Llama Factory
安装
如果是物理机安装,需要
- 安装 GCC
- 安装 cuda
- 安装显卡驱动
推荐容器安装
- 也需要先安装 显卡驱动
- PyTorch Release 24.02,nvidia 提供的 pytorch 镜像包,22G
- 包含 nvidia 相关的工具
- 镜像包内容详情介绍
docker compose 启动
|
|
支持 三种类型的 显卡
- nvidia 的
- amd 的
- 华为 的
执行
|
|
这步时也会下载一些东西,需要修改下载的源配置
docker file修改,修改成这个地址
|
|
docker-compose yaml 修改:
|
|
如上,修改了 PIP_INDEX,增加了一个 volumes,/data2
进入容器后,执行下面命令,启动 web ui
|
|
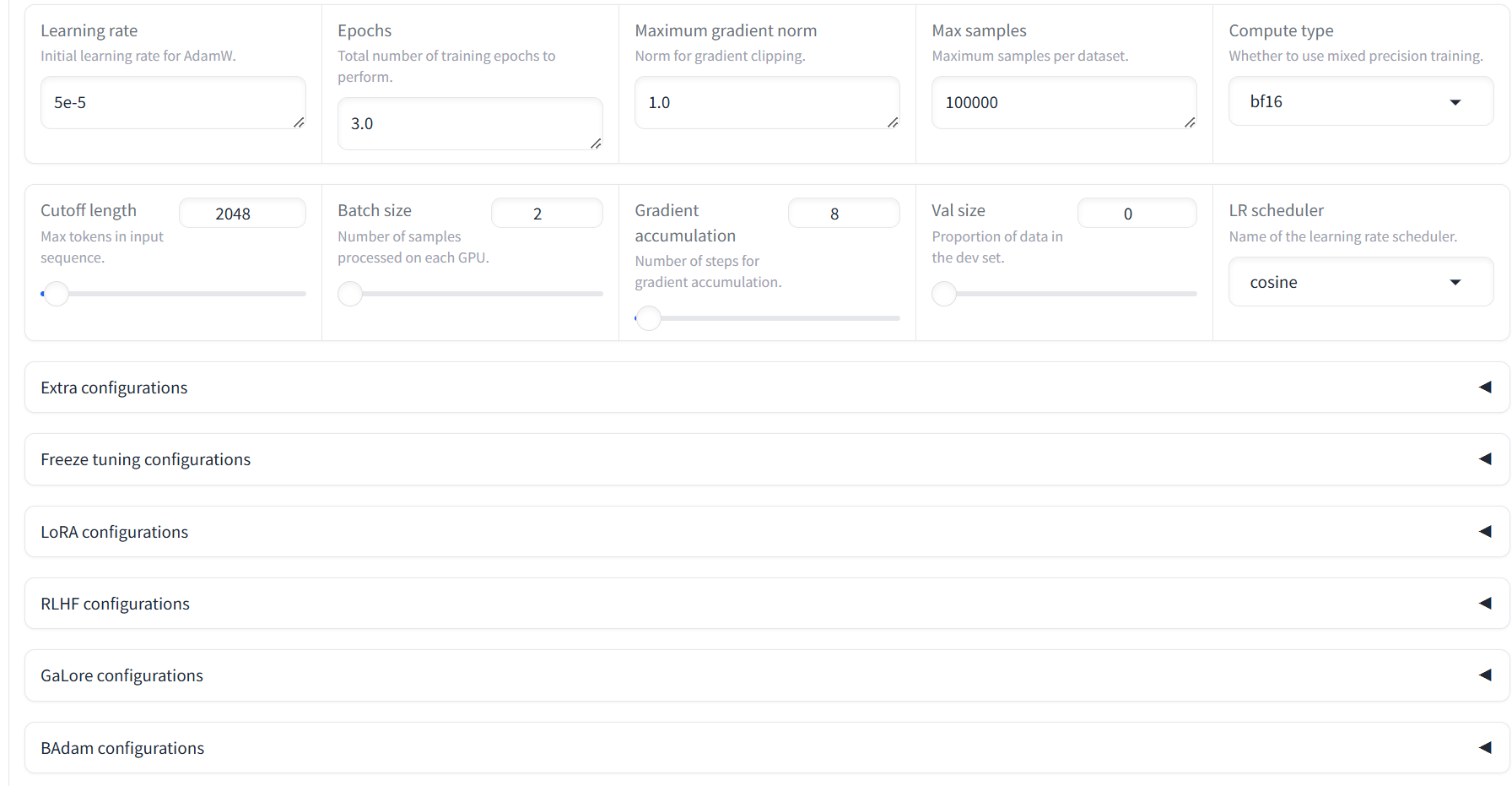
微调
命令行启动
|
|
自定义数据集的
|
|
详细分析
界面
指令格式
两种指令格式
- Alpaca
- ShareGPT
对比
| Feature | Alpaca Format | ShareGPT Format |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Instruction-following | Conversational AI |
| Structure | Instruction, Input (optional), Output | Multi-turn dialogue (user-assistant messages) |
| Flexibility | Handles single-turn, structured tasks | Handles multi-turn, natural conversations |
| Example Use Case | Chatbot following commands (e.g., write a story) | Multi-turn Q&A chatbot (e.g., customer support) |
Alpaca Format 例子
|
|
ShareGPT Format 例子
|
|
微调三种模式
| Aspect | LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) | Freeze | Full Fine-Tuning |
|---|---|---|---|
| How It Works | Adds small trainable low-rank matrices to specific layers (e.g., attention heads) while keeping the base model frozen. | Freezes most of the model’s layers and only fine-tunes specific layers (e.g., final layer or task-specific heads). | Updates all the parameters of the model, training the entire model for the new task. |
| Trainable Parameters | Introduces new parameters (low-rank matrices), significantly reducing the number of trainable parameters. | Trains only the selected layers, while the rest of the model remains unchanged. | All parameters are trainable, requiring large computational resources. |
