基础原理
JOIN 的语法定义

Spark SQL中支持的 Join类型主要包括
- Inner
- FullOuter
- LeftOuter
- RightOuter
- LeftSemi
- LeftAnti
- Cross
Spark SQL支持的Join类型
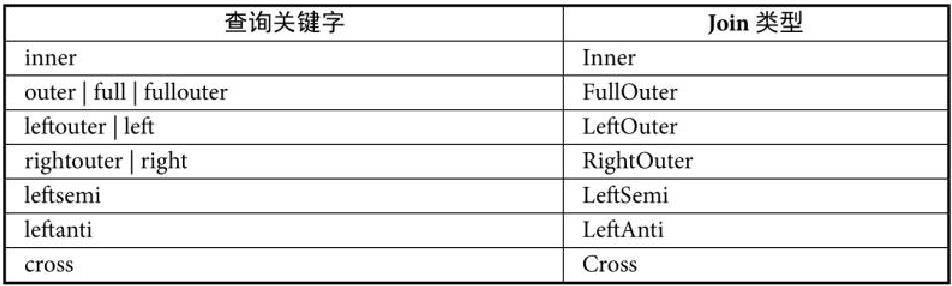
各种 JOIN 类型图形表示:
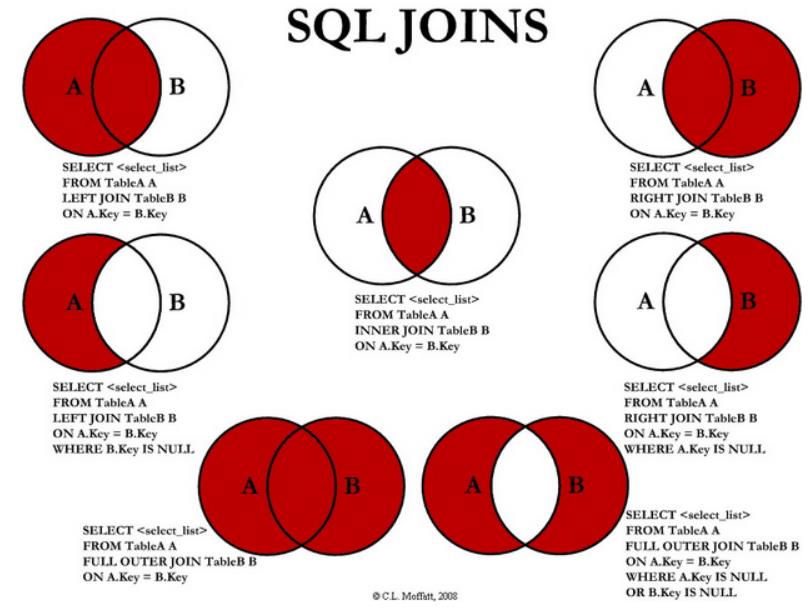
语法解析后的 AST
SEMI 等价写法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
SELECT student.id FROM student LEFT SEMI JOIN exam
ON student.id = exam.studentID
-- 等价于
SELECT id FROM student WHERE id IN(
SELECT studentId FROM exam
)
|
ANTI JOIN 等价写法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
SELECT student.id FROM student LEFT ANTI JOIN exam
ON student.id = exam.studentID
-- 等价于
SELECT id FROM student WHERE id NOT IN(
SELECT studentId FROM exam
)
|
关闭 codegen
1
2
3
4
5
|
spark = SparkSession.builder
.master("local[*]")
.appName("my_test")
.config("spark.sql.codegen.wholeStage", "false")
.getOrCreate
|
解析
JOIN type 的类图
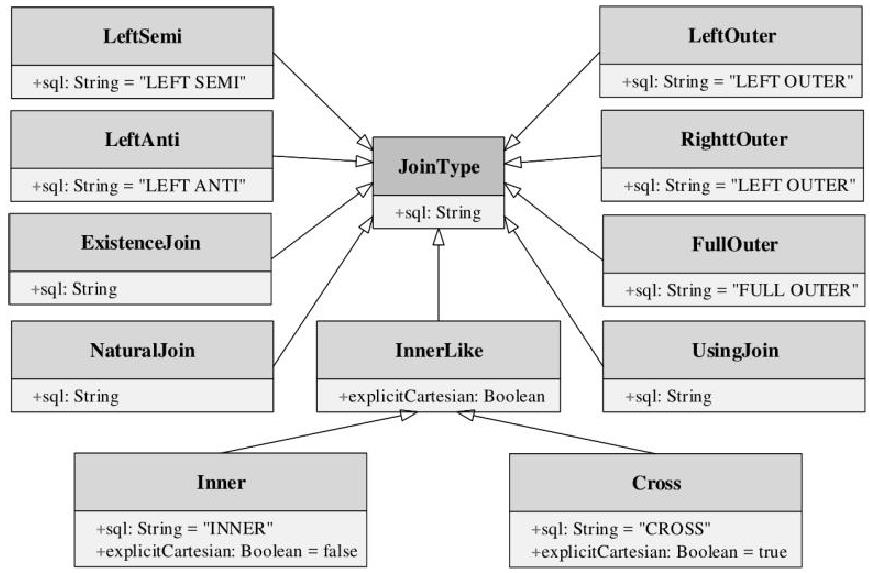
JOIN 逻辑算子节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
// 变量
lfet: LogicalPlan
right: LogicalPlan
joinType: JoinType
condition: Option[Expression]
// 函数
def resolvedExceptNatural: Boolean
def resolved: Boolean
def statistics: Statistics
def output: Seq[Attribute]
def validConstrains: Set[Expression]
def duplicateResolved: Boolean
|
未解析的逻辑 计划 -> 解析后的 logicalPlan

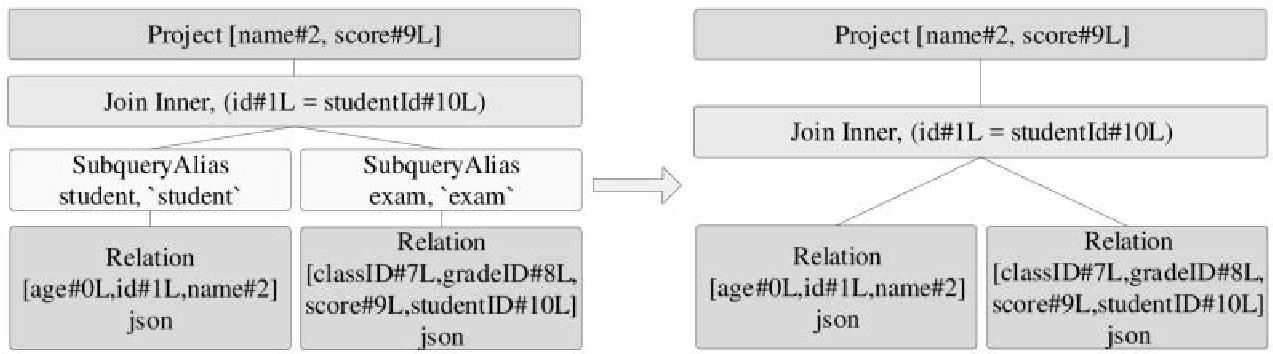
Elim inateSubqueryAliases优化规则,如下:
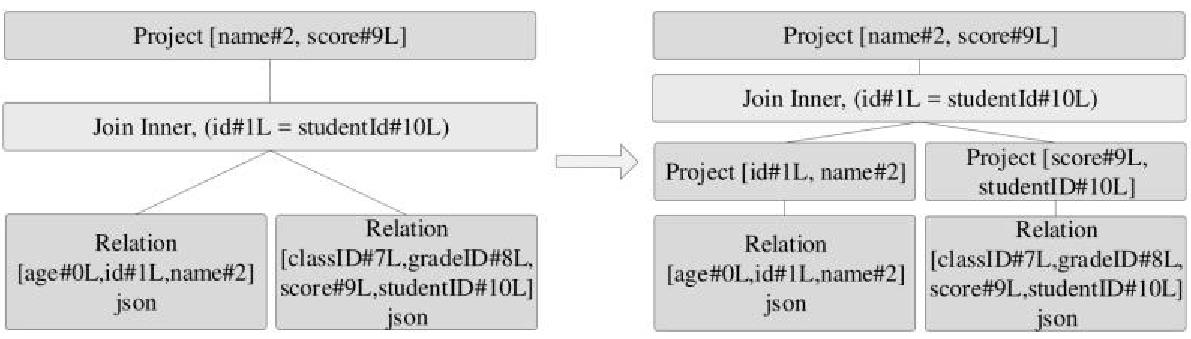
ColumnPruning优化规则 应用后如下:
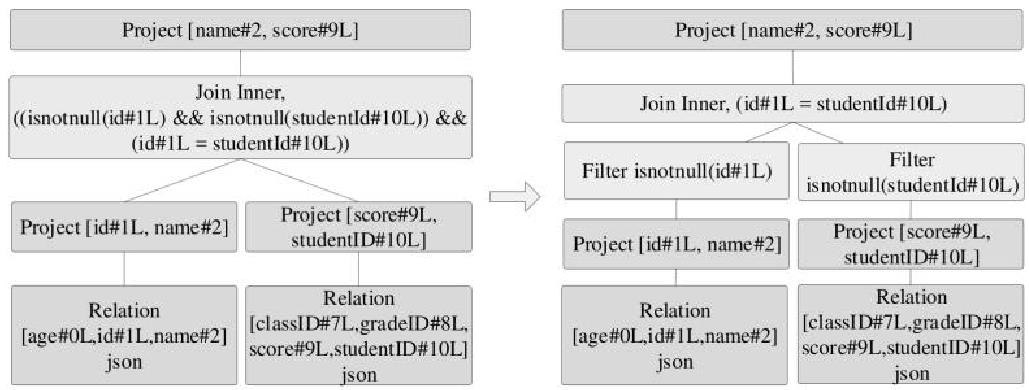
InferFiltersFrom Constraints优化规则,如下:

PushPredicateThroughJoin优化规则,如下:
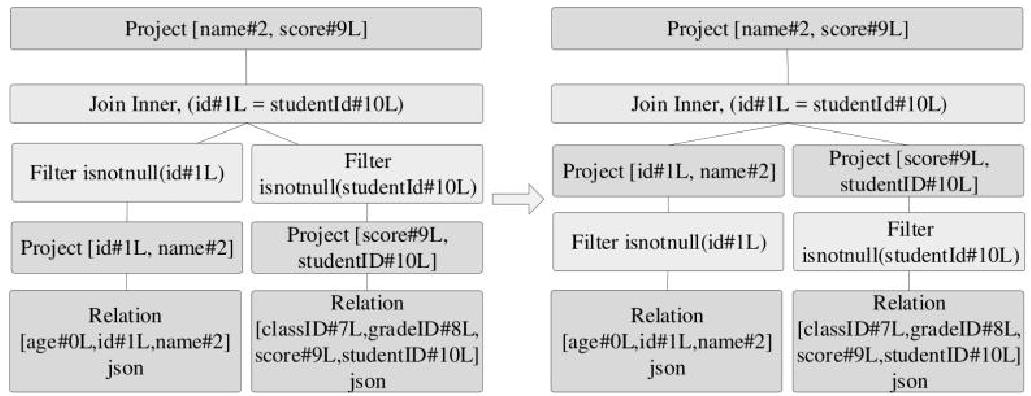
PushDownPredicate优化规则,如下:
生成物理计划
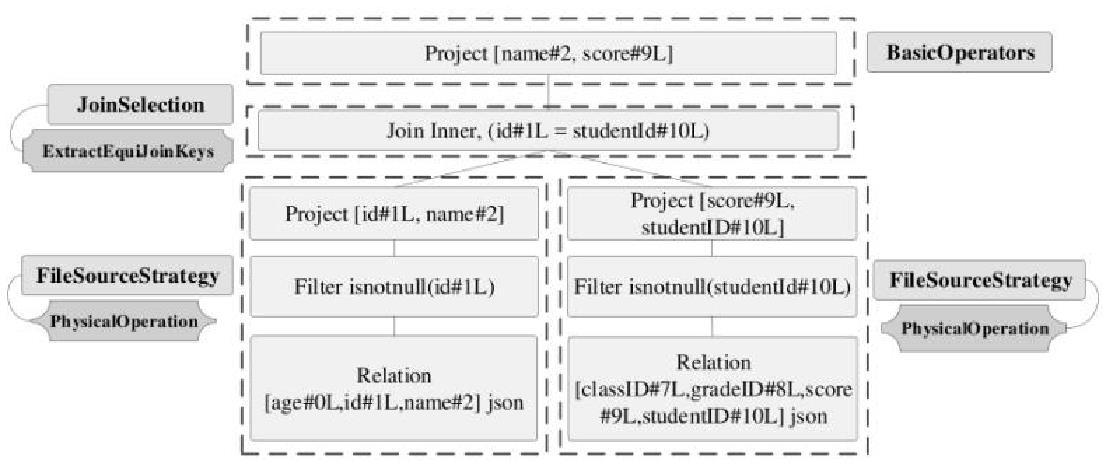
三个策略:
- 文件数据源(FileSource)策略,选择具体的 scan 物理算子
- 基本算子(BasicOperators)策略,做投影
- Join选择(JoinSelection),选择合适的 JOIN
Spark支持 这几种 join:
- BroadcastHashJoinExec
- ShuffledHashJoinExec
- SortMergeJoinExec
- CartesianProductExec
- BroadcastNestedLoopJoinExec
5 种 JOIN 执行效率
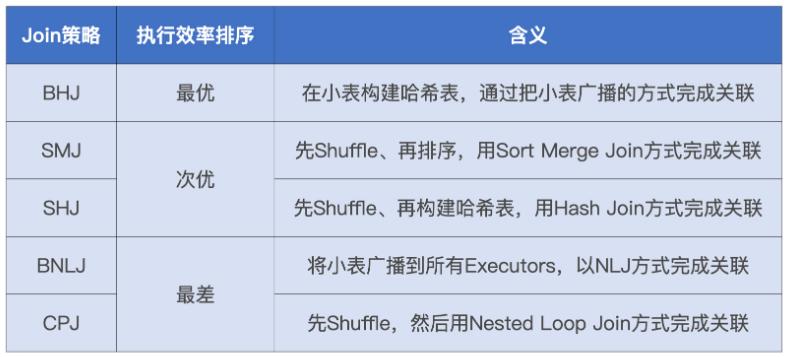
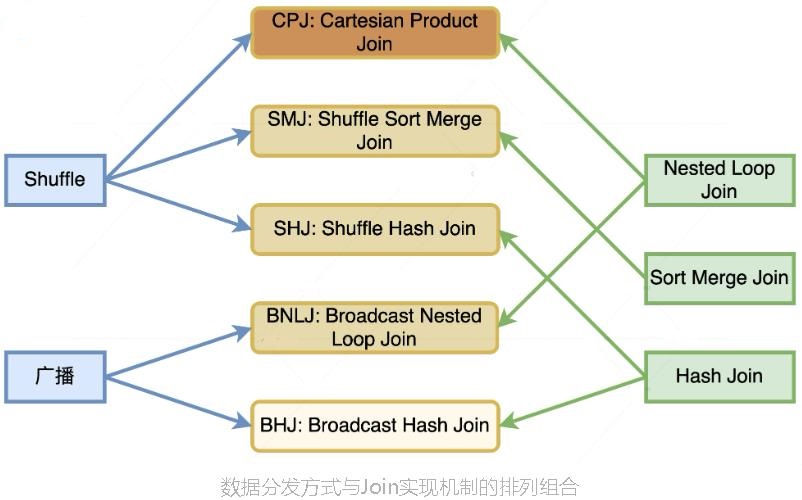
它们是来自 2 种数据分发方式(广播和 Shuffle)与 3 种 Join 实现机制(Hash Joins、Sort Merge Joins 和 Nested Loop Joins)的排列组合
The Join strategy selection takes three factors into account, including:
- Join type is equi-join or not
- Join strategy hint
- Size of Join relations
三种选择策略判断逻辑
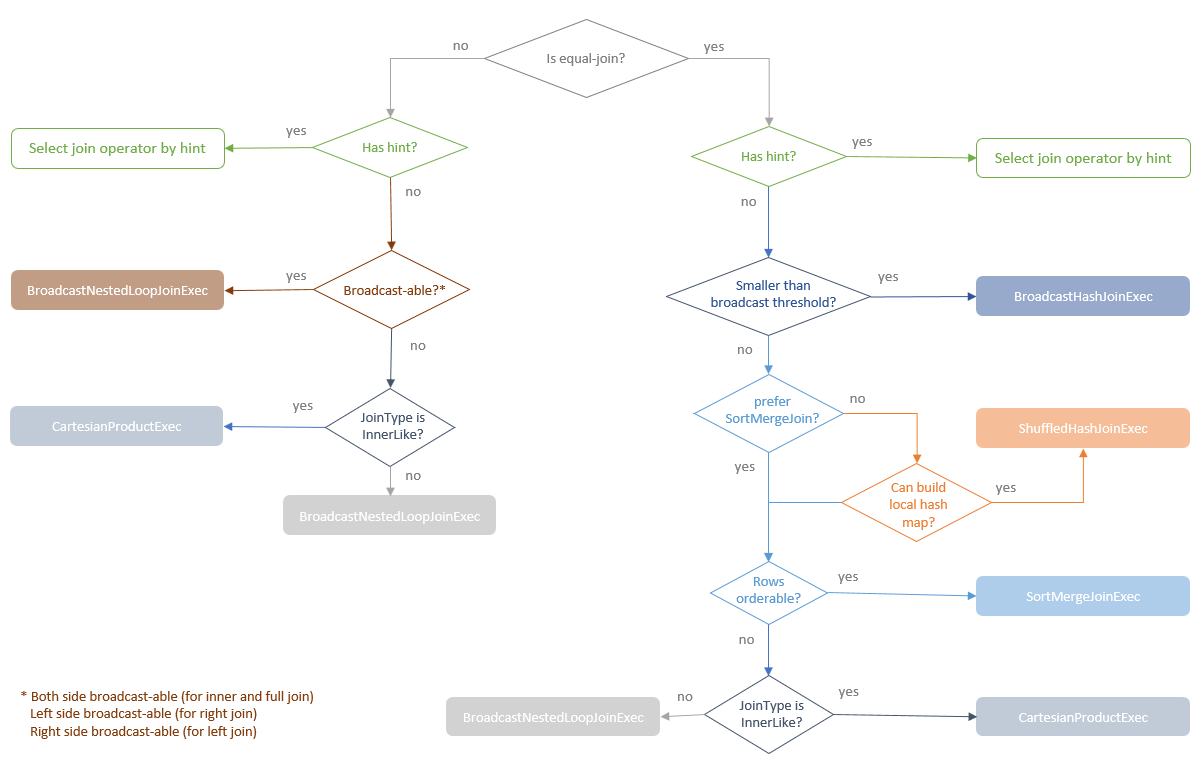
图片来自这里
Equi-Join vs Not
- 不相等 就是:<, >, >=, <= 这些比较方式
- not equi 只有:BroadcastNestedLoopJoinExec,CartesianProductExec 支持
- 所有的 5 个join 类型都支持 等值 join
在 join 选择策略时,用ExtractEquiJoinKeys 来提取 join 的相关新
- join type
- left keys
- right keys
- join condition
- left join relation
- right join relation
- join hint
ExtractEquiJoinKeys 的主要定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
object ExtractEquiJoinKeys extends Logging with PredicateHelper {
/** (joinType, leftKeys, rightKeys, otherCondition, conditionOnJoinKeys, leftChild,
* rightChild, joinHint).
