概览
Spark + Delta-Lake,写入Parquet 文件,总体流程如下:
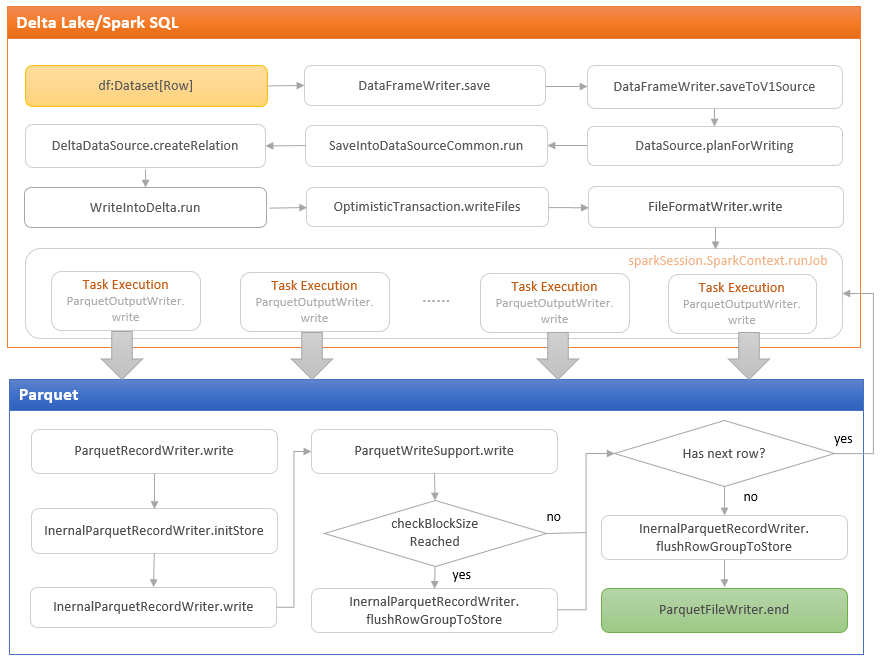
图片来自 -> 这里
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
df.write.format("delta").save(path)
def write: DataFrameWriter[T] = {
if (isStreaming) {
logicalPlan.failAnalysis(
"'write' can not be called on streaming Dataset/DataFrame")
}
new DataFrameWriter[T](this)
}
|
format(“delta”) 这个别名的注册,是通过DeltaDataSource实现了这个接口
以插件的形式,注入到 Spark 中
DataFrameWrite 会将执行流程 转到 saveToV1Source 函数,这个函数又会调用 planForWriting
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
def planForWriting(mode: SaveMode, data: LogicalPlan): LogicalPlan = {
providingInstance() match {
case dataSource: CreatableRelationProvider =>
disallowWritingIntervals(data.schema.map(_.dataType), forbidAnsiIntervals = true)
SaveIntoDataSourceCommand(data, dataSource, caseInsensitiveOptions, mode)
case format: FileFormat =>
disallowWritingIntervals(data.schema.map(_.dataType), forbidAnsiIntervals = false)
DataSource.validateSchema(data.schema)
planForWritingFileFormat(format, mode, data)
case _ => throw new IllegalStateException(
s"${providingClass.getCanonicalName} does not allow create table as select.")
