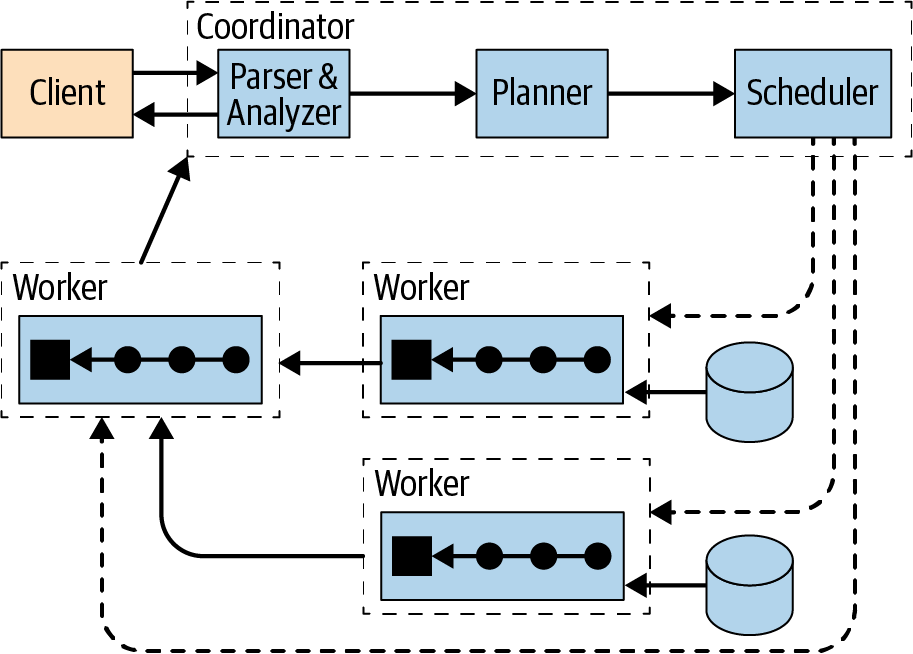
采用了 MPP 架构,coordinate 收到 SQL 后,语法解析,生成 plan,然后调度到 各个 worker 上执行
这里的 worker 跟 Spark 不同,它是常驻的进程
worker 会汇总数据,coordinate 收集汇总 workder 节点的数据并写到 buffer 中,然后返回给用户
实际上这里有三个角色
- discovery
- coordinate
- worker
连接器
使用这种连接器的架构,这样可以很方便的将外部数据源纳入进来
只要实现了相关的 API 接口,就可以扩展一个数据源
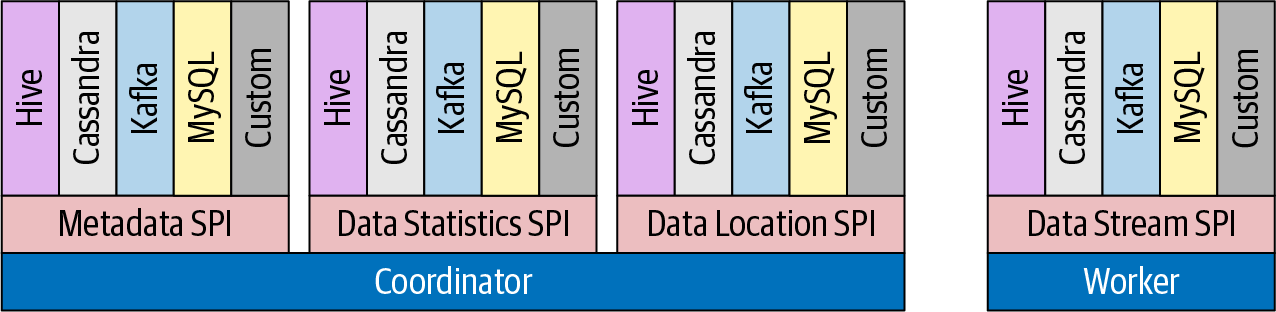
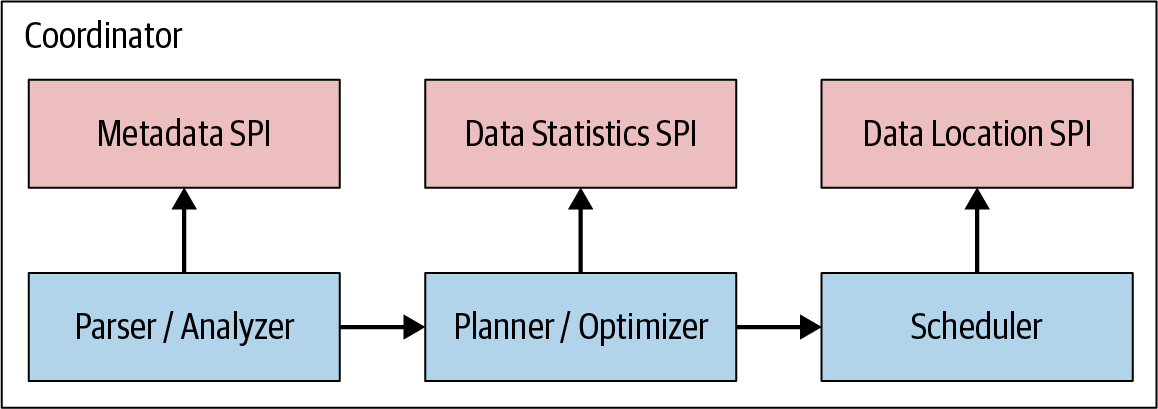
接口信息
- 在解析sql 时,需要 metadata 信息,获取表结构
- 在做 CBO 时,需要有表的统计信息
- 在调度时,需要有数据的位置信息,这也是对存算分离架构的一种优化
查询计划
将逻辑计划转换 分布式计划
会将大的逻辑计划,拆分成多个 Stage
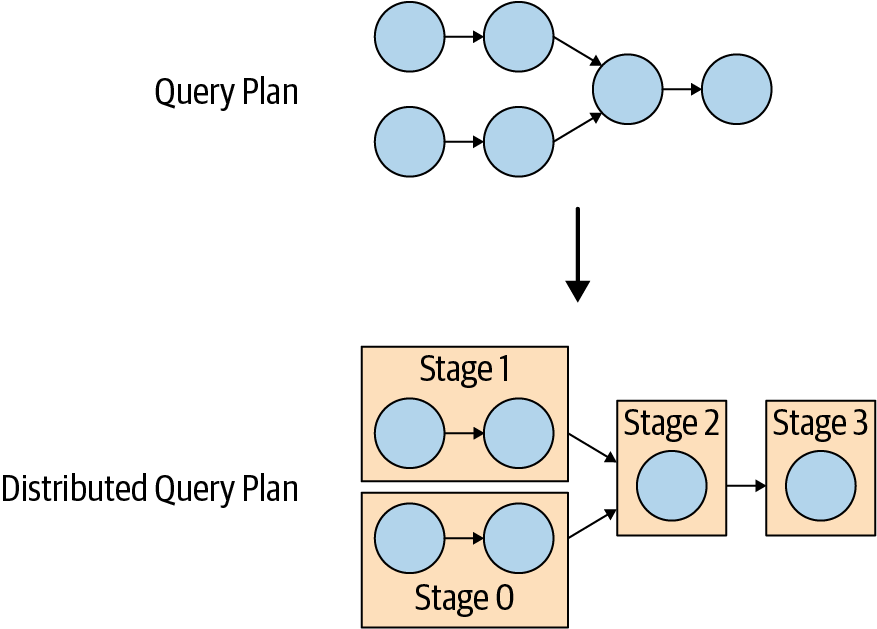
物理执行和调度
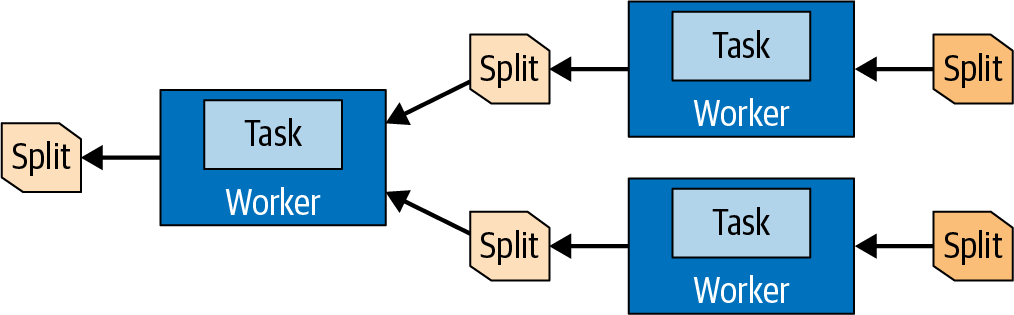
一个 Stage 会包含多个 Task
task就是计划段(plan fragment)分配给worker运行时的称呼
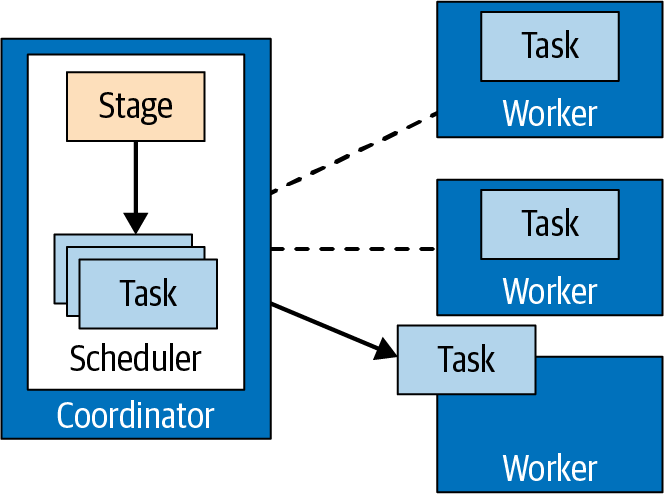
Split
Page
- 数据源阶段的task以page(页)这种格式生成数据
- page是以列式格式存储的多行数据集合
- page数据通过stage的依赖关系,流向下游的stage
- 不同的stage之间通过exchange运算交换数据,这种运算符从上游的stage中读取数据
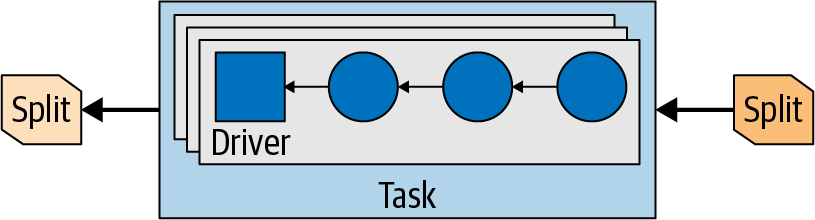
Driver
- 当一个task创建出来后,它为每一个split初始化一个driver
- 每个driver初始化一个流水线的operator,然后处理一个split的数据
- 一个task可能会使用多个driver,取决于Presto的配置
- 一旦所有的driver都完成了,数据被传递到了下一层split,driver和任务结束了他们的工作,之后被销毁
文档
优化
Dynamic filtering,这个跟 spark、impala 的类似
|
|
如果没有动态 filter,会全表扫描 事实表,加了 filter后,会将 维度表的 谓词 push 到 事实表,提升效率
