Spark Core相关-2
调度
调度概述
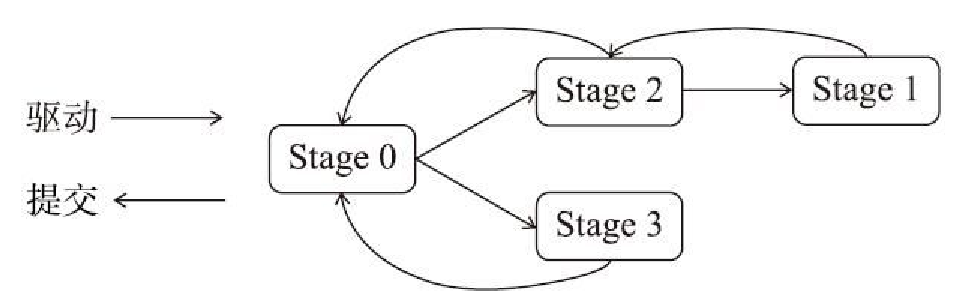
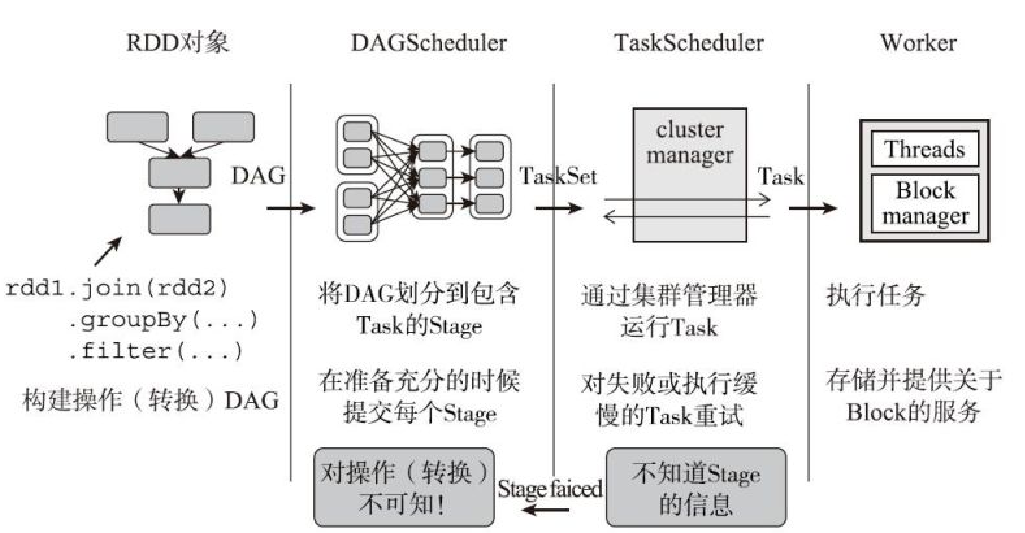
调度过程
- 将用户提交的 job 转换成 RDD,分解成 DAG
- 按照 shuffle 边界,拆分成若干个 stage,每个 stage 按照并行度分为若干个 task
- 将 task打包为 task-set 由DAGScheduler 调度 给 TaskScheduler
- 使用集群管理器分配资源,按照调度算法做调度
- executor 做执行
RDD 的几个核心函数
|
|
通常数据处理的模型包括迭代计算、关系查询、MapReduce、流式处理等
Hadoop采用MapReduce模型,Storm采用流式处理模型,而Spark则借助RDD实现了以上所有模型
Dependency 的几个实现类
- NarrowDependency
- OneToOneDependency
- RangeDependency
- PruneDependency
- RangeDependency
- ShuffleDependency
分区计算器,抽象类 Partitioner,实现类
- CoalescedPartitioner
- ConstantPartitioner
- GridPartitioner
- HashPartitioner
- PartitionIdPassthrough
- PythonPartitioner