*/
// Note that `otherCondition` is NOT the original Join condition and it contains only
// the subset that is not handled by the 'leftKeys' to 'rightKeys' equijoin.
// 'conditionOnJoinKeys' is the subset of the original Join condition that corresponds to the
// 'leftKeys' to 'rightKeys' equijoin.
type ReturnType =
(JoinType, Seq[Expression], Seq[Expression],
Option[Expression], Option[Expression], LogicalPlan, LogicalPlan, JoinHint)
def unapply(join: Join): Option[ReturnType] = join match {
。。。
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
/**
* The enumeration of join strategy hints.
*
* The hinted strategy will be used for the join with which it is associated if doable. In case
* of contradicting strategy hints specified for each side of the join, hints are prioritized as
* BROADCAST over SHUFFLE_MERGE over SHUFFLE_HASH over SHUFFLE_REPLICATE_NL.
*/
object JoinStrategyHint {
val strategies: Set[JoinStrategyHint] = Set(
BROADCAST,
SHUFFLE_MERGE,
SHUFFLE_HASH,
SHUFFLE_REPLICATE_NL)
}
|
hint 语法:
1
2
3
|
SELECT /*+ BROADCAST(a) */
* FROM people AS a JOIN employee AS b
ON a.id = b.id
|
从未解析的计划 –> 解析后的 –> 优化后的 –> 物理计划
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
== Parsed Logical Plan ==
'UnresolvedHint BROADCAST, ['a]
+- 'Project [*]
+- 'Join Inner, ('a.id = 'b.id)
:- 'SubqueryAlias a
: +- 'UnresolvedRelation [people], [], false
+- 'SubqueryAlias b
+- 'UnresolvedRelation [employee], [], false
== Analyzed Logical Plan ==
age: bigint, id: string, name: string, id: string, name: string, salary: bigint
Project [age#6L, id#7, name#8, id#18, name#19, salary#20L]
+- Join Inner, (id#7 = id#18)
:- ResolvedHint (strategy=broadcast)
: +- SubqueryAlias a
: +- SubqueryAlias people
: +- View (`people`, [age#6L,id#7,name#8])
: +- LogicalRDD [age#6L, id#7, name#8], false
+- SubqueryAlias b
+- SubqueryAlias employee
+- View (`employee`, [id#18,name#19,salary#20L])
+- LogicalRDD [id#18, name#19, salary#20L], false
== Optimized Logical Plan ==
Join Inner, (id#7 = id#18), leftHint=(strategy=broadcast)
:- Filter isnotnull(id#7)
: +- LogicalRDD [age#6L, id#7, name#8], false
+- Filter isnotnull(id#18)
+- LogicalRDD [id#18, name#19, salary#20L], false
== Physical Plan ==
AdaptiveSparkPlan isFinalPlan=false
+- BroadcastHashJoin [id#7], [id#18], Inner, BuildLeft, false
:- BroadcastExchange HashedRelationBroadcastMode(List(input[1, string, false]),false), [plan_id=115]
: +- Filter isnotnull(id#7)
: +- Scan ExistingRDD[age#6L,id#7,name#8]
+- Filter isnotnull(id#18)
+- Scan ExistingRDD[id#18,name#19,salary#20L]
|
等值 join 的选择策略,如下:
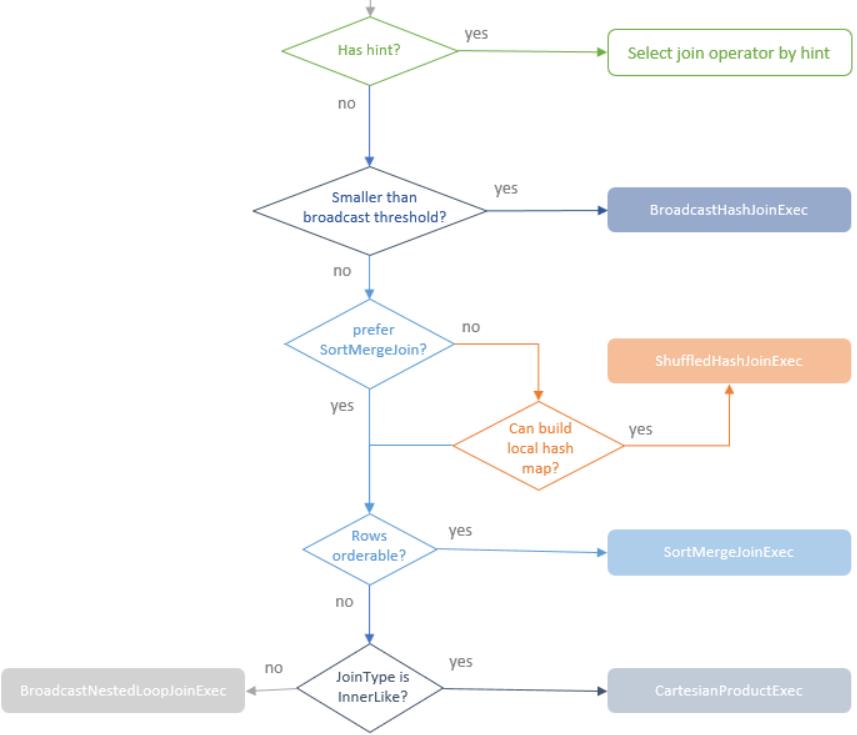
有效的 join hint基于如下:
- For BROADCAST hint, select the BroadcastHashJoinExec operator. when BROADCAST hint is specified on both sides of the join, select the smaller side.
- For SUFFLE_HASH hint, select the ShuffledHashJoinExec operator. when SUFFLE_HASH hint is specified on both sides of the join, select the smaller side.
- For SUFFLE_MERGE hint, select the SortMergeJoinExec operator if the join keys are sortable.
- For SUFFLE_REPLICATE_NL, select the CartesianProductExec operator if join type is inner like.
如果未指定连接提示或未满足指定连接提示的连接条件,则选择流将沿决策树向下移动
父类 HashJoin
HashJoin
- 根据数据表的角色不同分为streamedTable流式表和BuildTable构建表
- 通常将大表设定为流式表,将小表设定为构建表
- 在一次Build过程中,流式表迭代器streamedlter遍历流式表的每条记录,然后在构建表迭代器buildlter中查找相匹配的记录
- 每次Build的结果为一条JoinedRow(left, right)。如果left来自streamedlter,right来自buildlter,则为BuildRight操作
- 如果right来自 streamedlter,left来自 buildlter,则为BuildLeft操作
Join操作的基本流程

join 类型不同,输出也不同,这是由 output 函数控制的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
override def output: Seq[Attribute] = {
joinType match {
case _: InnerLike =>
left.output ++ right.output
case LeftOuter =>
left.output ++ right.output.map(_.withNullability(true))
case RightOuter =>
left.output.map(_.withNullability(true)) ++ right.output
case j: ExistenceJoin =>
left.output :+ j.exists
case LeftExistence(_) =>
left.output
case x =>
throw new IllegalArgumentException(s"HashJoin should not take $x as the JoinType")
}
}
|
outputPartitioning()
- 输出数据的分区模式,由streamedPlan决定
不同类型 join 的执行:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
protected def join(
streamedIter: Iterator[InternalRow],
hashed: HashedRelation,
numOutputRows: SQLMetric): Iterator[InternalRow] = {
val joinedIter = joinType match {
case _: InnerLike =>
innerJoin(streamedIter, hashed)
case LeftOuter | RightOuter =>