生成的查询计划如下:
|
|
dynamicFilterAssignments = {d_date_sk -> #df_370} 这里就是 动态 filter
Administration
- Observability with OpenTelemetry
- Spill to disk
- Resource groups,基于文件的方式、基于DB 的方式
- Graceful shutdown
- Distributed sort,多借点部分排序,但最后需要在单节点汇总
- Fault-tolerant execution,重试,或者其他组件来执行
- Event Listener,类似 spark 的 Event Listener
支持的连接器
- Accumulo
- Atop
- BigQuery
- Black
- Cassandra
- ClickHouse
- Delta
- Druid
- Elasticsearch
- Hive
- Hudi
- Iceberg
- Ignite
- JMX
- Kafka
- Kinesis
- Kudu
- Local
- MariaDB
- Memory
- MongoDB
- MySQL
- OpenSearch
- Oracle
- Phoenix
- Pinot
- PostgreSQL
- Prometheus
- Redis
- Redshift
- SingleStore
- Snowflake
- SQL
- System
- Thrift
- TPCDS
- TPCH
Query optimizer
Table statistics
Optimizer Properties
这里有很多优化规则,举几个
- optimizer.push-aggregation-through-outer-join 聚合函数,下推到 outer join
|
|
JOIN 策略
- optimizer.join-reordering-strategy
- optimizer.max-reordered-joins
并行读取表分区的 task
- optimizer.use-table-scan-node-partitioning
- optimizer.table-scan-node-partitioning-min-bucket-to-task-ratio
colocated-join
- optimizer.colocated-joins-enabled
- 这个 doris 也有,就是 join 两边的 join 条件,谓词条件都满足本地化,不用 exchange 了
其他一些
- 包括 task 输入大小的
- hash join 的build 端大小阈值
- 对于 filter 谓词后 rows 数量的评估
表统计信息输出的列
| Column | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| column_name | The name of the column | NULL in the table summary row |
| data_size | The total size in bytes of all of the values in the column | NULL in the table summary row. Available for columns of string data types with variable widths. |
| distinct_values_count | The estimated number of distinct values in the column | NULL in the table summary row |
| nulls_fractions | The portion of the values in the column that are NULL | NULL in the table summary row. |
| row_count | The estimated number of rows in the table | NULL in column statistic rows |
| low_value | The lowest value found in this column | NULL in the table summary row. Available for columns of DATE, integer, floating-point, and exact numeric data types. |
| high_value | The highest value found in this column | NULL in the table summary row. Available for columns of DATE, integer, floating-point, and exact numeric data types. |
CBO
普通 explain
EXPLAIN ANALYZE,统计运行时真正信息
explain 的 fragment 类型
- SINGLE,Fragment is executed on a single node.