- RangePartitioner
Stage 抽象类,以及实现类
- ResultStage
- ShuffleMapStage
一些信息类
- RDDInfo
- StageInfo
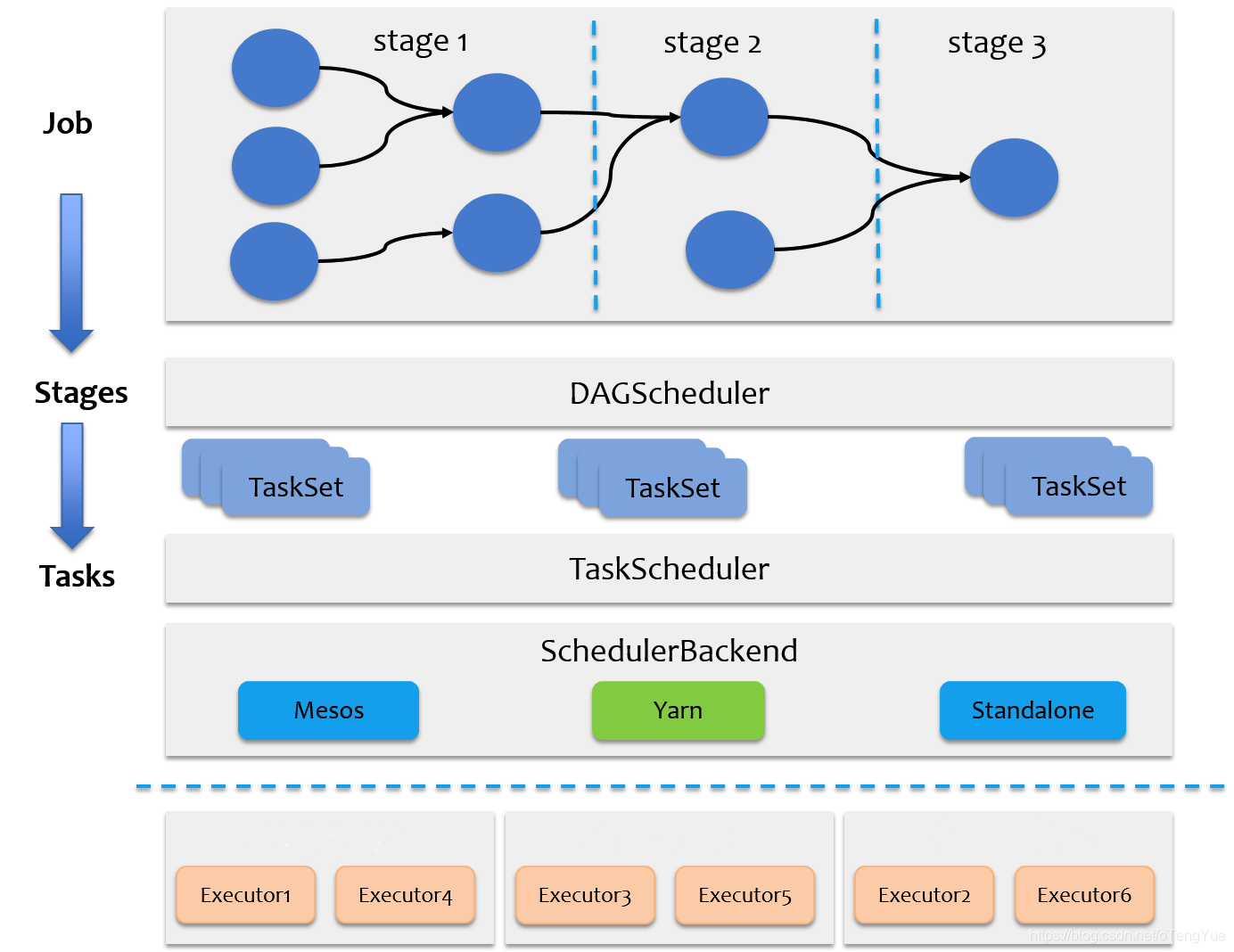
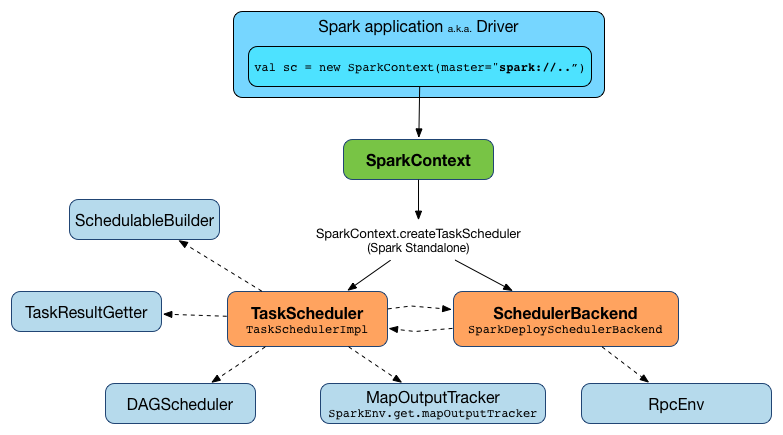
DAGScheduler
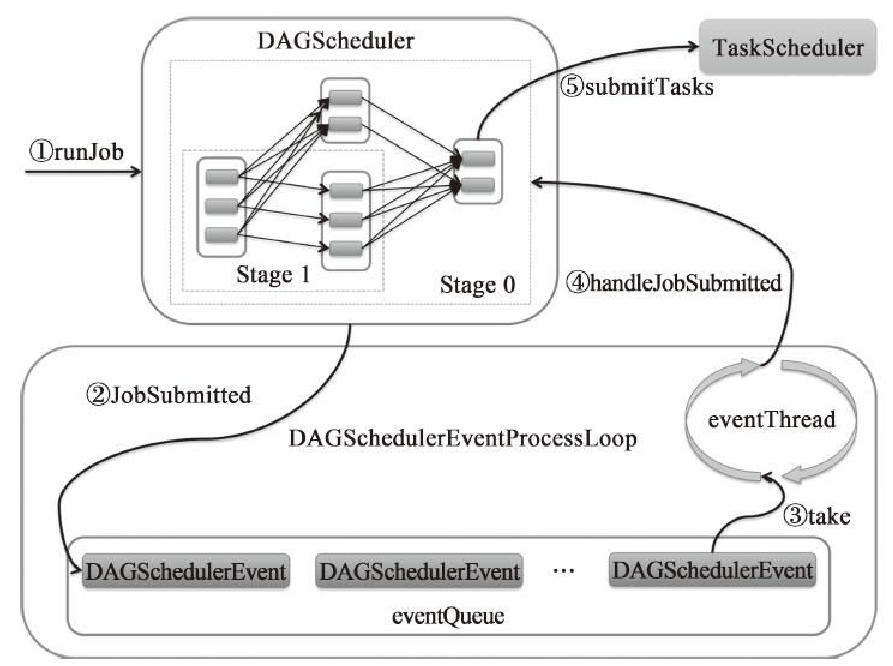
DAGScheduler实现了面向DAG的高层次调度
- DAG中的各个RDD划分到不同的Stage
- DAGScheduler可以通过计算将DAG中的一系列RDD划分到不同的Stage,然后构建这些Stage之间的父子关系
- 最后将每个Stage按照Partition切分为多个Task,并以Task集合(即TaskSet)的形式提交给底层的TaskScheduler
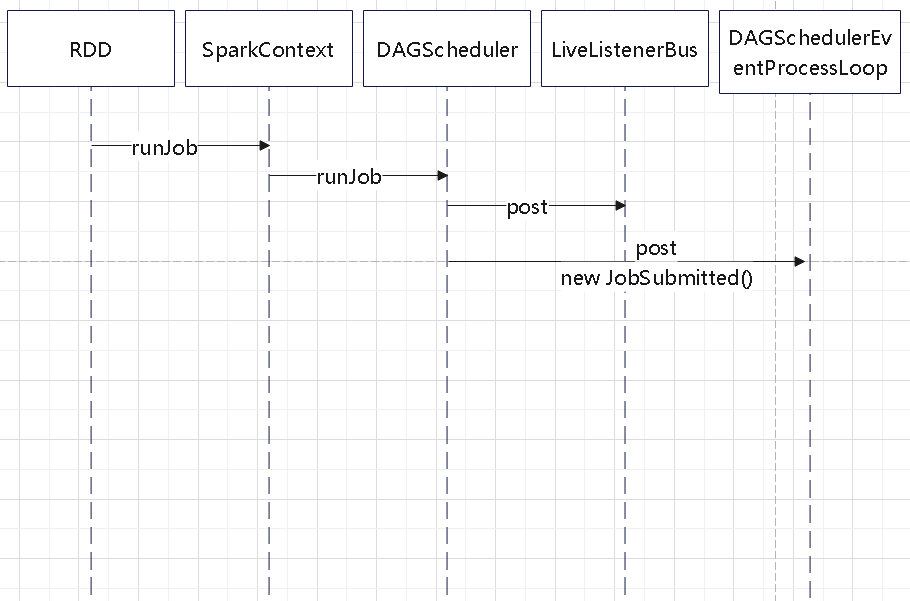
- 所有的组件都通过向DAGScheduler投递DAGSchedulerEvent来使用DAGScheduler
DAGScheduler 的一些依赖
- SparkContext
- TaskScheduler
- LiveListenerBus
- MapOutputTrackerMaster
- BlockManagerMaster
- SparkEnv
- SystemClock
使用到的一些类
