下载地址
简单例子
Janino as an Expression Evaluator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import org.codehaus.commons.compiler.CompileException;
import org.codehaus.janino.ExpressionEvaluator;
public class Simple1 {
public static void
main(String[] args) throws CompileException, InvocationTargetException {
// Now here's where the story begins...
ExpressionEvaluator ee = new ExpressionEvaluator();
// The expression will have two "int" parameters: "a" and "b".
ee.setParameters(new String[] { "a", "b" }, new Class[] { int.class, int.class });
// And the expression (i.e. "result") type is also "int".
ee.setExpressionType(int.class);
// And now we "cook" (scan, parse, compile and load) the fabulous expression.
ee.cook("a + b");
// Eventually we evaluate the expression - and that goes super-fast.
int result = (Integer) ee.evaluate(new Object[] { 19, 23 });
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(ee.evaluate(new Object[] { 123, 456 }));
}
}
|
结果:
Janino自带的例子
1
2
|
java -cp .;D:\janino-3.1.9.jar;D:\janino-commons-compiler-3.1.9.jar
org.codehaus.commons.compiler.samples.ExpressionDemo -et double -pn x -pt double "Math.sqrt(x)" 99
|
结果:
1
|
Result = 9.9498743710662
|
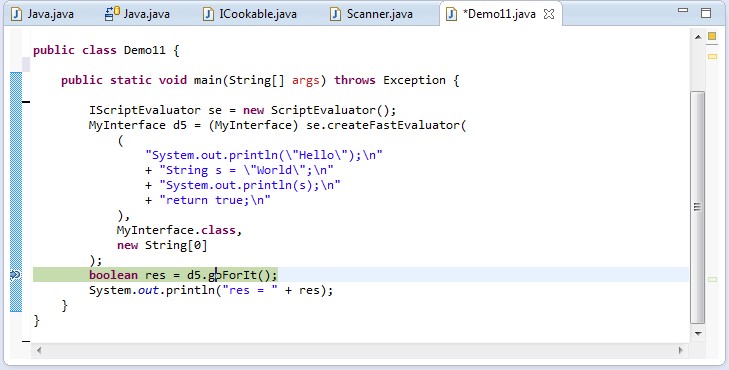
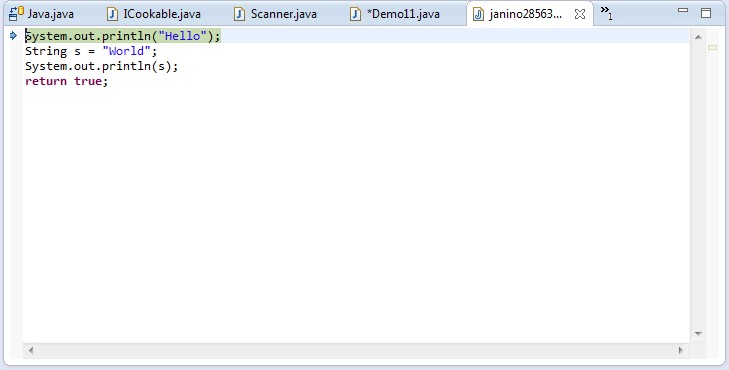
Janino as a Script Evaluator
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
test("simple 2") {
import org.codehaus.janino.ScriptEvaluator
val se: ScriptEvaluator = new ScriptEvaluator()
se.cook(
"""
| static void method1() {
| System.out.println("1111");
| }
| method1();
| method2();
| static void method2() {
| System.out.println("2222");
| }
|""".stripMargin)
se.evaluate()
}
|
结果:
自带的例子
1
2
|
java -cp .;D:\janino-3.1.9.jar;D:\janino-commons-compiler-3.1.9.jar
org.codehaus.commons.compiler.samples.ScriptDemo "for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { System.out.println(\"HELLO\"); }"
|
结果:
1
2
3
4
|
HELLO
HELLO
HELLO
Result = null
|
Janino as a Class Body Evaluator
自带的例子
1
2
3
4
|
java -cp .;D:\janino-3.1.9.jar;D:\janino-commons-compiler-3.1.9.jar
org.codehaus.commons.compiler.samples.ClassBodyDemo
" public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(java.util.Arrays.asList(args));} "
haha hello wokao good abc!!!
|
结果:
1
|
[haha, hello, wokao, good, abc!!!]