}
}
|
然后执行 SaveIntoDataSourceCommand
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
case class SaveIntoDataSourceCommand(
query: LogicalPlan,
dataSource: CreatableRelationProvider,
options: Map[String, String],
mode: SaveMode) extends LeafRunnableCommand {
override def innerChildren: Seq[QueryPlan[_]] = Seq(query)
override def run(sparkSession: SparkSession): Seq[Row] = {
val relation = dataSource.createRelation(
sparkSession.sqlContext, mode, options, Dataset.ofRows(sparkSession, query))
try {
val logicalRelation = LogicalRelation(relation, relation.schema.toAttributes, None, false)
sparkSession.sharedState.cacheManager.recacheByPlan(sparkSession, logicalRelation)
} catch {
case NonFatal(_) =>
// some data source can not support return a valid relation, e.g. `KafkaSourceProvider`
}
|
这里调用createRelation,所以会创建出DeltaDataSource
这里包含了 事务优化,写数据文件,写元数据等
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
override def createRelation(
sqlContext: SQLContext,
mode: SaveMode,
parameters: Map[String, String],
data: DataFrame): BaseRelation = {
val path = parameters.getOrElse("path", {
throw DeltaErrors.pathNotSpecifiedException
})
val partitionColumns = parameters.get(DeltaSourceUtils.PARTITIONING_COLUMNS_KEY)
.map(DeltaDataSource.decodePartitioningColumns)
.getOrElse(Nil)
val deltaLog = DeltaLog.forTable(sqlContext.sparkSession, new Path(path), parameters)
WriteIntoDelta(
deltaLog = deltaLog,
mode = mode,
new DeltaOptions(parameters, sqlContext.sparkSession.sessionState.conf),
partitionColumns = partitionColumns,
configuration = DeltaConfigs.validateConfigurations(
parameters.filterKeys(_.startsWith("delta.")).toMap),
data = data,
// empty catalogTable is acceptable as the code path is only for path based writes
// (df.write.save("path")) which does not need to use/update catalog
catalogTableOpt = None
).run(sqlContext.sparkSession)
deltaLog.createRelation()
}
|
参考代码,这里
最后是调用FileFormatWriter,将数据写入存储系统
这里会创建多个 Task,然后并行的写入
如果写入成功,最后会做一些统计信息,否则就是丢弃
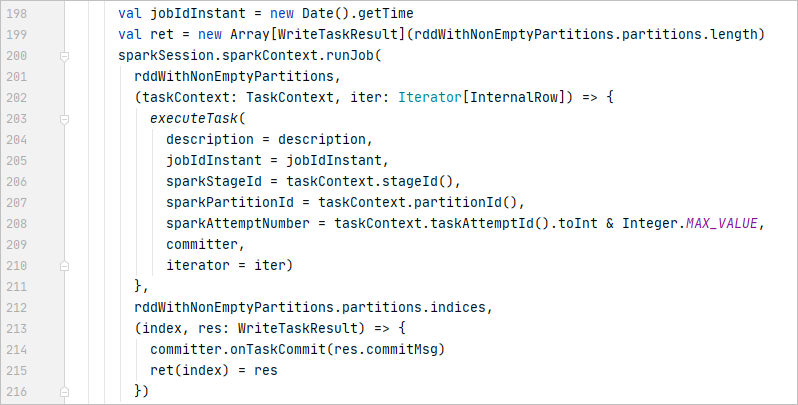
对于每个 Task内部,则是调用ParquetOutputWriter,开始写入 Parquet
Parquet 内部
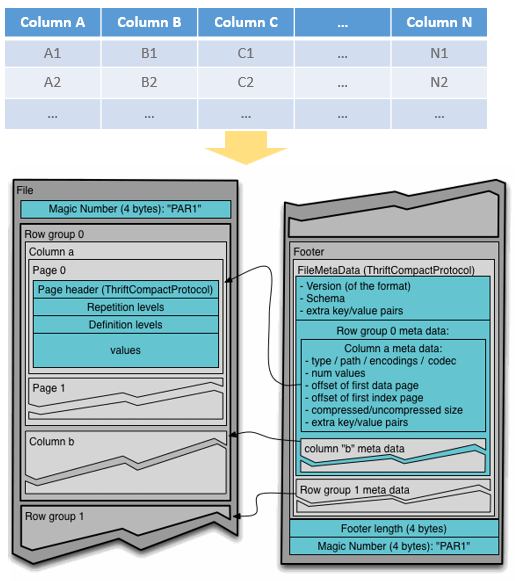
一些概念
- Magic Number and File Signature
- Row Group,数据按照 row 分成多块
- Column Chunk,每个 row group内部,按照 column 来存储
- Page,最小单元,每个 Column Chunk由多个 Page组成,page包括不同类型,page 中还包含了 head,用来描述结构
- Data Pages store the actual column data.
- Index Pages store the index of column data.
- Dictionary Pages store dictionary-encoded data (if applicable).