- JobListener(抽象类)
- ActiveJob,被活跃调度的 job
- DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop
最后统一处理这些 事件:
|
|
主要函数
- cleanupStateForJobAndIndependentStages
- updateJobIdStageIdMaps
- activeJobForStage
- getCacheLocs
- getPreferredLocs
- handleExecutorAdded
- executorAdded
- runJob
- 祖父 stage 先于 父 stage 提交
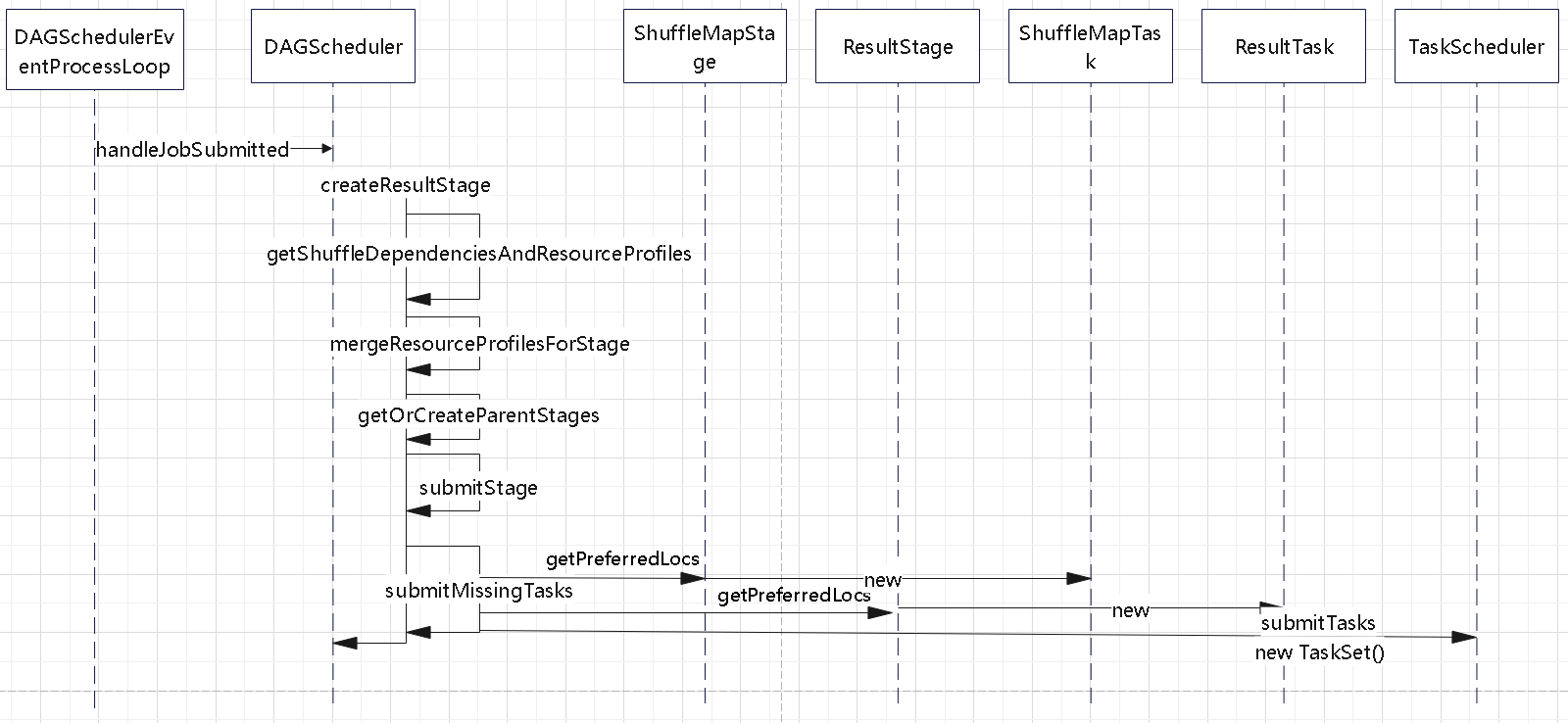
- createResultStage 创建 stage
- getShuffleDependenciesAndResourceProfiles:获取RDD的所有ShuffleDependency的序列,逐个访问每个RDD及其依赖的非Shuffle的RDD,获取所有非Shuffle的RDD的ShuffleDependency依赖
- mergeResourceProfilesForStage
- 获取所有父Stage的列表
- 将ResultStage注册到stageIdToStage中
getOrCreateParentStages
- 找到所有还未创建过ShuffleMapStage的祖先ShuffleDependency