outerJoin(streamedIter, hashed)
case LeftSemi =>
semiJoin(streamedIter, hashed)
case LeftAnti =>
antiJoin(streamedIter, hashed)
case _: ExistenceJoin =>
existenceJoin(streamedIter, hashed)
case x =>
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
s"HashJoin should not take $x as the JoinType")
}
val resultProj = createResultProjection
joinedIter.map { r =>
numOutputRows += 1
resultProj(r)
}
}
|
JoinedRow 的结构
1
2
3
|
class JoinedRow extends InternalRow {
private[this] var row1: InternalRow = _
private[this] var row2: InternalRow = _
|
私有函数 InnerLike(innter 和 cross) 执行过
- 对应的JoinType为Inner和Cross。hashedRelation对应的是构建表的HashMap结构
- 遍历流式表,将连接键相同的构建表的行与流式表的当前行组合成JoinedRow,流式表的一行可能和多个构建表的行对应
- 从代码中可以看出此函数中对JoinRow进行了复用,如果直接物化返回的迭代器将会导致重复
- 但是由于函数返回的是迭代器类型,最后进行计算ResultTask时,遍历innerJoin()返回的迭代器的同时从内存中取出对应数据,这样就不会产生重复
outerJoin()
- 对应的JoinType为LeftOuter和RightOuter
- 如果流式表中的连接键在构建表中没有,则会返回流式表对应行和空值连接的行。其余情况与innerJoin()一致
semiJoin()
- 对应的JoinType为LeftSemi
- 当流式表的连接键不为空且构建表中存在对应的行时,返回流式表的行
antiJoin()
- 对应的JoinType为LeftAnti
- 当流式表的连接键不为空且构建表中不存在对应的行时,返回流式表的行
HashJoin 的 doConsume(),用于生成 code gen 过程:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
override def doConsume(ctx: CodegenContext, input: Seq[ExprCode], row: ExprCode): String = {
joinType match {
case _: InnerLike => codegenInner(ctx, input)
case LeftOuter | RightOuter => codegenOuter(ctx, input)
case LeftSemi => codegenSemi(ctx, input)
case LeftAnti => codegenAnti(ctx, input)
case _: ExistenceJoin => codegenExistence(ctx, input)
case x =>
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
s"HashJoin should not take $x as the JoinType")
}
}
|
几个 join 的类图
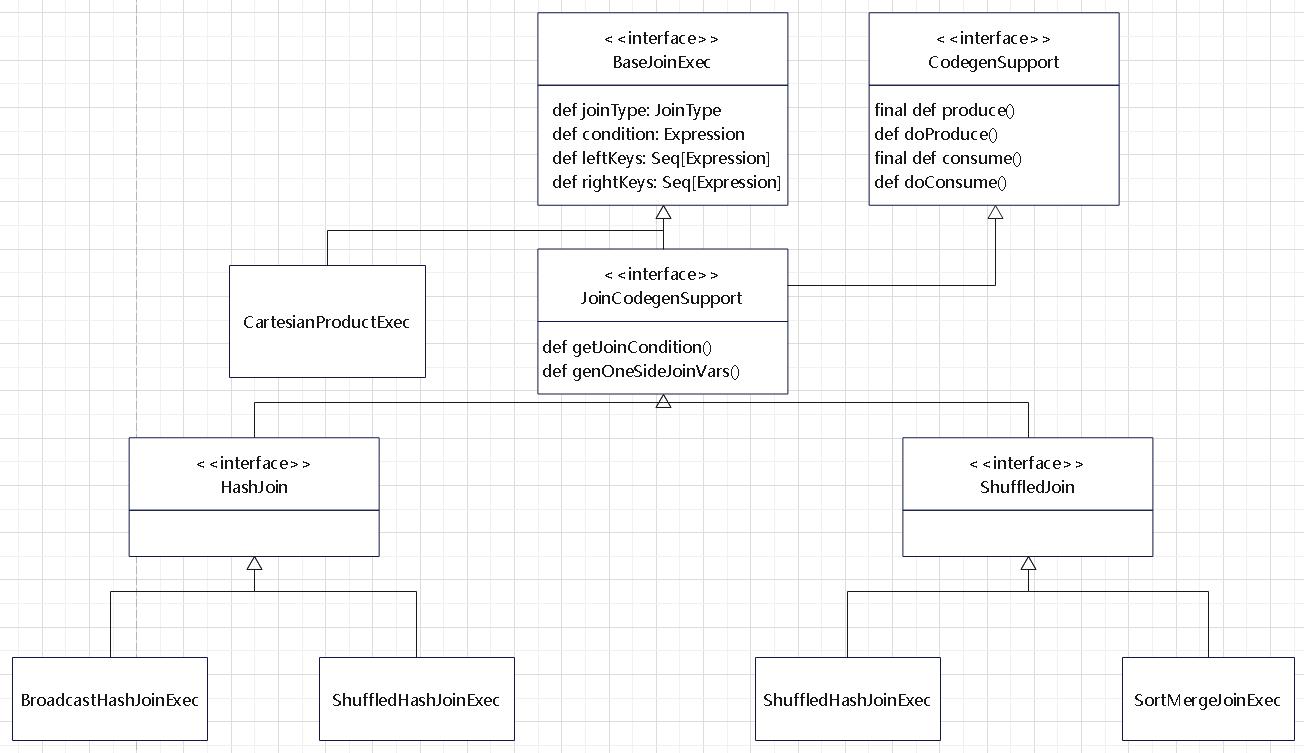
JOIN 的执行
Broadcast Hash Join
测试代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
test("broadcast json data test") {
val peopleData = Seq(
"""{"id":1,"name":"Michael"}""",
"""{"id":2,"name":"Andy", "age":30}""",
"""{"id":3,"name":"Justin", "age":19}"""
)
val employeeData = Seq(
"""{"id":1,"name":"Michael", "salary":3000}""",
"""{"id":2,"name":"Andy", "salary":4500}""",
"""{"id":3,"name":"Justin", "salary":3500}""",
"""{"id":4,"name":"Berta", "salary":4000}"""
)
spark.read.json(spark.sparkContext.parallelize(peopleData)).createTempView("people")
spark.read.json(spark.sparkContext.parallelize(employeeData)).createTempView("employee")
val df = spark.sql(
"""
|SELECT /*+ BROADCAST(a) */
|* FROM people AS a JOIN employee AS b
|ON a.id = b.id
|""".stripMargin)
df.show()
df.explain("extended")
}
|
广播之前,需要确保子节点满足需求requiredChildDistribution ,增加 BroadcastExchange 节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
override def requiredChildDistribution: Seq[Distribution] = {
val mode = HashedRelationBroadcastMode(buildBoundKeys, isNullAwareAntiJoin)
buildSide match {
case BuildLeft =>
BroadcastDistribution(mode) :: UnspecifiedDistribution :: Nil
case BuildRight =>
UnspecifiedDistribution :: BroadcastDistribution(mode) :: Nil
}
}
|
几个 Exchange 的关系
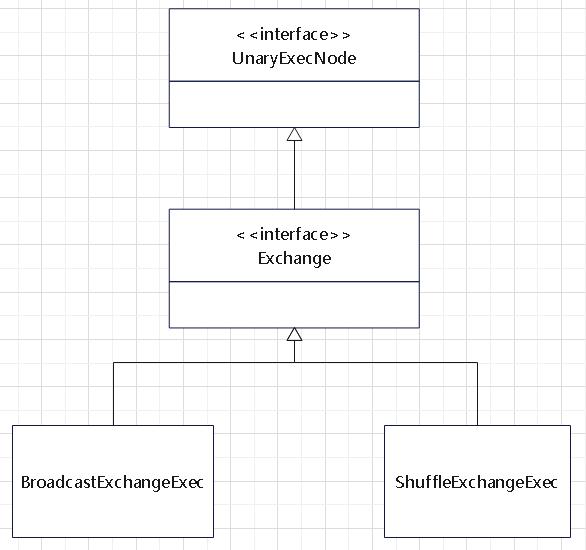
增加需要的节点后的物理计划,此时多了BroadcastExchange
也就是把 people 广播出去
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
== Physical Plan ==
AdaptiveSparkPlan isFinalPlan=false
+- BroadcastHashJoin [id#7L], [id#18L], Inner, BuildLeft, false
:- BroadcastExchange HashedRelationBroadcastMode(List(input[1, bigint, false]),false), [plan_id=115]
: +- Filter isnotnull(id#7L)
: +- Scan ExistingRDD[age#6L,id#7L,name#8]
+- Filter isnotnull(id#18L)
+- Scan ExistingRDD[id#18L,name#19,salary#20L]
|
当 BroadcastExchange 执行时,driver 会收集所有 executor 端的数据
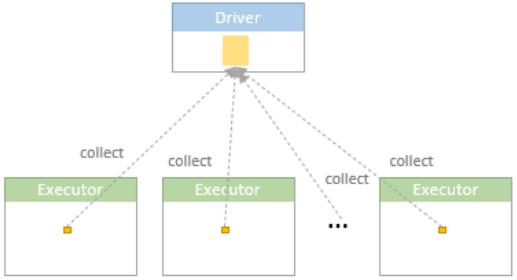
这里有两个 广播的控制变量
- spark.sql.autoBroadcastJoinThreshold,控制 hash join 的广播阈值,默认 10M
- MAX_BROADCAST_TABLE_ROWS,控制 broadcast exchange 时的阈值,默认约 341 million rows
之后每个 executor 端都收到了 广播表,建立 BuildTable
然遍历流表,再去 BuildTable 中查找是否匹配
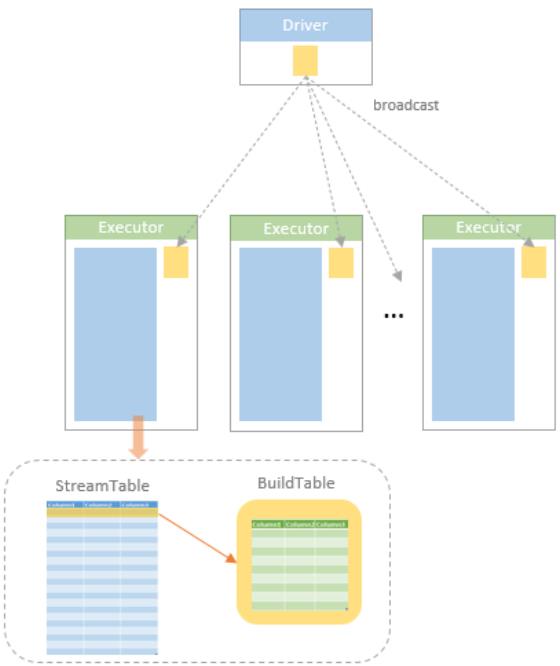
BroadcastExchangeExec 的执行过程
- child.executeCollectIterator() 收集数据
- sparkContext.broadcastInternal(relation, serializedOnly = true) 广播
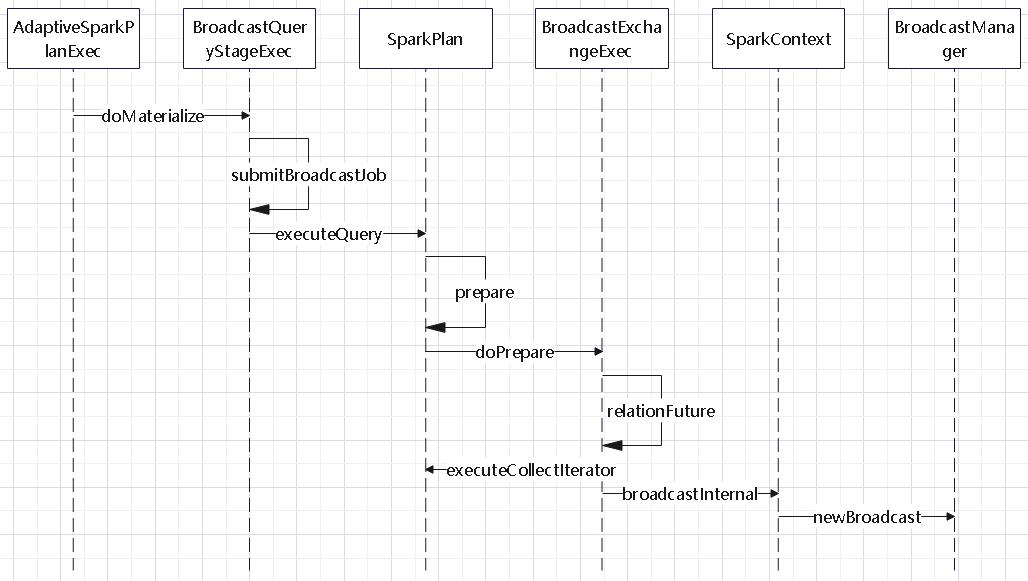
非 code-gen执行时,会用到 SparkPlan 的 execute()
- execute 中会先调用 executeQuery,这里会做一些 prepare 的动作
- prepare 中调用 doPrepare,由子类完成具体的准备
- execute 再调用子类的 doExecute,执行具体操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
final def execute(): RDD[InternalRow] = executeQuery {
if (isCanonicalizedPlan) {
throw SparkException.internalError("A canonicalized plan is not supposed to be executed.")