- Footer,包括:FileMetaData,Row Group MetaData,其中第二个又包括:
- Column paths and encodings
- Number of values
- Offsets for the first data and index pages
- Compressed/uncompressed sizes
- Additional key/value metadata.
- Metadata
Spark内部执行 ParquetOutputWriter,然后创建 ParquetOutputFormat
 之后会将 Spark SQL Catalyst InternalRow 转为 Parquet messages
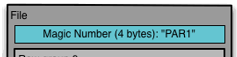
ParquetFileWriter 封装了文件级别操作,然后设置 magic number
之后会将 Spark SQL Catalyst InternalRow 转为 Parquet messages
ParquetFileWriter 封装了文件级别操作,然后设置 magic number
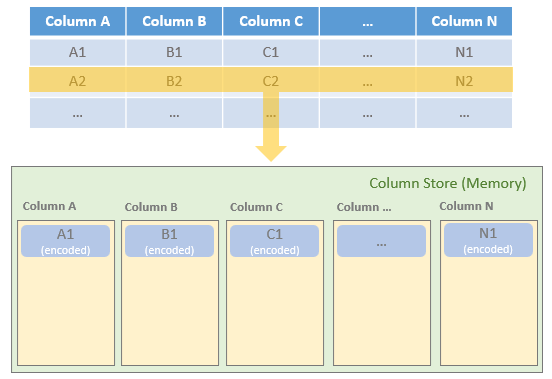
Parquet 虽然是按照列来存储的,但是 DataFrame 是按照 row by row 处理的
也就是不断遍历:Iterator[InternalRow]
调用org.apache.parquet.hadoop.InternalParquetRecordWriter
1
2
3
4
5
|
public void write(T value) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
writeSupport.write(value);
++ recordCount;
checkBlockSizeReached();
}
|
再调用 实现类org.apache.spark.sql.execution.datasources.parquet.ParquetWriteSupport
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
override def write(row: InternalRow): Unit = {
consumeMessage {
writeFields(row, schema, rootFieldWriters)
}
}
private def writeFields(
row: InternalRow, schema: StructType, fieldWriters: Array[ValueWriter]): Unit = {
var i = 0
while (i < row.numFields) {
if (!row.isNullAt(i)) {
consumeField(schema(i).name, i) {
fieldWriters(i).apply(row, i)
}
}
i += 1
}
}
|
在 Parquet 端,调用 ValuesWriter对输入的值做编码
相关的编码实现类如下:
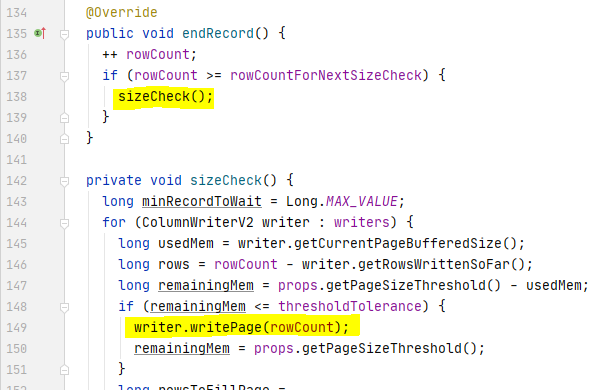
当达到 page 的阈值后,就会压缩这些数据,包括
- value count
- null value count
- min/max value
parquet 内部按照 array list of byte[] (List<byte[]>) 存储的
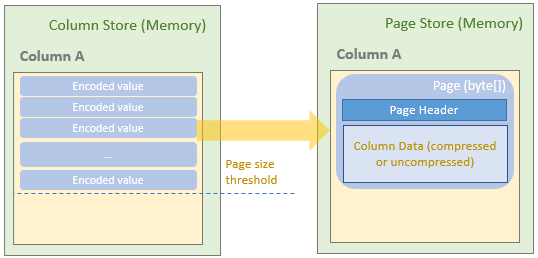
以上都是发生在 memory 中,真正的写磁盘是触发到了 row group 阈值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
private void flushRowGroupToStore()
throws IOException {
recordConsumer.flush();