- 将其记录保存
- 根据 shuffle 的边界,递归的创建
- 递归的触发:getOrCreateParentStages
- 根据 shuffle 边界,拆分 stage
TaskScheduler
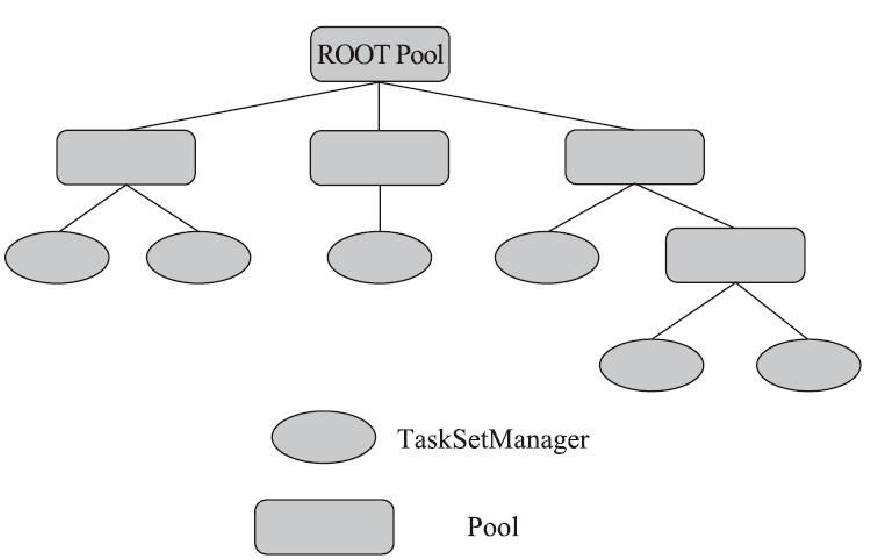
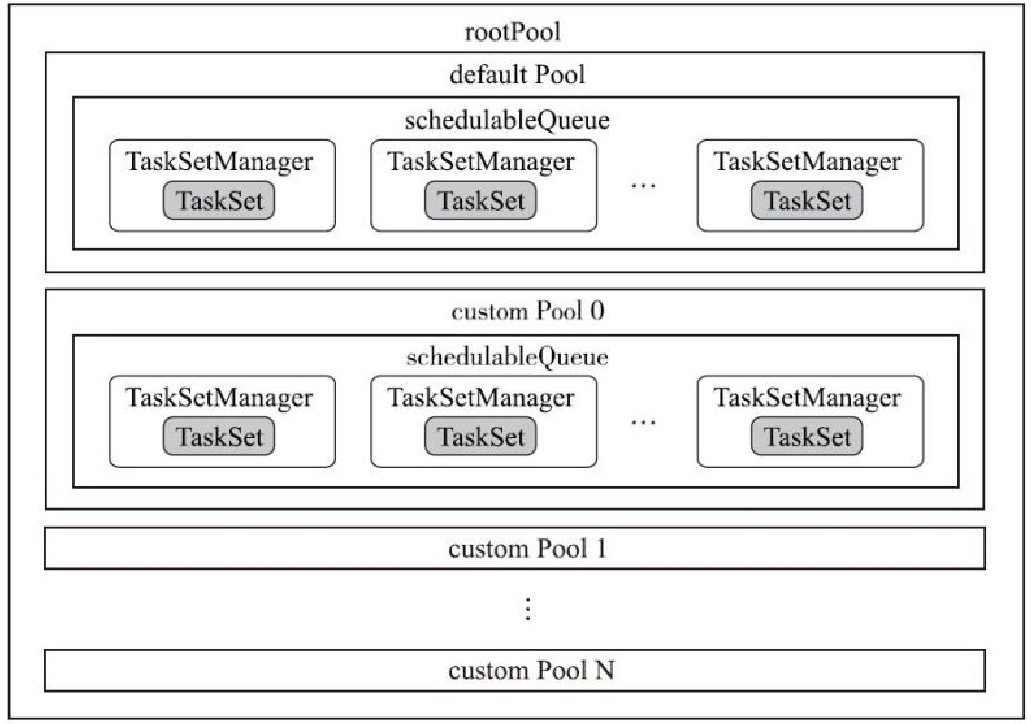
Pool 提供的函数
- addSchedulable
- removeSchedulable
- getSchedulableByName
- executorLost
- executorDecommission
调度算法
- 抽象类:SchedulingAlgorithm
- FIFOSchedulingAlgorithm
- FairSchedulingAlgorithm
- getSortedTaskSetQueue
- decreaseRunningTasks
调度配置
|
|
数据本地性
- PROCESS_LOCAL
- NODE_LOCAL
- NO_PREF
- RACK_LOCAL
- ANY
TaskSetManager 主要函数
- TaskSetManager
- dequeueTaskFromList
- dequeueTask
- addRunningTask与removeRunningTask
- maybeFinishTaskSet
TaskResultGetter
- 任务结果获取器
- 处理成功、失败的 task
