相比java的不同
类型层次

scala 相比 java,特有的特性:
- 高阶函数,函数柯里化
- 隐式转换
- case class,消除了set、get
- lazy 延迟计算
- if else 中可以直接返回结果,没有return了
- 内置的可变,不可变集合类
- 自动类型推导
- 操作符重载
- 模式匹配
- 内部函数
- 对象值的 apply,unapply
- None,Some,Option
例子
apply 和 unapply
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import scala.util.Random
object CustomerID {
def apply(name: String) = s"$name--${Random.nextLong()}"
def unapply(customerID: String): Option[String] = {
val stringArray: Array[String] = customerID.split("--")
if (stringArray.tail.nonEmpty) Some(stringArray.head) else None
}
}
val customer1ID = CustomerID("Sukyoung") // Sukyoung--23098234908
customer1ID match {
case CustomerID(name) => println(name) // prints Sukyoung
case _ => println("Could not extract a CustomerID")
}
|
case class
1
|
case class Point(x: Int, y: Int)
|
入口点
1
2
3
4
|
object Main {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit =
println("Hello, Scala developer!")
}
|
constructors
1
2
3
4
5
|
class Point(var x: Int = 0, var y: Int = 0)
val origin = new Point // x and y are both set to 0
val point1 = new Point(1) // x is set to 1 and y is set to 0
println(point1) // prints (1, 0)
|
trait
1
2
3
4
|
trait Iterator[A] {
def hasNext: Boolean
def next(): A
}
|
tuple
1
|
val ingredient = ("Sugar", 25)
|
高阶函数
1
2
3
|
val salaries = Seq(20_000, 70_000, 40_000)
val doubleSalary = (x: Int) => x * 2
val newSalaries = salaries.map(doubleSalary)
|
函数 柯里化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
// A normal function that adds two numbers
def add(x: Int, y: Int): Int = x + y
// A curried version of the same function
def addCurried(x: Int)(y: Int): Int = x + y
// Usage
val add5 = addCurried(5) _ // Partially apply the function
println(add5(10)) // Outputs: 15
// Alternatively
println(addCurried(3)(7)) // Outputs: 10
|
foldLeft
1
2
3
|
val numbers = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
val res = numbers.foldLeft(0)((m, n) => m + n)
println(res) // 55
|
模式匹配
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
def showImportantNotification(notification: Notification, importantPeopleInfo: Seq[String]): String = {
notification match {
case Email(sender, _, _) if importantPeopleInfo.contains(sender) =>
"You got an email from special someone!"
case SMS(number, _) if importantPeopleInfo.contains(number) =>
"You got an SMS from special someone!"
case other =>
showNotification(other) // nothing special, delegate to our original showNotification function
}
}
|
for 循序,有点像 python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
case class User(name: String, age: Int)
val userBase = List(
User("Travis", 28),
User("Kelly", 33),
User("Jennifer", 44),
User("Dennis", 23))
val twentySomethings =
for (user <- userBase if user.age >=20 && user.age < 30)
yield user.name // i.e. add this to a list
twentySomethings.foreach(println) // prints Travis Dennis
|
隐式类型转换
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
object FileExtensions {
implicit class RichFile(file: File) {
// Method to read the entire file content as a string