LOG.debug("Flushing mem columnStore to file. allocated memory: {}", columnStore.getAllocatedSize());
if (columnStore.getAllocatedSize() > (3 * rowGroupSizeThreshold)) {
LOG.warn("Too much memory used: {}", columnStore.memUsageString());
}
if (recordCount > 0) {
rowGroupOrdinal++;
parquetFileWriter.startBlock(recordCount);
columnStore.flush();
pageStore.flushToFileWriter(parquetFileWriter);
recordCount = 0;
parquetFileWriter.endBlock();
this.nextRowGroupSize = Math.min(
parquetFileWriter.getNextRowGroupSize(),
rowGroupSizeThreshold);
}
columnStore = null;
pageStore = null;
}
|
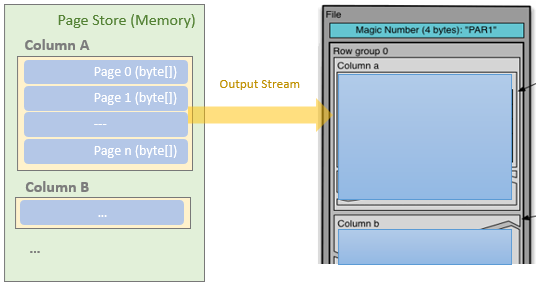
之后,Parquet解除当前的列存储和页存储并重新初始化新的存储,并继续读取剩余的数据框行并重复该过程
FileMetaData Write
在最后,将所有 row group 的 meta 信息存储

Parquet Encoding
Dictionary Encoding
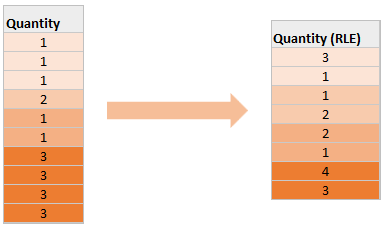
Run Length Encoding (RLE)
- 可以看做是 dictionary encoding 的补充
- 如果一个值反复出现了多次,就记录【出现的次数】- 【值的内容】
- 如果column 中包括的都是不相同的值,则效果就不好了
Delta Encoding
- 适合时间戳这样的,用 long 来表示每个时间戳的值
- 起始值是一个比较大的值,而后面每次变化其实不大
- 只需要很少的 bit 就可以存储每次增量的变化

parquet 如何实现 encoding
- 根类是 ValuesWriter
- 实现的抽象类是 DictionaryValuesWriter,它下面还有各种类型的 具体实现类

下面是 PlainBinaryDictionaryValuesWriter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
public static class PlainBinaryDictionaryValuesWriter extends DictionaryValuesWriter {
/* type specific dictionary content */
protected Object2IntMap<Binary> binaryDictionaryContent = new Object2IntLinkedOpenHashMap<>();
public PlainBinaryDictionaryValuesWriter(int maxDictionaryByteSize, Encoding encodingForDataPage,
Encoding encodingForDictionaryPage, ByteBufferAllocator allocator) {
super(maxDictionaryByteSize, encodingForDataPage, encodingForDictionaryPage, allocator);
binaryDictionaryContent.defaultReturnValue(-1);
}
@Override
public void writeBytes(Binary v) {
int id = binaryDictionaryContent.getInt(v);
if (id == -1) {
id = binaryDictionaryContent.size();