}
doExecute()
}
protected final def executeQuery[T](query: => T): T = {
RDDOperationScope.withScope(sparkContext, nodeName, false, true) {
prepare()
waitForSubqueries()
query
}
}
|
这里会使用HashedRelation类,它有两个子类
- LongHashedRelation
- UnsafeHashedRelation
执行过程如下(非 codegen 模式):
- 首先由 AdaptiveSparkPlanExec 触发,经过SparkPlan一些通用函数后
- 调用到 BroadcastHashJoinExec,这个类再委托 SparkPlan,调用 doExecuteBroadcast
- 然后由 BroadcastExchangeExec 负责执行广播,这个类又会调用到 TorrentBroadcast,最后由 BlockManager 负责读取本地、或者远程的数据块
- 回到 BroadcastHashJoinExec,它会调用子类 FilterExec、RDDScanExec 读取过滤数据
- 之后执行 join 算法,这块由父类 HashJoin 统一执行
- 遍历流表,然后从 LongToUnsafeRowMap 这个hash 表中读取数据做匹配
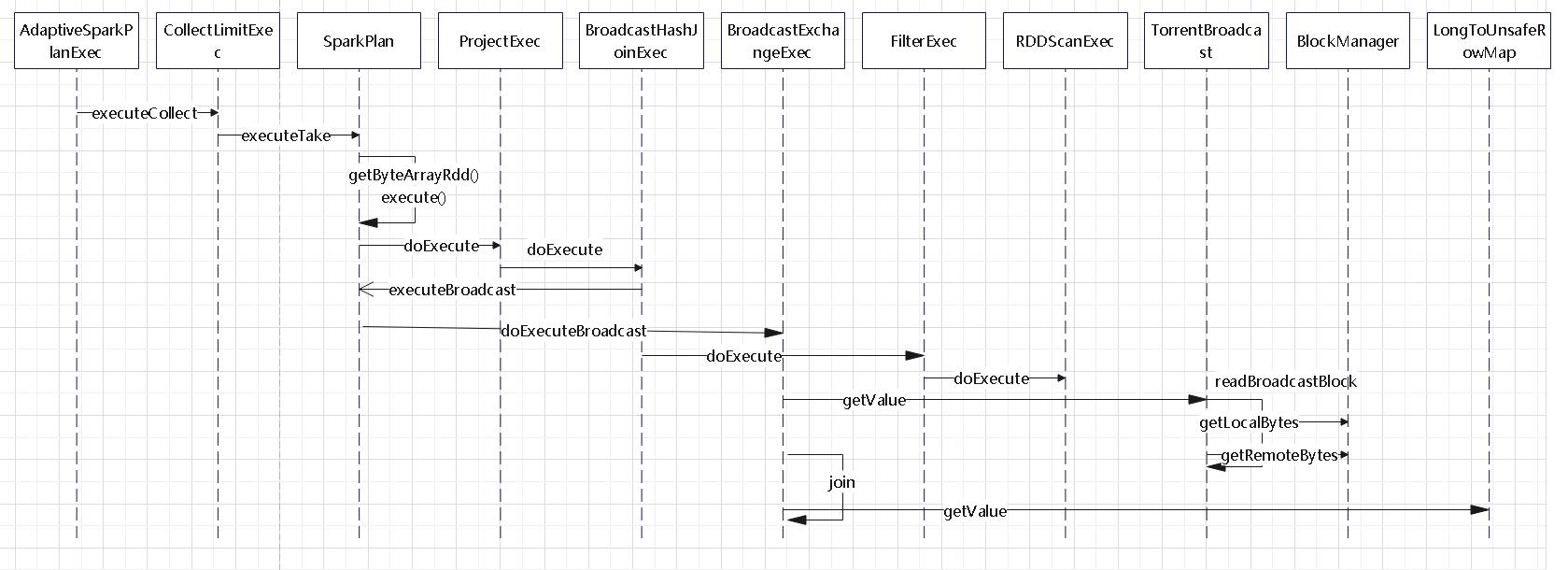
Shuffle Hash Join
测试代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
val df = spark.sql(
"""
|SELECT /*+ SHUFFLE_HASH(a) */
|* FROM people AS a JOIN employee AS b
|ON a.id = b.id
|""".stripMargin)
df3.show()
|
生成的物理计划:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
== Physical Plan ==
AdaptiveSparkPlan isFinalPlan=false
+- ShuffledHashJoin [id#7L], [id#18L], Inner, BuildLeft
:- Exchange hashpartitioning(id#7L, 200), ENSURE_REQUIREMENTS, [plan_id=142]
: +- Filter isnotnull(id#7L)
: +- Scan ExistingRDD[age#6L,id#7L,name#8]
+- Exchange hashpartitioning(id#18L, 200), ENSURE_REQUIREMENTS, [plan_id=143]
+- Filter isnotnull(id#18L)
+- Scan ExistingRDD[id#18L,name#19,salary#20L]
|
要求
- 在外连接中,基表不能被广播
- spark.sql.join.preferSortMergeJoin参数必须设置为 false
- 小表小于spark.sql.autoBroadcastJoinThreshold*spark.sql.shuffle.partitions
- 小表远远小于(muchSmaller())大表
对于子节点的要求:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
override def requiredChildDistribution: Seq[Distribution] = {
if (isSkewJoin) {
// We re-arrange the shuffle partitions to deal with skew join, and the new children
// partitioning doesn't satisfy `HashClusteredDistribution`.
UnspecifiedDistribution :: UnspecifiedDistribution :: Nil
} else {
ClusteredDistribution(leftKeys) :: ClusteredDistribution(rightKeys) :: Nil
}
}
|
Distribution 表示节点间的数据分布,其类的继承关系
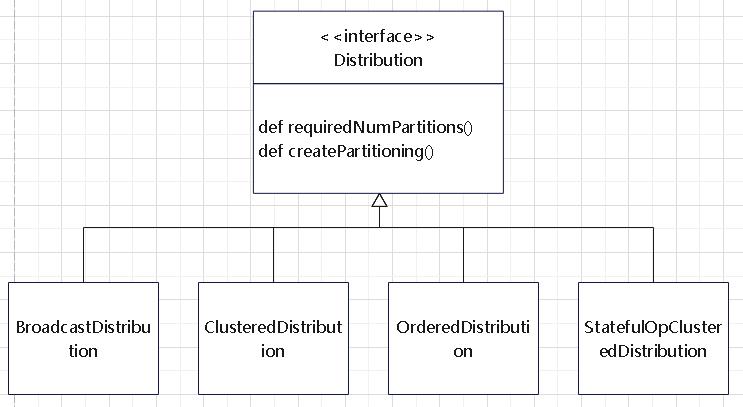
选择策略:
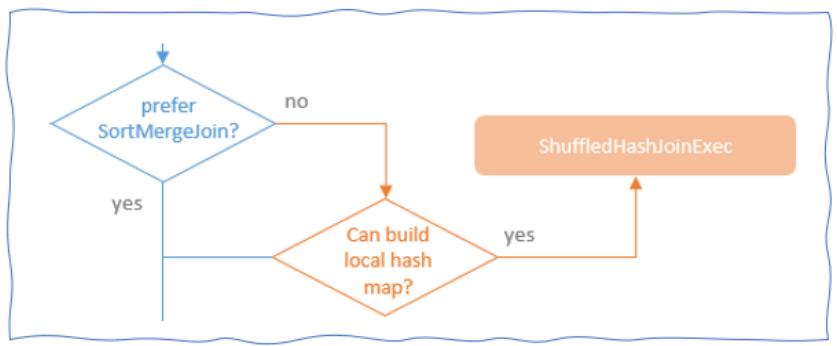
需要节点的要求:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
override def requiredChildDistribution: Seq[Distribution] = {
if (isSkewJoin) {
// We re-arrange the shuffle partitions to deal with skew join, and the new children
// partitioning doesn't satisfy `HashClusteredDistribution`.