|
Janino as a Simple Compiler
源文件 Hello.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public class Foo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Bar().meth();
}
}
public class Bar {
public void meth() {
System.out.println("HELLO!");
}
}
|
编译命令
1
2
|
java -cp .;D:\janino-3.1.9.jar;D:\janino-commons-compiler-3.1.9.jar
org.codehaus.janino.SimpleCompiler Hello.java Foo
|
结果:
Janino as a Compiler
完整的例子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
import org.codehaus.commons.compiler.ICompiler;
import org.codehaus.commons.compiler.util.ResourceFinderClassLoader;
import org.codehaus.commons.compiler.util.resource.MapResourceCreator;
import org.codehaus.commons.compiler.util.resource.MapResourceFinder;
import org.codehaus.commons.compiler.util.resource.Resource;
import org.codehaus.commons.compiler.util.resource.StringResource;
import org.junit.Assert;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class JaninoExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ICompiler compiler = new org.codehaus.janino.CompilerFactory().newCompiler();
// Store generated .class files in a Map:
Map<String, byte[]> classes = new HashMap<String, byte[]>();
compiler.setClassFileCreator(new MapResourceCreator(classes));
// Now compile two units from strings:
compiler.compile(new Resource[] {
new StringResource(
"pkg1/A.java",
"package pkg1; public class A { public static int meth() { return pkg2.B.meth(); } }"
),
new StringResource(
"pkg2/B.java",
"package pkg2; public class B { public static int meth() { return 77; } }"
),
});
// Set up a class loader that uses the generated classes.
ClassLoader cl = new ResourceFinderClassLoader(
new MapResourceFinder(classes), // resourceFinder
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader() // parent
);
Object res1 = cl.loadClass("pkg1.A").getDeclaredMethod("meth").invoke(null);
System.out.println(res1.getClass().getName() + "\t" + res1);
Assert.assertEquals(77, cl.loadClass("pkg1.A").getDeclaredMethod("meth").invoke(null));
}
}
|
结果:
高级
Janino as a Source Code Class Loader
janino 扩展了 JDK 的classloader,也有 loader 类的功能
他在运行期读取源文件,编译不会在磁盘上产生 .class 文件
假设如下 A.java 放在 D:\test\gg\pkg1 中
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
package pkg1;
import pkg2.*;
public class A extends B {
}
|
B.java 放在 D:\test\gg\pkg2 中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
package pkg2;
public class B implements Runnable {
public void run() {
System.out.println("HELLO");
}
}
|
完整的例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
test("advanced example loader java files") {
import org.codehaus.janino.JavaSourceClassLoader
val loader = new JavaSourceClassLoader(
this.getClass.getClassLoader, // parentClassLoader
Array[java.io.File] {
new java.io.File("D:\\test")
}, // optionalSourcePath
null)
// Load class A from "srcdir/pkg1/A.java", and also its superclass
// B from "srcdir/pkg2/B.java":
val obj = loader.loadClass("pkg1.A").newInstance()
// Class "B" implements "Runnable", so we can cast "o" to
// "Runnable".
obj.asInstanceOf[Runnable].run()
}
|
执行结果:
运行后观察目录,没有 .class 文件
高级特性
- 减少编译时间,带缓存的,可以用:CachingJavaSourceClassLoader
- 源文件可以放在网络,数据库中,自定义读取
jsh - the Java shell
janino 的子项目,jshell
不过感觉用处不大,现在 JDK 也有 jshell 了
Compiler Plugin
可以作为 tomcat 编译 jsp 的插件
Tomcat 的 conf/web.xml 定义如下:
1
2
3
4
|
<init-param>
<param-name>compiler</param-name>
<param-value>org.codehaus.janino.AntCompilerAdapter</param-value>
</init-param>
|
代码分析
命令:
1
2
|
java -cp .;D:\janino-3.1.9.jar;D:\janino-commons-compiler-3.1.9.jar
org.codehaus.janino.samples.DeclarationCounter Hello.java`
|
打印结果:
1
2
3
4
|
Class declarations: 1
Interface declarations: 0
Fields: 4
Local variables: 3
|
debug
命令:
1
2
3
4
5
|
$ java \
> ... \
> -Dorg.codehaus.janino.source_debugging.enable=true \
> -Dorg.codehaus.janino.source_debugging.dir=C:\tmp \
> ...
|
参考