| Memory/Compute Usage | Very efficient; requires far less memory and compute compared to full fine-tuning. | Moderate efficiency; requires less memory than full fine-tuning but more than LoRA. | High memory and compute usage, as the entire model is updated. |
| Base Model Dependency | The base model remains fully intact; LoRA layers can be added or removed modularly. | The base model is partially frozen, and updates are made to selected layers. | The base model is entirely modified, making it task-specific. |
| Modularity | Highly modular; you can share LoRA weights separately without altering the base model. | Less modular than LoRA; trained layers are not as easily reusable across tasks. | Not modular; the fine-tuned model is specific to the task. |
| Flexibility | Designed for specific parts of the model (e.g., attention layers), limiting flexibility. | Highly flexible; any layer or combination of layers can be chosen for fine-tuning. | Fully flexible; every parameter is trainable. |
| Fine-Tuning Speed | Very fast; only a small number of parameters are optimized. | Moderate speed; faster than full fine-tuning but slower than LoRA. | Slow; training the entire model requires significant time. |
| Storage Requirements | Stores only the additional LoRA parameters, which are very small in size. | Saves the modified layers; smaller storage requirements than full fine-tuning. | Requires storing the entire updated model, consuming significant storage. |
| Resource Efficiency | Extremely efficient for large models (e.g., LLaMA, GPT); can work with limited hardware. | Less efficient than LoRA but more efficient than full fine-tuning. | Requires substantial hardware and resources. |