UnspecifiedDistribution :: UnspecifiedDistribution :: Nil
} else {
ClusteredDistribution(leftKeys) :: ClusteredDistribution(rightKeys) :: Nil
}
}
|
doExecute()
- doExecute()函数返回RDD[InternalRow],显示了具体的运算逻辑
- 在调用prepareForExecution()进行准备工作时,会添加 Exchange物理计划对流式表和构建表分别进行shuffle,让两张表中拥有相同连接键哈希值的行分到相同的分区中
- 调用流式表物理计划的RDD[InternalRow]的zipPartitions()函数转化为新的RDD,在RDD内将构建表构造成HashedRelation,然后调用其父类的HashJoin.join()函数计算出Join后的行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
protected override def doExecute(): RDD[InternalRow] = {
val numOutputRows = longMetric("numOutputRows")
streamedPlan.execute().zipPartitions(buildPlan.execute()) { (streamIter, buildIter) =>
val hashed = buildHashedRelation(buildIter)
joinType match {
case FullOuter => buildSideOrFullOuterJoin(streamIter, hashed, numOutputRows,
isFullOuterJoin = true)
case LeftOuter if buildSide.equals(BuildLeft) =>
buildSideOrFullOuterJoin(streamIter, hashed, numOutputRows, isFullOuterJoin = false)
case RightOuter if buildSide.equals(BuildRight) =>
buildSideOrFullOuterJoin(streamIter, hashed, numOutputRows, isFullOuterJoin = false)
case _ => join(streamIter, hashed, numOutputRows)
}
}
}
|
执行过程:
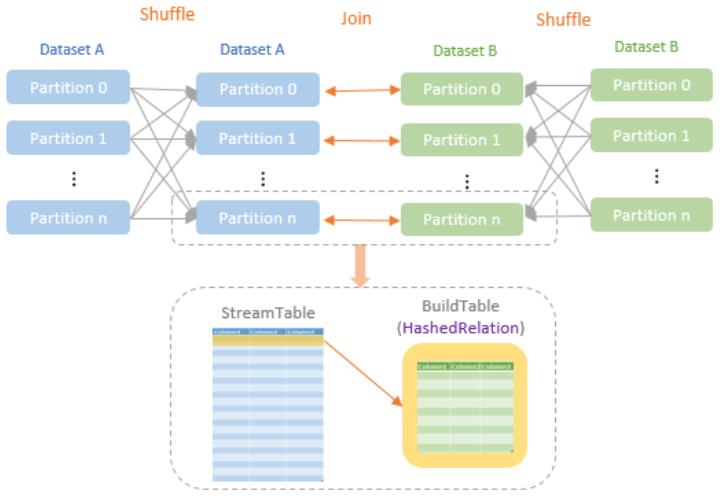
具体执行时,分两部
- 先物化,等待 shuffle 等结果
- 然后执行 shuffle hash
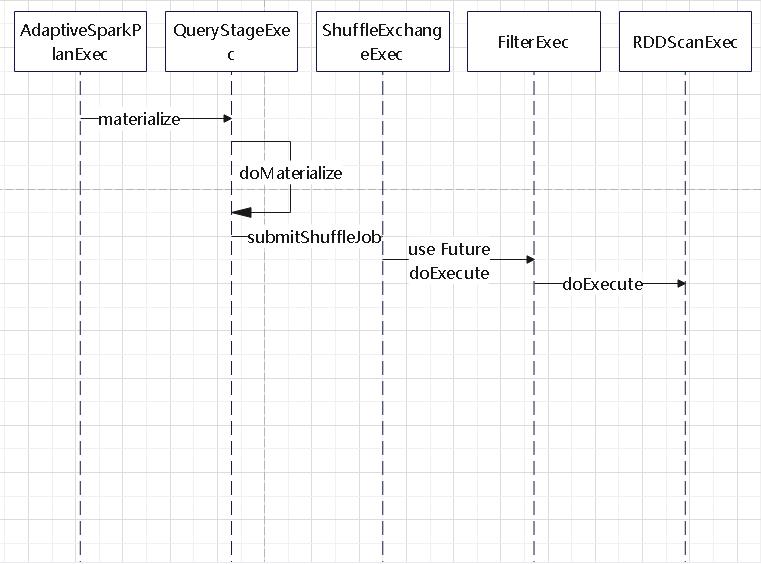
第一步,materialize 的执行过程,比如执行广播等操作,调用者会执行 Future 等待其完成
- 这里先由 AdaptiveSparkPlanExec 触发
- 之后调用到 ShuffleExchangeExec,执行 shuffle操作,然后每个分区内再执行 filter + scan
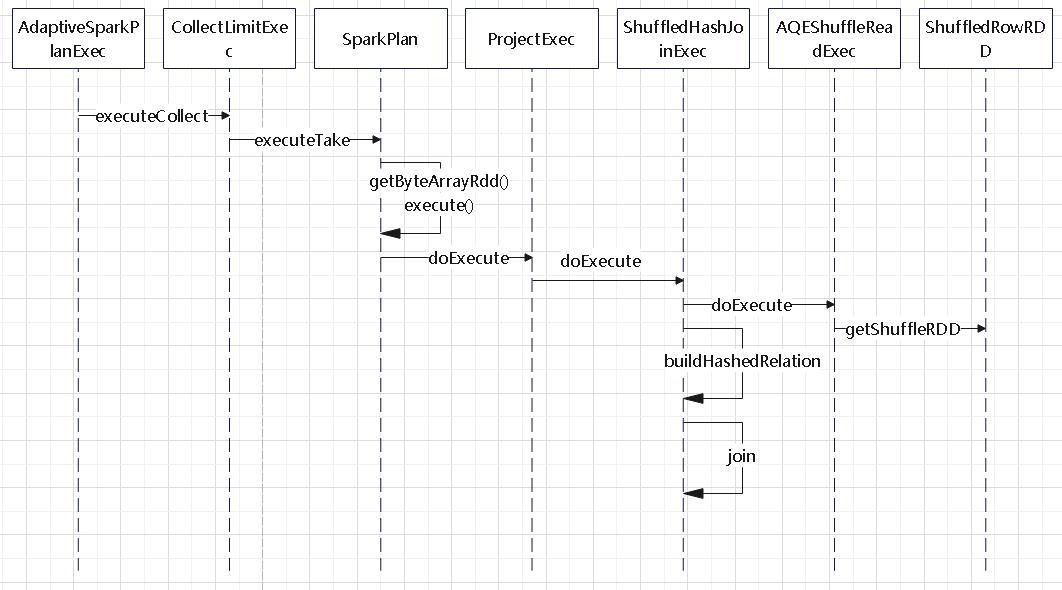
在 ShuffledHashJoinExec#doExecute 中,获取 hash 端、流表端的时候,是通过 AQEShuffleRead 获取的
hash 端,流表端都是通过 AQEShuffleRead 拿到的
1
2
3
4
5
|
AQEShuffleRead coalesced
+- ShuffleQueryStage 0
+- Exchange hashpartitioning(id#7L, 200), ENSURE_REQUIREMENTS, [plan_id=54]
+- Filter isnotnull(id#7L)
+- Scan ExistingRDD[age#6L,id#7L,name#8]
|
第二步,执行过程如下(非 codegen 模式):
- 也是由 AdaptiveSparkPlanExec 触发
- 先是投影操作,然后到 ShuffleExchangeExec,之后委托 AQEShuffleReadExec 读取 shuffle 数据
- 等拿到数据后,就 build hash 关系,然后调用 join() 函数,这个是父类 HashJoin的函数
- 后面的流程跟 BroadcastHashJoinExec 调用的 join是类似的
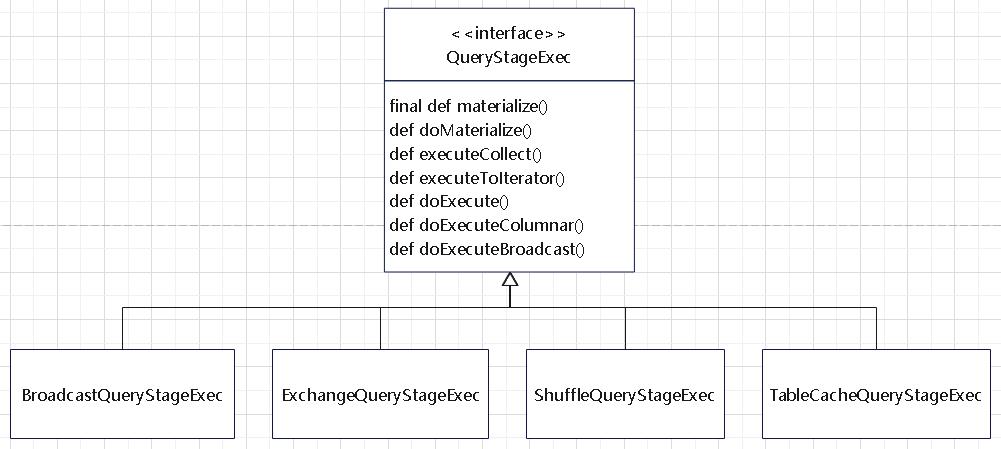
QueryStageExec 的继承关系
- 查询阶段是查询计划的独立子图
- AQE框架将在执行查询计划的其他操作符之前实现其输出
- 物化输出的数据统计信息可用于优化查询计划的其余部分
Shuffle Sort Merge Join
测试代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
val df = spark.sql(
"""
|SELECT
|* FROM people AS a JOIN employee AS b
|ON a.id = b.id
|""".stripMargin)
df.show()
|
生成的物理计划:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
== Physical Plan ==
AdaptiveSparkPlan isFinalPlan=false
+- SortMergeJoin [id#7L], [id#18L], Inner
:- Sort [id#7L ASC NULLS FIRST], false, 0
: +- Exchange hashpartitioning(id#7L, 200), ENSURE_REQUIREMENTS, [plan_id=136]
: +- Filter isnotnull(id#7L)
: +- Scan ExistingRDD[age#6L,id#7L,name#8]
+- Sort [id#18L ASC NULLS FIRST], false, 0
+- Exchange hashpartitioning(id#18L, 200), ENSURE_REQUIREMENTS, [plan_id=137]
+- Filter isnotnull(id#18L)
+- Scan ExistingRDD[id#18L,name#19,salary#20L]
|
介绍
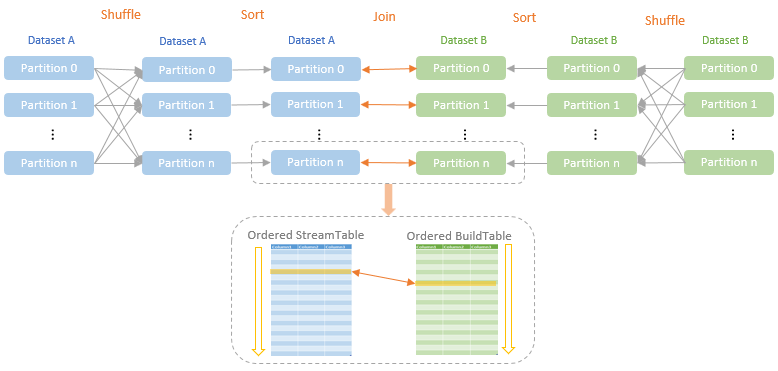
- 当两个表的数据量都非常大时,会使用SortMergeJoin方式进行Join
- 对两张表参与Join的连接键使用相同的分区算法和分区数进行分区,目的就是保证相同的连接键的行都落到相同的分区里面
- 之后再对每个分区按照连接键进行排序,最后Reduce端获取两张表相同分区的数据进行Merge Join
不满足BroadcastHashJoin和ShuffledHashJoin
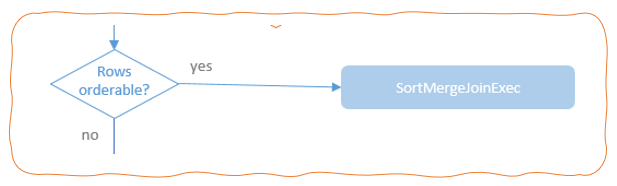
只支持等值连接,并且要求参与Join的连接键可排序
选择过程
对于子节点的要求:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
override def requiredChildOrdering: Seq[Seq[SortOrder]] =
requiredOrders(leftKeys) :: requiredOrders(rightKeys) :: Nil
private def requiredOrders(keys: Seq[Expression]): Seq[SortOrder] = {
// This must be ascending in order to agree with the `keyOrdering` defined in `doExecute()`.
keys.map(SortOrder(_, Ascending))
}
|
doExecute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