binaryDictionaryContent.put(v.copy(), id);
// length as int (4 bytes) + actual bytes
dictionaryByteSize += 4L + v.length();
}
encodedValues.add(id);
}
。。。
|
内部使用 hash-map 做编号的,超过阈值后,将 这个编号信息 flush
RLE 的实现是RunLengthBitPackingHybridValuesWriter
如果重复的次数超过 8 次,使用下面算法
1
2
3
4
|
rle-run := <rle-header> <repeated-value>
rle-header := varint-encode((rle-run-len) << 1)
repeated-value := value that is repeated, using a fixed-width of round-up-to-next-byte(bit-width)
*varint-encode is ULEB0128 coding
|
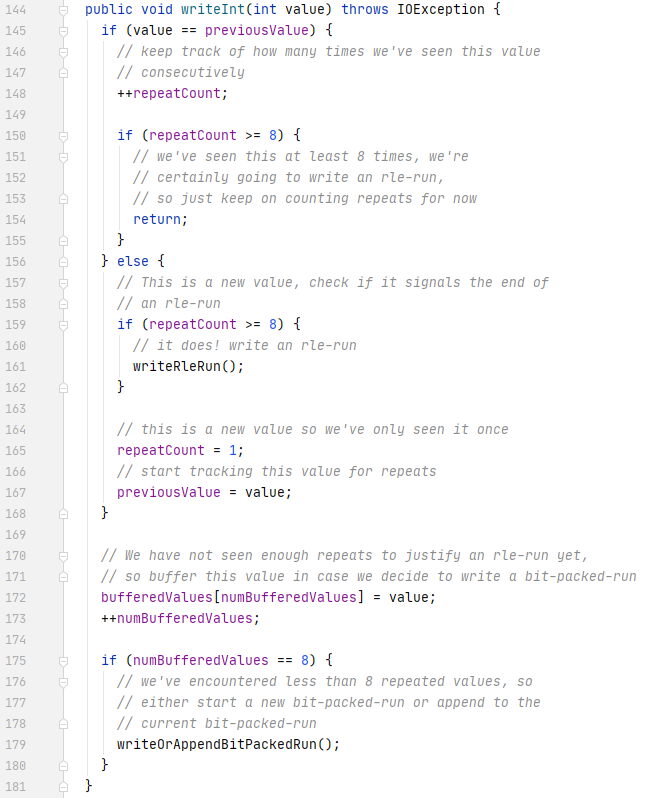
否则使用下面算法
1
2
3
|
bit-packed-run := <bit-packed-header> <bit-packed-values>
bit-packed-header := varint-encode(<bit-pack-scaled-run-len> << 1 | 1)
bit-pack-scaled-run-len := (bit-packed-run-len) / 8
|
delta 的实现很多,包括
- DeltaBinaryPackingValuesWriter , Int32
- DeltaLengthByteArrayValuesWriter ,Int64
- DeltaLengthByteArrayValuesWriter
- DeltaByteArrayWriter
就是通过计算本次,前一次的差值来写入的
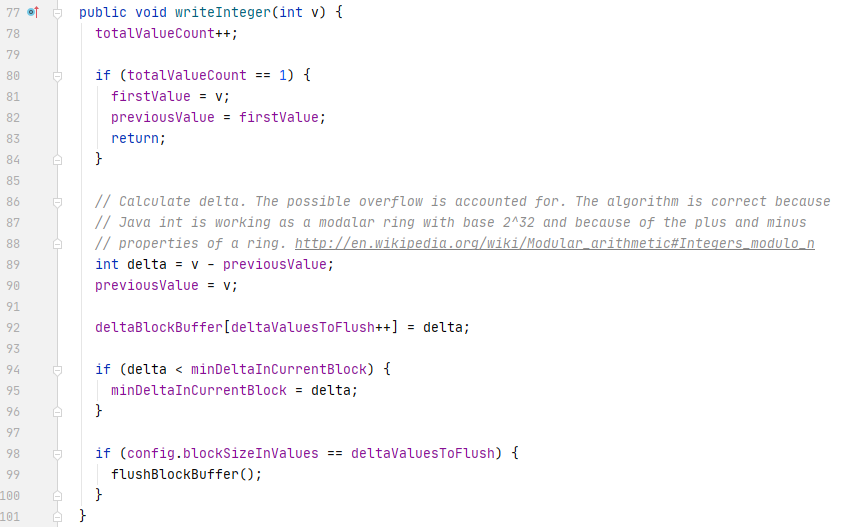
parquet 通过 factory 创建不同的 writer
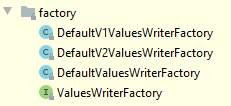
接口类
1
2
3
4
5
|
public interface ValuesWriterFactory {
void initialize(ParquetProperties var1);
ValuesWriter newValuesWriter(ColumnDescriptor var1);
}
|
DefaultValuesWriterFactory 的主要实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
public ValuesWriter newValuesWriter(ColumnDescriptor descriptor) {
return this.delegateFactory.newValuesWriter(descriptor);
}
static DictionaryValuesWriter dictionaryWriter(ColumnDescriptor path, ParquetProperties properties, Encoding dictPageEncoding, Encoding
dataPageEncoding) {
switch(path.getType()) {
case BOOLEAN:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("no dictionary encoding for BOOLEAN");
case BINARY:
return new PlainBinaryDictionaryValuesWriter(properties.getDictionaryPageSizeThreshold(), dataPageEncoding, dictPageEncoding,