def readAsString(): String = {
val sb = new StringBuilder
var reader: BufferedReader = null
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file))
var line: String = reader.readLine()
while (line != null) {
sb.append(line)
sb.append(System.lineSeparator()) // For new line
line = reader.readLine()
}
} catch {
case e: IOException => e.printStackTrace()
} finally {
if (reader != null) reader.close()
}
sb.toString()
}
}
}
val file = new File("example.txt")
file.readAsString
|
隐式转换的几个例子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
// 1、类型转换
implicit def doubleToInt(d: Double): Int = d.toInt
val x: Int = 42.5 // Implicitly converts Double to Int
println(x) // Outputs: 42
// 2、隐式类
implicit class RichInt(val x: Int) {
def square: Int = x * x
}
println(5.square) // Outputs: 25
// 3、隐式参数
implicit val defaultMultiplier: Int = 2
def multiply(x: Int)(implicit multiplier: Int): Int = x * multiplier
println(multiply(5)) // Outputs: 10, using the implicit multiplier (2)
|
操作符重载
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
case class Vec(x: Double, y: Double) {
def +(that: Vec) = Vec(this.x + that.x, this.y + that.y)
}
val vector1 = Vec(1.0, 1.0)
val vector2 = Vec(2.0, 2.0)
val vector3 = vector1 + vector2
vector3.x // 3.0
vector3.y // 3.0
|
By-name Parameters,传递参数的时候,可以延迟计算
1
|
def calculate(input: => Int) = input * 37
|
package
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
package users {
package administrators {
class NormalUser
}
package normalusers {
class NormalUser
}
}
|
逆变、协变
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
object Demo {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//非变案例演示
val A:Temp1[Sub] = new Temp1[Sub]
//val B:Temp1[Super] = A //非变, 编译报错,不能赋值。
//尽管类型A是B的子类型,Pair[A]和Pair[B]没有任何从属关系,参数化类型之间没有关系,不管原类型之间的关系
// 协变案例演示
val C: Temp2[Sub] = new Temp2[Sub]
val D: Temp2[Super] = C
//类型C是D的子类型,Pair[C]可以认为是Pair[D]的子类型,参数化类型的方向和类型的方向是一致的。
// 逆变案例演示
val E: Temp3[Super] = new Temp3[Super]
val F: Temp3[Sub] = E
//类型F是E的子类型,Pair[E]反过来可以认为是Pair[F]的子类型。参数化类型的方向和类型的方向是相反的
}
}
|
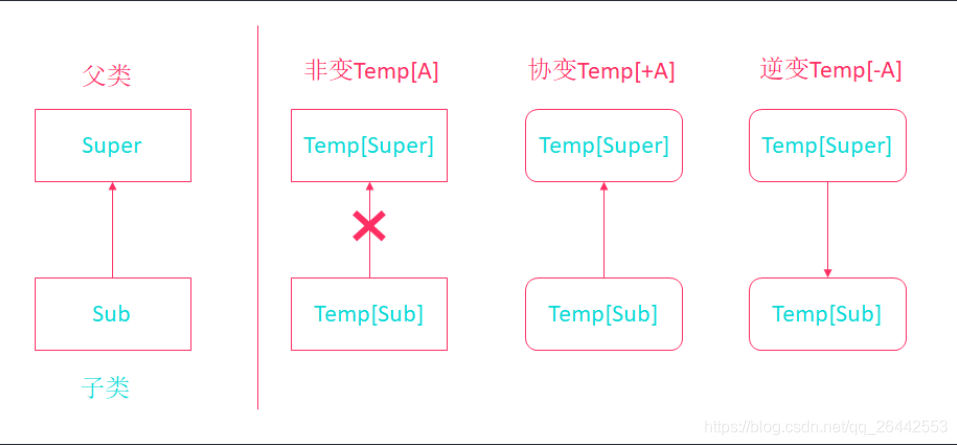
协变解释
- Covariance (+A)
- 类型B是A的子类型,Pair[B]可以认为是Pair[A]的子类型
- 参数化类型的方向和类型的方向是一致的
逆变解释
- Contravariance (-A)
- 类型B是A的子类型,Pair[A]反过来可以认为是Pair[B]的子类型
- 参数化类型的方向和类型的方向是相反的
上界、下界
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
// 使用<: 类型名表示给类型添加一个上界,表示泛型参数必须要从该类(或本身)继承
class Person
class Student extends Person
def demo[T <: Person](a:Array[T]) = println(a)
def demo2[T >: Student](a:Array[T]) = println(a)
// A method that combines both upper and lower bounds
// T must be a supertype of Student (lower bound) and a subtype of Person (upper bound)
def demo3[T >: Student <: Person](a: Array[T]): Unit = {
a.foreach(_.speak()) // Call the speak method on each element
}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
demo(Array(new Person))
demo(Array(new Student))
// 编译出错,必须是Person的子类
// demo(Array("hadoop"))
}
|
解释
- 上界:T <: Person,表示 T 必须是 Person 的子类型
- 下界:T >: Student,表示 T 必须是 Student 的父类型
- T >: Student <: Person:表示 T 是Student的父类型,又是 Person的子类型
参考