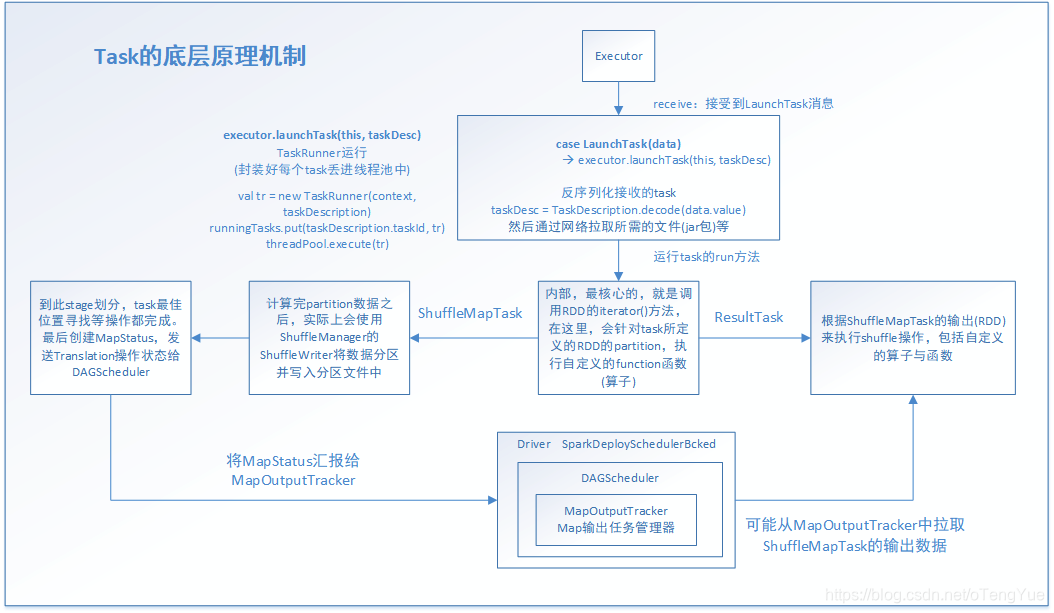
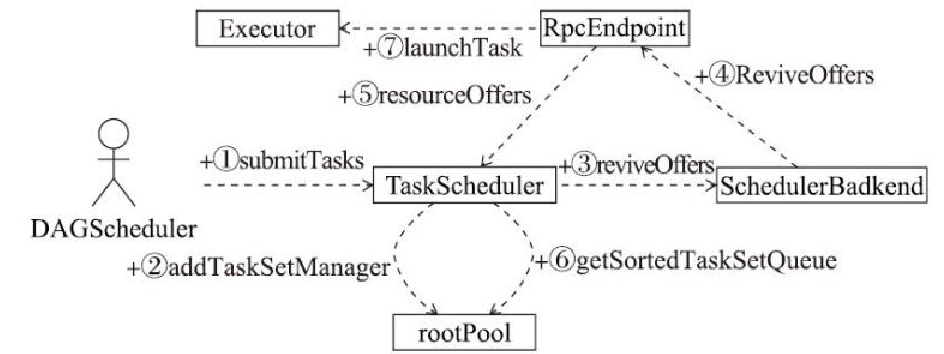
TaskSchedulerImpl 调度流程 如下
- 3、代表TaskScheduler调用SchedulerBackend的reviveOffers方法给Task提供资源
- 4、SchedulerBackend向RpcEndpoint发送ReviveOffers消息
- 5、RpcEndpoint将调用TaskScheduler的resourceOffers方法给Task提供资源
- 6、根据调度池的 getSortedTaskSetQueue做排序
- 7、调用Executor的launchTask方法运行Task尝试
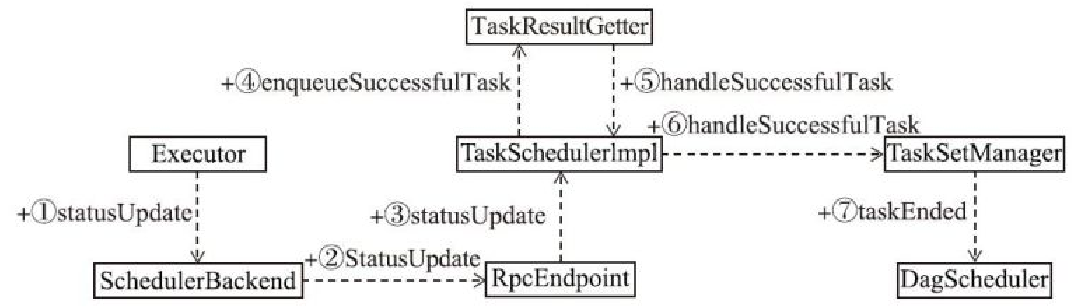
TaskSchedulerImpl对执行结果的处理 如下
- 1、Executor将状态返回给 SchedulerBackend
- 2、将状态封装后发送给 RpcEndpoint的实现类
- 3、RpCEndpoint实现类收到消息后更新 TaskSchedulerImpl
- 4、如果是成功状态,则调用TaskResultGetter的enqueueSuccessfulTask方法
- 5、将结果交给 TaskSchedulerImpl处理
- 6、更新 TaskSetManager
- 7、触发调用 DAGScheduler的taskEnded方法,交给 JobWaiter的resultHandler函数来处理