| Pretrained Knowledge Preservation | Excellent; the base model is untouched, so pre-trained knowledge is preserved. | Good; frozen layers retain pre-trained knowledge, while tuned layers adapt to the new task. | Risk of overfitting or catastrophic forgetting of pre-trained knowledge. |
| Use Case Examples | Fine-tuning very large models on specific tasks with limited resources. | Adapting the model to new tasks by tuning only a few task-relevant layers. | Training the model for a completely new domain or task with ample resources. |
| Common Scenarios | Fine-tuning large LLMs like GPT, LLaMA, or BERT on specific downstream tasks. | Updating final layers for classification or regression tasks with pre-trained features. | Building a domain-specific model from scratch using pre-trained weights. |
| Key Advantages | - Highly efficient. - Small storage overhead. - Easy to switch tasks by loading specific LoRA weights. | - Flexible in selecting which layers to train. - Retains much of the pre-trained knowledge. | - Full control over the model’s behavior. - Best for completely transforming the model. |
| Key Disadvantages | - Limited to parts of the model where LoRA is implemented. - May not be sufficient for complex adaptations. | - Requires careful selection of layers to tune. - May not fully adapt the model to challenging tasks. | - Expensive in terms of memory, compute, and storage. - Risk of overfitting. |
几种方法
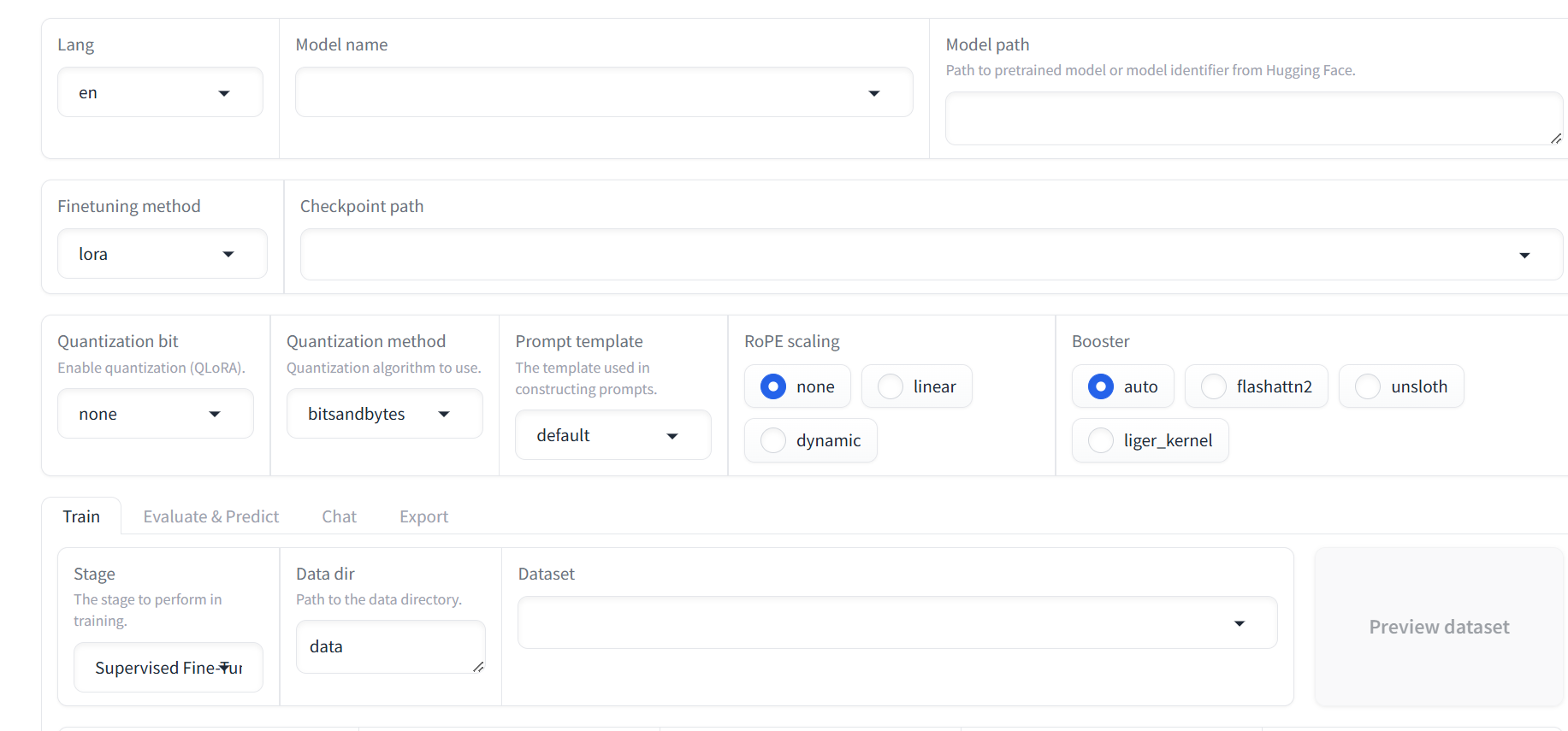
量化等级 (Quantization Level)
Quantization level refers to the precision of numerical representations used during training or inference. Lower precision reduces model size and computation requirements.