properties.getAllocator());
case INT32:
return new PlainIntegerDictionaryValuesWriter(properties.getDictionaryPageSizeThreshold(), dataPageEncoding, dictPageEncoding,
properties.getAllocator());
case INT64:
return new PlainLongDictionaryValuesWriter(properties.getDictionaryPageSizeThreshold(), dataPageEncoding, dictPageEncoding,
properties.getAllocator());
case INT96:
return new PlainFixedLenArrayDictionaryValuesWriter(properties.getDictionaryPageSizeThreshold(), 12, dataPageEncoding,
dictPageEncoding, properties.getAllocator());
case DOUBLE:
return new PlainDoubleDictionaryValuesWriter(properties.getDictionaryPageSizeThreshold(), dataPageEncoding, dictPageEncoding,
properties.getAllocator());
case FLOAT:
return new PlainFloatDictionaryValuesWriter(properties.getDictionaryPageSizeThreshold(), dataPageEncoding, dictPageEncoding,
properties.getAllocator());
case FIXED_LEN_BYTE_ARRAY:
return new PlainFixedLenArrayDictionaryValuesWriter(properties.getDictionaryPageSizeThreshold(), path.getTypeLength(),
dataPageEncoding, dictPageEncoding, properties.getAllocator());
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown type " + path.getType());
}
}
|
也实现自定义的 encoding 类,只要继承 ValuesWriterFactory 即可
然后 在 org.apache.parquet.column.Build#withValuesWriterFactory 进行设置
Vectorised Parquet Reading
早期的时候是一次读一行,现在改为一次读一个 batch
ColumnBatch 包装了若干个 ColumnVectors,ColumnVectors 包括了一个列的若干值
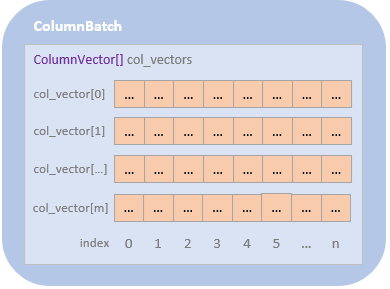
ColumnBatch 也提供了 row 迭代的访问方式,
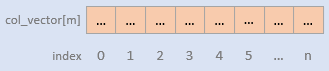
提供了获取各种数据类型的方式
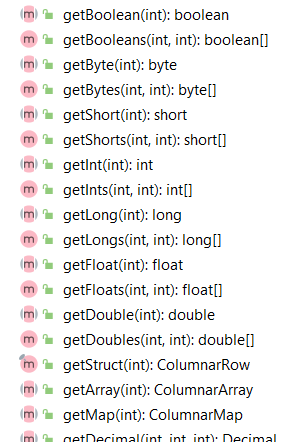
Spark 在读取的时候,是重用了 ColumnVector 实例,这样开销就很小了
Spark实现的parquet 主要包含
- VectorizedParquetRecordReader
- VectorizedColumnReader
- VectorizedValuersReader
执行过程
- 初始化 VectorizedParquetRecordReader,调用nextKeyValue
- 创建多个 VectorizedColumnReaders,每个对应一个column