- HASH,Fragment is executed on a fixed number of nodes with the input data distributed using a hash function.
- ROUND_ROBIN,Fragment is executed on a fixed number of nodes with the input data distributed in a round-robin fashion.
- BROADCAST,Fragment is executed on a fixed number of nodes with the input data broadcasted to all nodes.
- SOURCE,Fragment is executed on nodes where input splits are accessed.
join enumeration 的属性
- AUTOMATIC (default) - enable full automatic join enumeration
- ELIMINATE_CROSS_JOINS - eliminate unnecessary cross joins
- NONE - purely syntactic join order
join 类型:
- BROADCAST - broadcast join distribution is used for all joins
- PARTITIONED - partitioned join distribution is used for all join
限制广播的参数
- join-max-broadcast-table-size,默认 100MB
- join_max_broadcast_table_size,session property
join order
- 默认是 最右边作为 build,但是多表时情况更复杂
- join策略是 largest tables to the smallest,最大 join 最小,跟 doris 类似
|
|
Pushdown
The results of this pushdown can include the following benefits:
- Improved overall query performance
- Reduced network traffic between Trino and the data source
- Reduced load on the remote data source
支持的下推种类
- Predicate pushdown
- Projection pushdown
- Dereference pushdown,复杂类型时,下推读取内嵌的某个类型
- Aggregation pushdown
- Join pushdown
- Limit pushdown
- Top-N pushdown
下推可能只是支持 PG,官网文档给出的例子是 基于 PG 的
|
|
scan table 的时候的 sql 为:
|
|
也就是将 join 直接下推到数据源了
但是测试了 mysql 则不行
sql为
|
|
explain 后的查询计划,看起来是在 trino 端做了 join,没有下推成功
|
|
SQL
支持的对象存储
- Delta Lake connector
- Hive connector
- Hudi connector
- Iceberg connector
SQL 语法
支持的 函数类型
- Aggregate
- Array
- Binary
- Bitwise
- Color
- Comparison
- Conditional
- Conversion
- Date
- Decimal
- Geospatial
- HyperLogLog
- IP
- JSON
- Lambda
- Logical
- Machine
- Map
- Math
- Quantile
- Regular
- Session
- Set
- String
- System
- Table
- Teradata
- T-Digest
- URL
- UUID
- Window
支持的 SQL 语法
- ALTER
- ALTER
- ALTER
- ALTER
- ANALYZE
- CALL
- COMMENT
- COMMIT
- CREATE
- CREATE
- CREATE
- CREATE
- CREATE
- CREATE
- CREATE
- CREATE
- DEALLOCATE
- DELETE
- DENY
- DESCRIBE
- DESCRIBE
- DESCRIBE
- DROP
- DROP
- DROP
- DROP
- DROP
- DROP
- DROP
- EXECUTE
- EXECUTE
- EXPLAIN
- EXPLAIN
- GRANT
- GRANT
- INSERT
- MATCH_RECOGNIZE
- MERGE
- PREPARE
- REFRESH
- RESET
- RESET
- REVOKE
- REVOKE
- ROLLBACK
- SELECT
- SET
- SET
- SET
- SET
- SET
- SHOW
- SHOW
- SHOW
- SHOW
- SHOW
- SHOW
- SHOW
- SHOW
- SHOW
- SHOW
- SHOW
- SHOW
- SHOW
- SHOW
- START
- TRUNCATE
- UPDATE
- USE
- VALUES
SQL routines
有点像存储过程
- 内联方式
|
|
- A very simple routine that returns a static value without requiring any input:
|
|
- string 的例子
|
|
- 基于条件的
|
|