SchedulerBackend
SchedulerBackend 抽象类
- LocalSchedulerBackend
- CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend
CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend 的实现类
- StandaloneSchedulerBackend
- YarnSchedulerBackend
- 其子类:YarnClientSchedulerBackend
- YarnClusterSchedulerBackend
- KubernetesClusterSchedulerBackend
- MesosCoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend
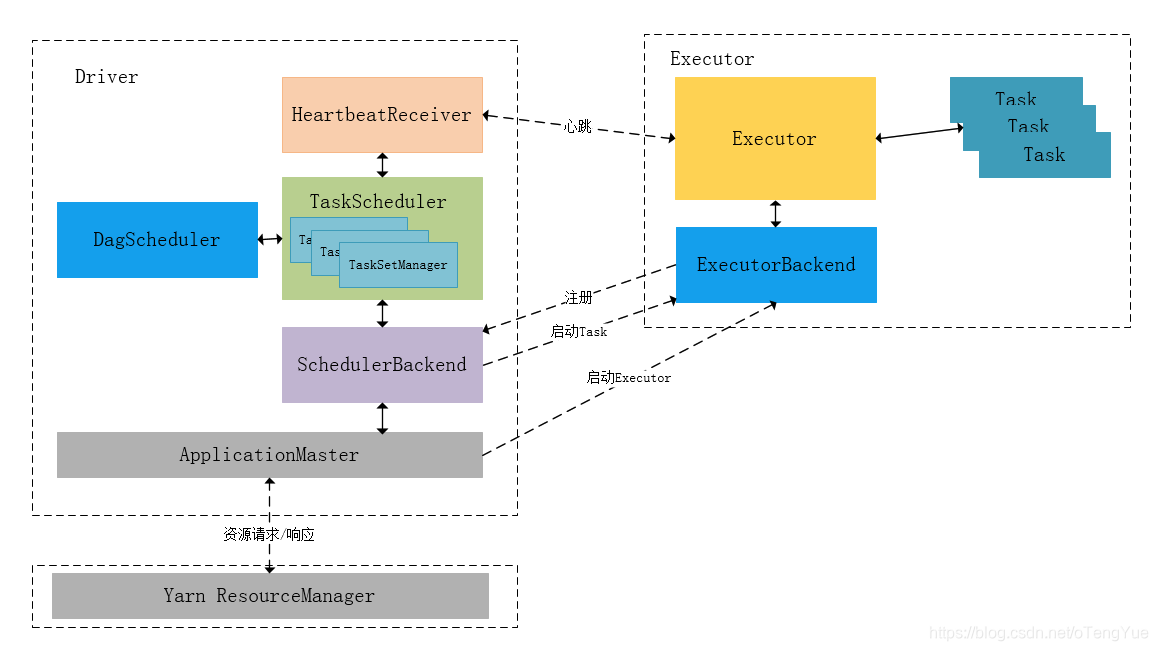
DAGScheduler 将任务分解,交给 TaskScheduler
再交给 CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend
之后启动 Executor 执行任务的过程
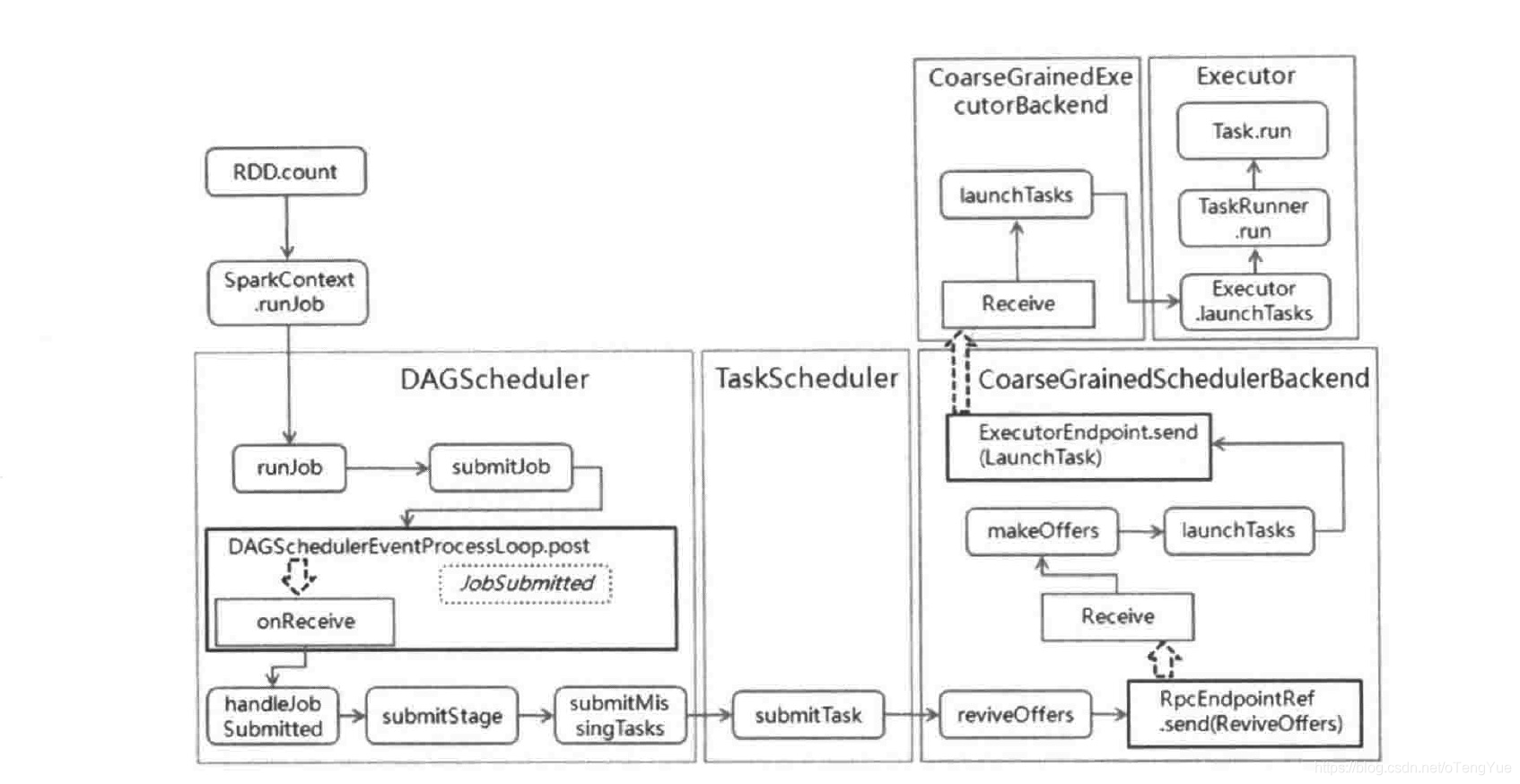
计算引擎
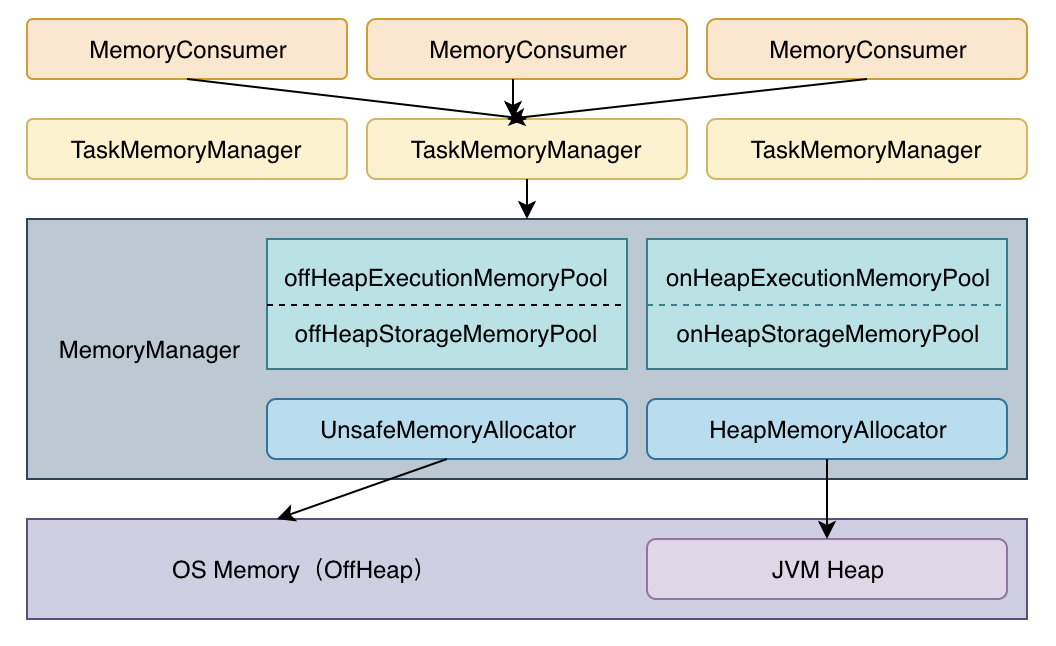