- 之后通过VectorizedValuesReader,用来读取和解码数据
- 有两个版本的VectorizedRleValuesReader (RLE/Bit-PackingHybrid)
- 以及VectorizedPlainValuesReader(for plain encoding)
- 最后将这些数据返回给 VectorizedParquetRecordReader,再由上层进一步消费
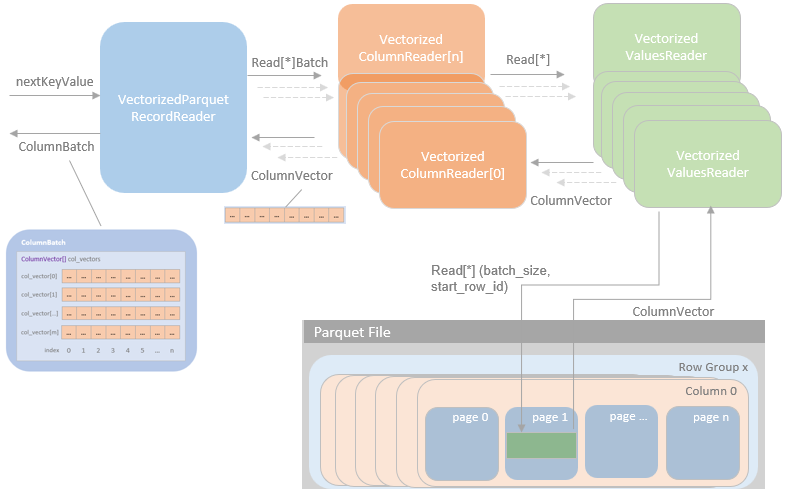
VectorizedParquetRecordReader
- 继承自抽象类RecordReader,覆盖了 nextKeyValue 函数
- 读之前会创建capacity 和 内存模式(on-heap or off-heap)
- 首先创建 ColumnBatch,然后创建 ColumnVector(对应于每个column)
- 再通过VectorizedColumnReader 读每个 batach column
VectorizedParquetRecordReader#nextBatch 主要逻辑:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public boolean nextBatch() throws IOException {
for (ParquetColumnVector vector : columnVectors) {
vector.reset();
}
columnarBatch.setNumRows(0);
if (rowsReturned >= totalRowCount) return false;
checkEndOfRowGroup();
int num = (int) Math.min(capacity, totalCountLoadedSoFar - rowsReturned);
for (ParquetColumnVector cv : columnVectors) {
for (ParquetColumnVector leafCv : cv.getLeaves()) {
VectorizedColumnReader columnReader = leafCv.getColumnReader();
if (columnReader != null) {
columnReader.readBatch(num, leafCv.getValueVector(),
leafCv.getRepetitionLevelVector(), leafCv.getDefinitionLevelVector());
}
}
cv.assemble();
}
rowsReturned += num;
columnarBatch.setNumRows(num);
numBatched = num;
batchIdx = 0;
return true;
}
|
VectorizedColumnReader & VectorizedValuesReader
- VectorizedColumnReader 创建对应的 ColumnDescriptor
- 执行readBatch 时,传递两个参数,total(读batch 的数量),column
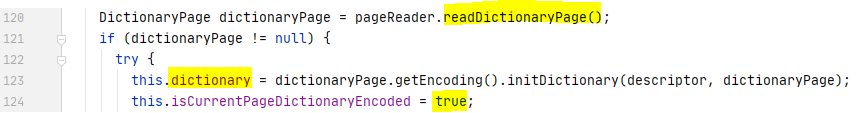
如果 isCurrentPageDictionaryEncoded 被打开,则计算 dictionary encoded column values
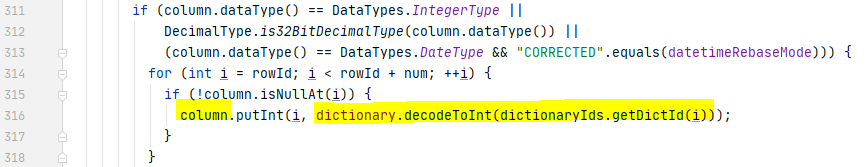
如果isCurrentPageDictionaryEncoded 关闭,则根据类型做解码
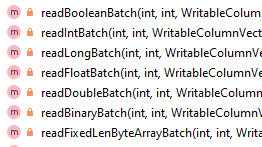
这里是通过 VectorizedValueReader 来读取,并解码的
参考




之后会将 Spark SQL Catalyst InternalRow 转为 Parquet messages
ParquetFileWriter 封装了文件级别操作,然后设置 magic number




