-
Options:
none: No quantization is applied; the model uses full precision (e.g., FP32 or FP16). This results in the highest accuracy but requires more memory and compute.4-bit/8-bit: Reduces numerical precision to 4-bit or 8-bit integers or floats, significantly lowering memory and compute usage while sacrificing a small amount of accuracy.
-
Purpose:
- Reduce memory and computational requirements for large models.
- Enable deployment on resource-constrained hardware like GPUs with limited memory.
量化方法 (Quantization Method)
Quantization methods define how the quantization process is applied to the model’s weights or activations.
-
Options:
bitsandbytes:- A widely-used library for efficient quantization.
- Supports 4-bit and 8-bit quantization for large models with negligible performance degradation.
- Commonly used with LLMs like GPT and LLaMA.
hqq:- A hypothetical or custom quantization algorithm (specific to your framework).
- Could have specific optimizations for performance or compatibility.
-
Purpose:
- Reduce model size during training or inference.
- Allow for high-speed computations on hardware with limited precision support (e.g., GPUs with Tensor Cores).
RoPE插值方法 (RoPE Interpolation Method)
RoPE (Rotary Position Embedding) is a technique used in transformer models to encode positional information.
-
Options:
none:- No interpolation applied; uses standard rotary embeddings as defined during training.
- Suitable for fixed-length input sequences.
linear:- Applies linear interpolation to extend the range of rotary embeddings.
- Useful for models trained on shorter sequences but used for longer sequences during inference.
dynamic:- Dynamically adjusts rotary embeddings based on the sequence length or other factors.
- Provides more flexibility but may introduce overhead.
-
Purpose:
- Enhance the model’s ability to process sequences of varying lengths.
- Adapt rotary embeddings to new contexts or longer sequences.
加速方法 (Acceleration Method)
Acceleration methods refer to optimizations used to speed up model inference or training by leveraging efficient algorithms or hardware-specific features.
-
Options:
auto:- Automatically selects the best acceleration method based on the hardware and framework configuration.
flashattn2:- Refers to Flash Attention 2, an optimized attention mechanism that improves speed and memory usage for transformer models.
- Ideal for large-scale models and long sequences.
unsloth:- Likely a custom or experimental acceleration method (specific to your framework).
- May focus on balancing memory efficiency and computation speed.
liger_kernel:- A custom kernel optimized for specific hardware or computation patterns.
- Could provide tailored optimizations for matrix multiplications or attention mechanisms.
-
Purpose:
- Improve training and inference speed.
- Reduce memory consumption without affecting accuracy.
几种方法总结
| Feature | Purpose | Key Options |
|---|---|---|
| 量化等级 | Control model precision and resource usage. | none, 4-bit, 8-bit |
| 量化方法 | Define the quantization algorithm. | bitsandbytes, hqq |
| RoPE插值方法 | Adjust rotary embeddings for flexibility. | none, linear, dynamic |
| 加速方法 | Optimize training/inference for speed. | auto, flashattn2, unsloth, liger_kernel |
LoRA
LoRA 秩 (LoRA Rank)
- Meaning: Determines the rank of the low-rank decomposition matrices used in LoRA.
- Impact:
- A higher rank increases the capacity of LoRA, allowing it to learn more complex patterns but uses more memory.
- A lower rank makes the model more lightweight but might limit its adaptability.