内存管理
内存分配
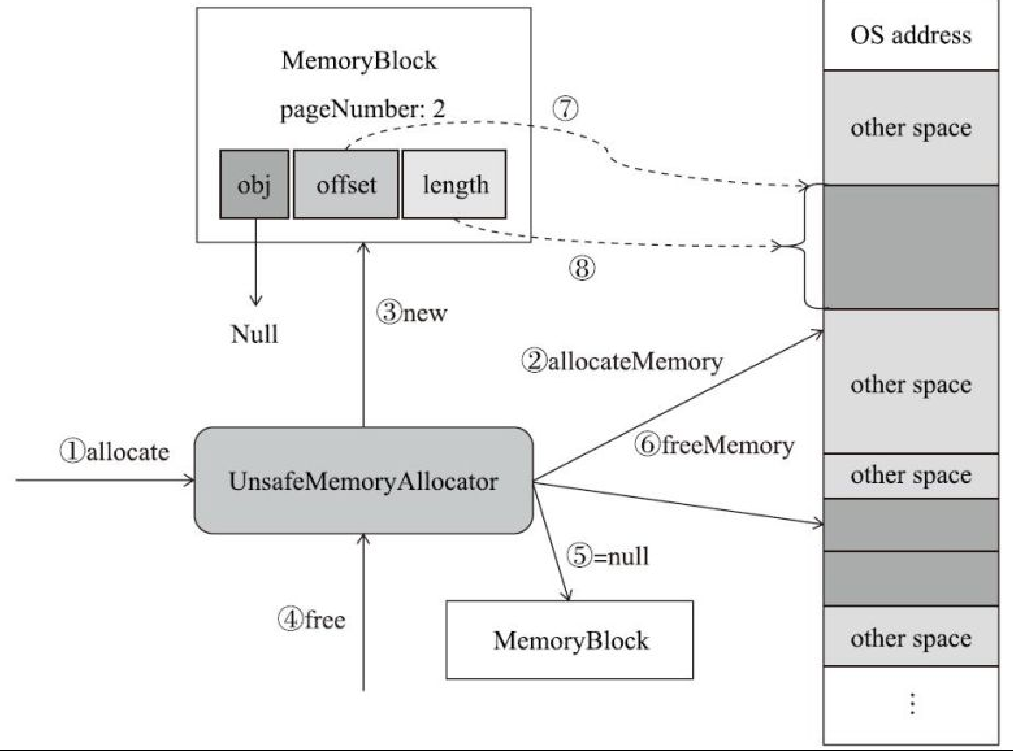
- 抽象类 MemoryAllocator
- UnsafeMemoryAllocator
- HeapMemoryAllocator
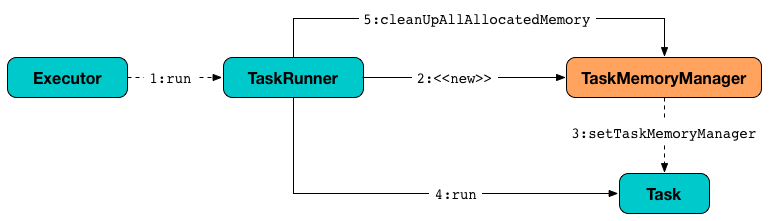
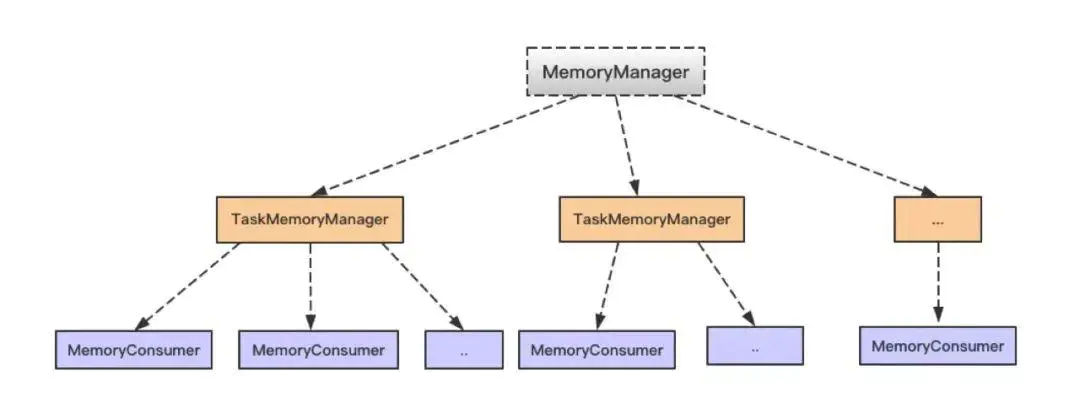
TaskMemoryManager提供的主要函数
- acquireExecutionMemory
- releaseExecutionMemory
- showMemoryUsage
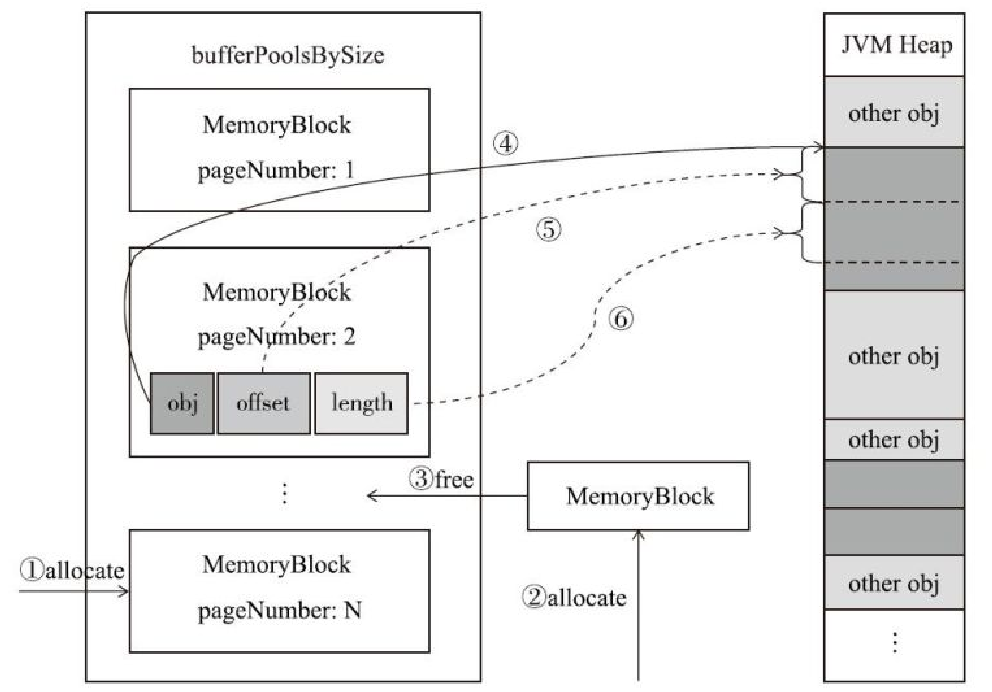
- pageSizeBytes
- allocatePage
- freePage
- encodePageNumberAndOffset
- decodePageNumber
- decodeOffset
- getPage
- getOffsetInPage
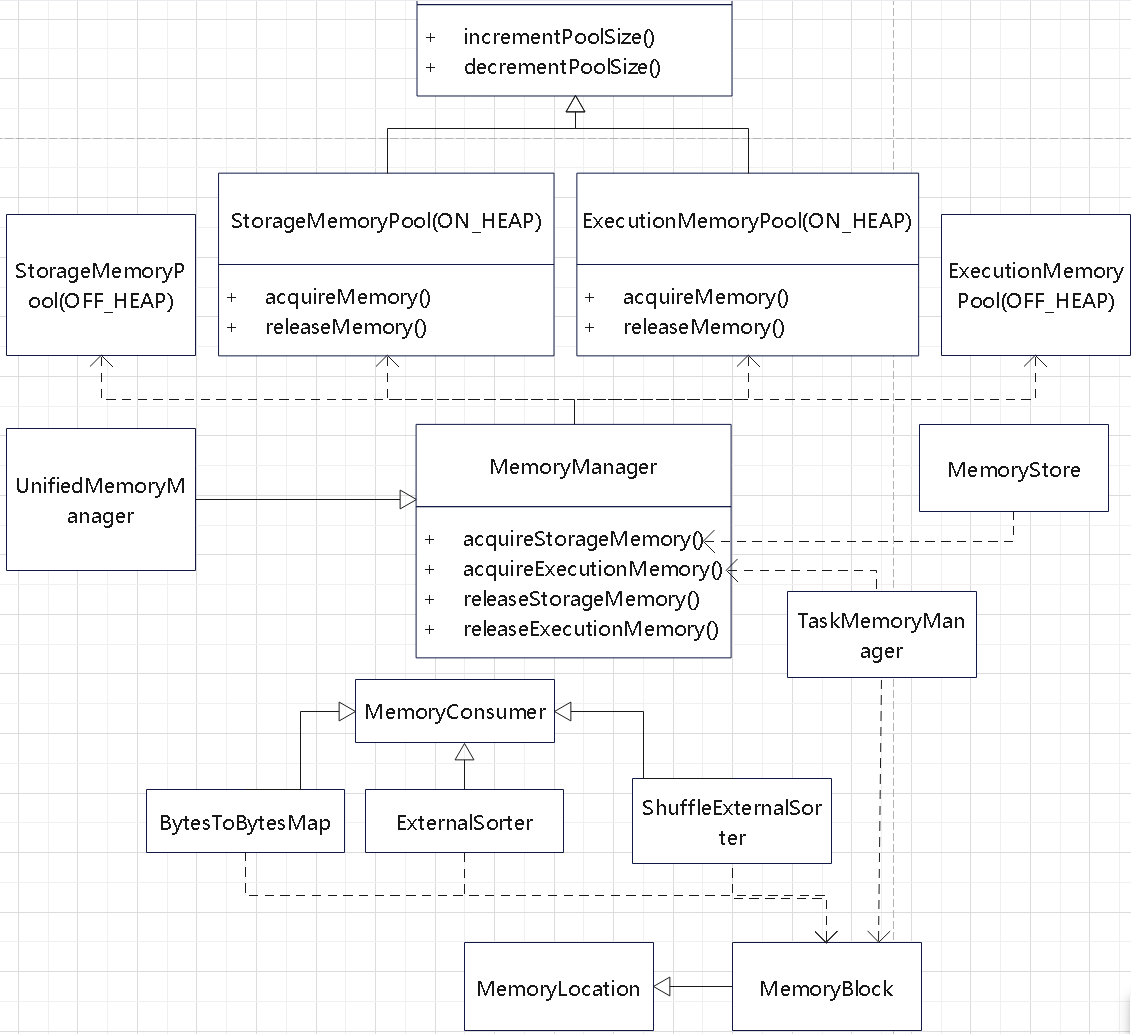
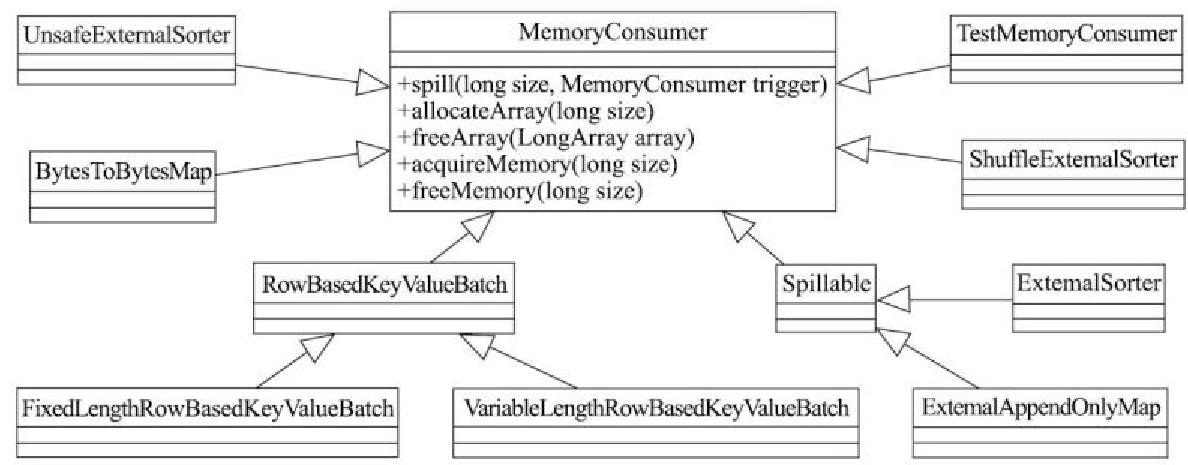
MemoryConsumer 主要结构
|
|
MemoryConsumer 两个子类
- ExecutionMemoryConsumer: Manages memory used for execution tasks like shuffles, joins,aggregations.