protected override def doExecute(): RDD[InternalRow] = {
val numOutputRows = longMetric("numOutputRows")
val spillSize = longMetric("spillSize")
val spillThreshold = getSpillThreshold
val inMemoryThreshold = getInMemoryThreshold
val evaluatorFactory = new SortMergeJoinEvaluatorFactory(
leftKeys,
rightKeys,
joinType,
condition,
left,
right,
output,
inMemoryThreshold,
spillThreshold,
numOutputRows,
spillSize,
onlyBufferFirstMatchedRow
)
if (conf.usePartitionEvaluator) {
left.execute().zipPartitionsWithEvaluator(right.execute(), evaluatorFactory)
} else {
left.execute().zipPartitions(right.execute()) { (leftIter, rightIter) =>
val evaluator = evaluatorFactory.createEvaluator()
evaluator.eval(0, leftIter, rightIter)
}
}
}
|
总结
- 速度上可能没有 hash 的快,但是也比 nested loop join 更好,属于性能适中的
- 不需要全部加载到内存,所以对内存没有限制
- StreamTable or BuildTable 对于 join 两边都合适,反正都不用放到内存中
- 两边都是使用迭代遍历的方式,遍历流表,然后遍历迭代表查找匹配的 结果
执行过程:
时序图
从分区读取数据的过程,跟 shuffle hash join 类似

Sort merge join 的 join 执行过程
- 跟 shuffle-hash-join不同,这里多了一个 SortExec 子节点
- 后面的流程跟 shuffle-hash-join 差不多,也是通过 AQEShuffleReadExec 读数据

读取 shuffle 数据的过程
- sort-merge-join,shuffle-hash-join 都会使用到这个流程
- 通过 SortShuffleManager 读取网络数据

SortMergeJoinScanner
RowIterator
- advanceNext()方法将Iterator向前移动一行
- getRow()获取当前行
SortMergeJoinScanner 的构造参数中会传递
- streamedlter: streamedTable的迭代器
- bufferedlter: bufferedTable的迭代器
- streamedKeyGenerator, bufferedKeyGenerator: streamedTable和bufferedTable的连接键
- keyOrdering: 连接键的排序器
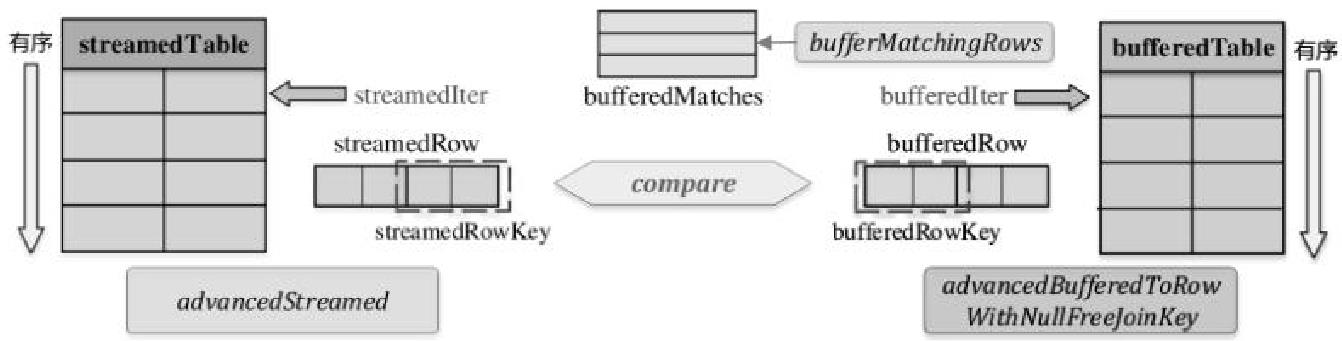
如上
- streamedTable与bufferedTable都是shuffle后的数据,所以都是已经排好序的
- 在匹配满足条件数据的过程中只需要不断移动迭代器,得到新的数据行进行比较再Join即可
- 与当前steamedTable行匹配的所有bufferedTable缓存在bufferedMatches中
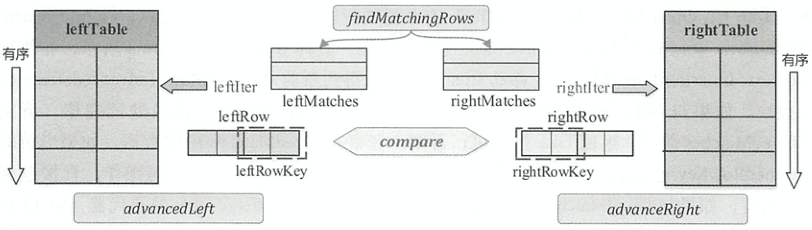
SortMergeJoinScanner#findNextInnerJoinRows 执行流程
- 循环调用advancedStreamed()直到当前streamedTable连接键streamRowKey不包含null字段
- 如果streamedTable行streamRow为null或者bufferedTable行bufferedRow为null,说明streamedTable或者bufferedTable处理完毕,清空bufferedMatches,返回false
- 如果streamedTable连接键streamedRowKey和bufferedTable连接键bufferedRowKey相等,那么bufferedMatches数组已经是可以和streamRow连接的bufferedTable中的所有行
- 不断比较streamedRowKey和bufferedRowKey,如果streamedRowKey值较小,则调用advancedStreamed()获取streamedTable下一行
- 如果bufferedRowKey值较小,则调用advancedBufferedToRowWithNullFreeJoinKey()获取bufferedTable下一行。直到两者相等或者其中一行为null
- 当满足Join条件时,执行bufferMatchingRows()方法得到bufferedMatches数组
SortMergeJoinScanner#findNextOuterJoinRows 执行流程
- 如果streamedTable全部行都已经处理完,则清空bufferedMatches,并返回false
- 如果两个连接键相等,则直接返回true
- 如果不相等,那么不断迭代bufferedTable直到当前bufferedRowKey值比streamedRowKey值大或两者相等
- 如果相等则调用bufferMatchingRows()方法获得bufferedMatches并返回true,否则直接返回true
SortMergeJoinScanner 依赖的外部类
ExternalAppendOnlyUnsafeRowArray 是暂存数据的地方,也会溢出到磁盘
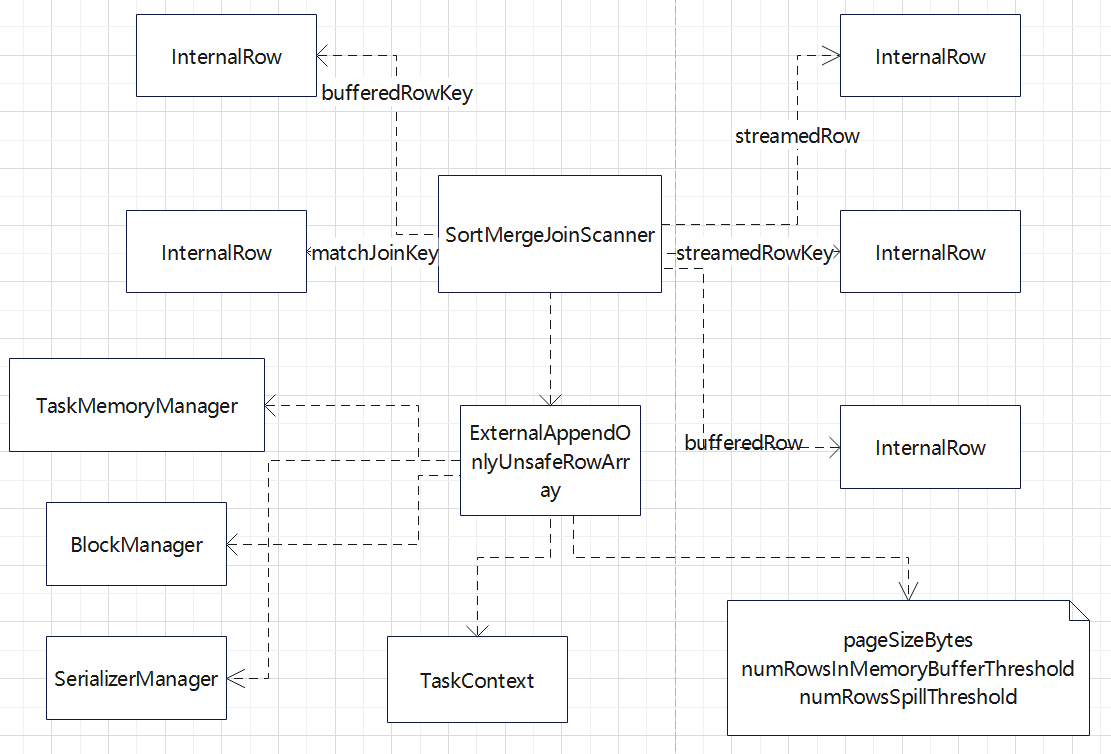
SortMergeFullOuterJoinScanner
执行过程
- 左表和右表分别前移的方法为advancedLeft()和advancedRight()
- 在SortMergeFullOuterJoinScanner遍历数据过程中会构造两个缓冲区leftMatches和rightMatches
- 来缓存匹配右表当前数据行的数据与缓存匹配左表当前数据行的数据
- scanNextlnBuffered()方法返回两个缓冲区full join的数据放入joinedRow
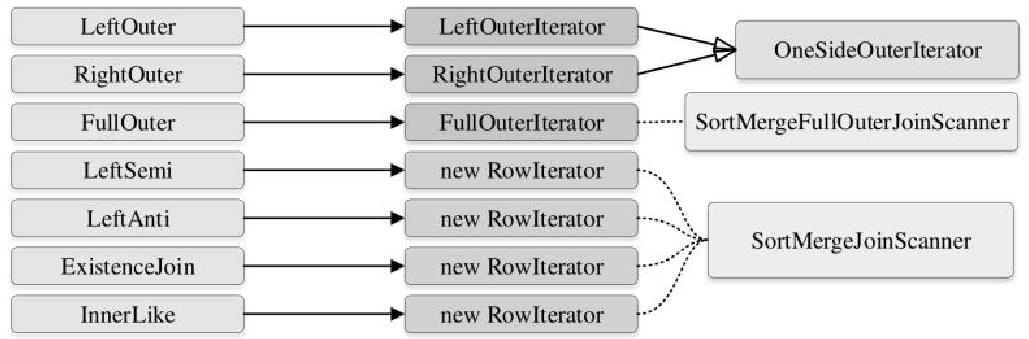
不同 join 类型对应的 迭代算法
BroadcastNestedLoopJoinExec
测试代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
val df = spark.sql(
"""
|SELECT /*+ BROADCAST(a), SHUFFLE_REPLICATE_NL(b) */
|* FROM people AS a LEFT OUTER JOIN employee AS b
|ON a.id != b.id WHERE a.id > 10 and b.id > 10
|""".stripMargin)
df.show()
|
生成的物理计划:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
== Physical Plan ==
AdaptiveSparkPlan isFinalPlan=false
+- BroadcastNestedLoopJoin BuildLeft, Inner, NOT (id#7L = id#18L)
:- BroadcastExchange IdentityBroadcastMode, [plan_id=87]
: +- Filter (isnotnull(id#7L) AND (id#7L > 10))
: +- Scan ExistingRDD[age#6L,id#7L,name#8]
+- Filter (isnotnull(id#18L) AND (id#18L > 10))
+- Scan ExistingRDD[id#18L,name#19,salary#20L]