- Default: Often set between 4 and 16 depending on the model and hardware.
LoRA 缩放系数 (LoRA Scaling Factor)
- Meaning: A scaling factor applied to the LoRA parameters to adjust their contribution to the model.
- Impact:
- Higher scaling factors emphasize LoRA’s contribution.
- Lower scaling factors blend LoRA more subtly with the base model.
LoRA 随机丢弃 (LoRA Dropout)
- Meaning: Adds dropout regularization to the LoRA weights during training.
- Purpose:
- Helps prevent overfitting.
- Improves generalization of the fine-tuned model.
- Range: Typically between
0(no dropout) and0.5.
LoRA+ 学习率比例 (LoRA+ Learning Rate Scale)
- Meaning: Scales the learning rate applied to the LoRA parameters.
- Purpose:
- Fine-tune LoRA parameters more efficiently by adjusting their learning rate.
- Impact:
- Higher values speed up learning but risk instability.
- Lower values ensure stability at the cost of slower training.
新建适配器 (New Adapter)
- Meaning: Creates a new, randomly initialized adapter configuration on top of the existing one.
- Purpose:
- Useful for training different configurations for multiple tasks without overwriting existing ones.
使用 rslora (Use rslora)
- Meaning: Enables a “stable LoRA” method that adds regularization for better training convergence.
- Purpose:
- Prevents LoRA parameters from diverging significantly during training.
使用 DoRA (Use DoRA)
- Meaning: Stands for Decomposed Residual Adapter, which provides a more granular decomposition in fine-tuning.
- Purpose:
- Improves efficiency by focusing on specific residual connections in the model.
使用 PiSSA 方法 (Use PiSSA)
- Meaning: PiSSA refers to a custom or experimental optimization technique for LoRA training.
- Purpose:
- Adds advanced optimizations for parameter-efficient fine-tuning.
LoRA 作用模块 (LoRA Target Modules)
- Meaning: Specifies the target modules (e.g., attention layers, feed-forward layers) where LoRA is applied.
- Purpose:
- Fine-tune only specific parts of the model to save resources or improve performance on specific tasks.
附加模块 (Additional Modules)
- Meaning: Specifies additional trainable modules outside of LoRA layers.
- Purpose:
- Enables training of non-LoRA components, offering broader customization for specific tasks.
Summary Table
| Parameter | Purpose |
|---|---|
| LoRA 秩 | Sets the rank of the LoRA matrices, controlling model complexity and resource usage. |
| LoRA 缩放系数 | Adjusts the scale of LoRA parameters to balance their influence in the model. |
| LoRA 随机丢弃 | Introduces dropout for regularization to prevent overfitting. |
| LoRA+ 学习率比例 | Scales the learning rate of LoRA parameters for balanced fine-tuning. |
| 新建适配器 | Creates a new adapter configuration for multi-domain or task-specific tuning. |
| 使用 rslora | Ensures stable training of LoRA parameters with added regularization. |
| 使用 DoRA | Adds decomposed residual adapters for more granular fine-tuning. |
| 使用 PiSSA | Adds experimental methods for advanced LoRA optimization. |
| LoRA 作用模块 | Defines the modules (e.g., attention layers) where LoRA will be applied. |
| 附加模块 | Specifies trainable modules beyond LoRA layers, enabling broader customization. |
评估
命令
|
|
配置文件
|
|
参考
- GitHub
- 文档
- LlaMA-Factory WebUI Beginner’s Guide: Fine-Tuning LLMs
- Huggingface镜像站:加速你的AI之旅,体验国内高速下载
- 微调神器LLaMA-Factory官方保姆级教程来了,从环境搭建到模型训练评估全覆盖
- LLaMA-Factory自定义数据集微调
- LLaMA-Factory 大模型微调超简单,从零开始玩转大模型微调
- dcgm-exporter
- NVIDIA Optimized Frameworks
- Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct 模搭社区下载
- data_set运行的数据集
- 大模型高效训练一体框架 LLaMA Factory