|
BroadcastNestedLoopJoinExec会根据相关条件对小表进行广播,以减少表的扫描次数。触发广播的需要满足以下三个条件之一
- right outer join是会广播左表
- left outer, left semi, left anti或者 existence join时会广播右表
- inner join的时候两张表都会广播
对子节点的要求:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
override def requiredChildDistribution: Seq[Distribution] = buildSide match {
case BuildLeft =>
BroadcastDistribution(IdentityBroadcastMode) :: UnspecifiedDistribution :: Nil
case BuildRight =>
UnspecifiedDistribution :: BroadcastDistribution(IdentityBroadcastMode) :: Nil
}
|
doExecute:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
protected override def doExecute(): RDD[InternalRow] = {
val broadcastedRelation = broadcast.executeBroadcast[Array[InternalRow]]()
val resultRdd = (joinType, buildSide) match {
case (_: InnerLike, _) =>
innerJoin(broadcastedRelation)
case (LeftOuter, BuildRight) | (RightOuter, BuildLeft) =>
outerJoin(broadcastedRelation)
case (LeftSemi, _) =>
leftExistenceJoin(broadcastedRelation, exists = true)
case (LeftAnti, _) =>
leftExistenceJoin(broadcastedRelation, exists = false)
case (_: ExistenceJoin, _) =>
existenceJoin(broadcastedRelation)
case _ =>
/**
* LeftOuter with BuildLeft
* RightOuter with BuildRight
* FullOuter
*/
defaultJoin(broadcastedRelation)
}
val numOutputRows = longMetric("numOutputRows")
resultRdd.mapPartitionsWithIndexInternal { (index, iter) =>
val resultProj = genResultProjection
resultProj.initialize(index)
iter.map { r =>
numOutputRows += 1
resultProj(r)
}
}
}
|
innerJoin 实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
private def innerJoin(relation: Broadcast[Array[InternalRow]]): RDD[InternalRow] = {
streamed.execute().mapPartitionsInternal { streamedIter =>
val buildRows = relation.value
val joinedRow = new JoinedRow
streamedIter.flatMap { streamedRow =>
val joinedRows = buildRows.iterator.map(r => joinedRow(streamedRow, r))
if (condition.isDefined) {
joinedRows.filter(boundCondition)
} else {
joinedRows
}
}
}
}
|
基本上就等价于 两个for循环
1
2
3
|
for record_1 in relation_1:
for record_2 in relation_2:
# join condition is executed
|
CartesianProduct
如果两张参与Join的表没有连接条件且是内连接类型,那么会产生CartesianProduct,得到笛卡尔积
测试代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
val df = spark.sql(
"""
|SELECT /*+ SHUFFLE_REPLICATE_NL(a), SHUFFLE_REPLICATE_NL(b) */
|* FROM people AS a LEFT OUTER JOIN employee AS b
|ON a.id == b.id WHERE a.id > 10 and b.id > 10
|""".stripMargin)
df.show()
|
生成的物理计划:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
== Physical Plan ==
CartesianProduct (id#7L = id#18L)
:- Filter (isnotnull(id#7L) AND (id#7L > 10))
: +- Scan ExistingRDD[age#6L,id#7L,name#8]
+- Filter (isnotnull(id#18L) AND (id#18L > 10))
+- Scan ExistingRDD[id#18L,name#19,salary#20L]
|
对子节点的分布没有要求
doExecute,比较简单,就是 两个 for 循环
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
protected override def doExecute(): RDD[InternalRow] = {
val numOutputRows = longMetric("numOutputRows")
val leftResults = left.execute().asInstanceOf[RDD[UnsafeRow]]
val rightResults = right.execute().asInstanceOf[RDD[UnsafeRow]]
val pair = new UnsafeCartesianRDD(
leftResults,
rightResults,
conf.cartesianProductExecBufferInMemoryThreshold,
conf.cartesianProductExecBufferSpillThreshold)
pair.mapPartitionsWithIndexInternal { (index, iter) =>
val joiner = GenerateUnsafeRowJoiner.create(left.schema, right.schema)
val filtered = if (condition.isDefined) {
val boundCondition = Predicate.create(condition.get, left.output ++ right.output)
boundCondition.initialize(index)
val joined = new JoinedRow
iter.filter { r =>
boundCondition.eval(joined(r._1, r._2))
}
} else {
iter
}
filtered.map { r =>
numOutputRows += 1
joiner.join(r._1, r._2)
}
}
}
|
参考




