- StorageMemoryConsumer: Handles memory used for caching RDDs and broadcast variables.
几个了之间的关系
- MemoryConsumer: Abstract base class responsible for tracking and managing memory usage for different tasks and operations.
- TaskMemoryManager: Manages memory allocations specific to individual tasks, ensuring isolation and adherence to memory limits.
- MemoryManager: Centralized manager that oversees global memory allocation, handling both on-heap and off-heap memory pools.
- MemoryStore: Handles the actual allocation and deallocation of memory blocks, distinguishing between on-heap and off-heap memory.
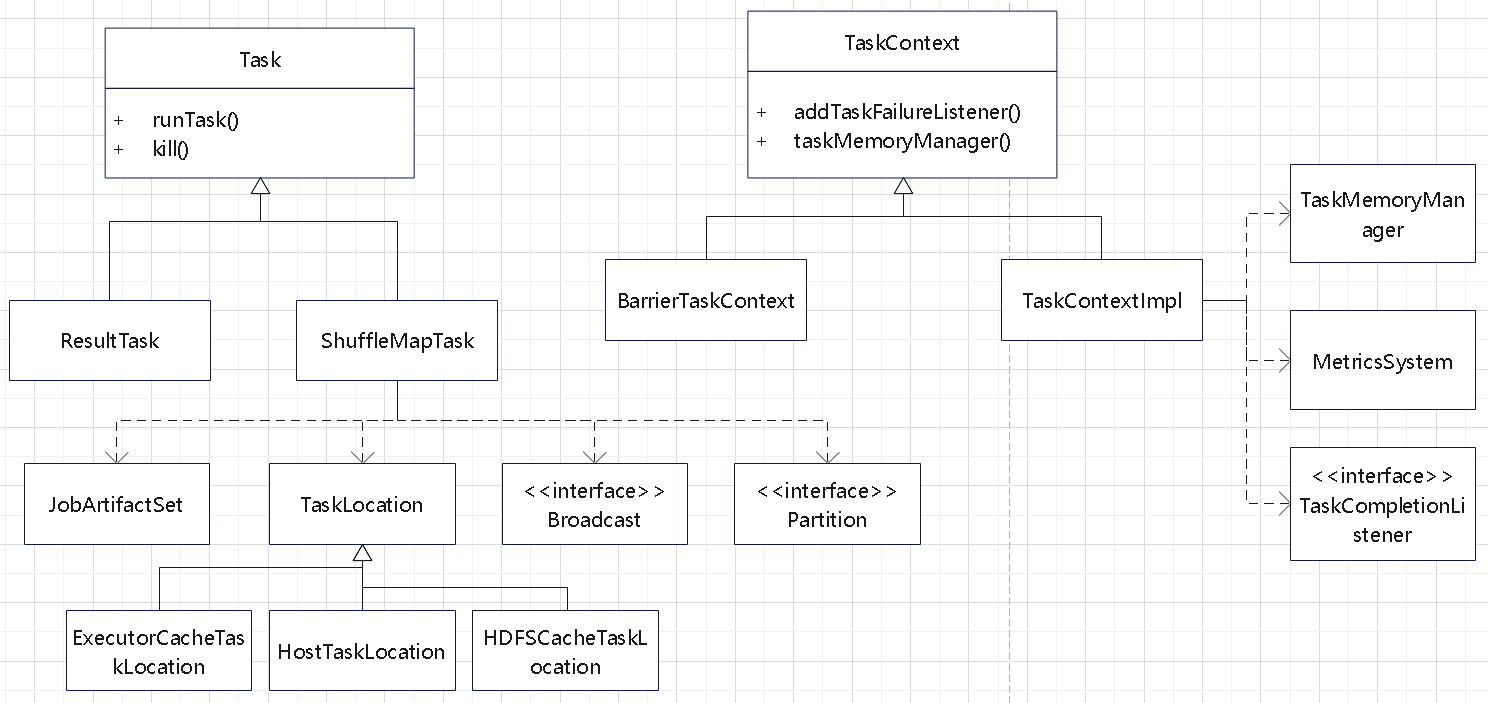
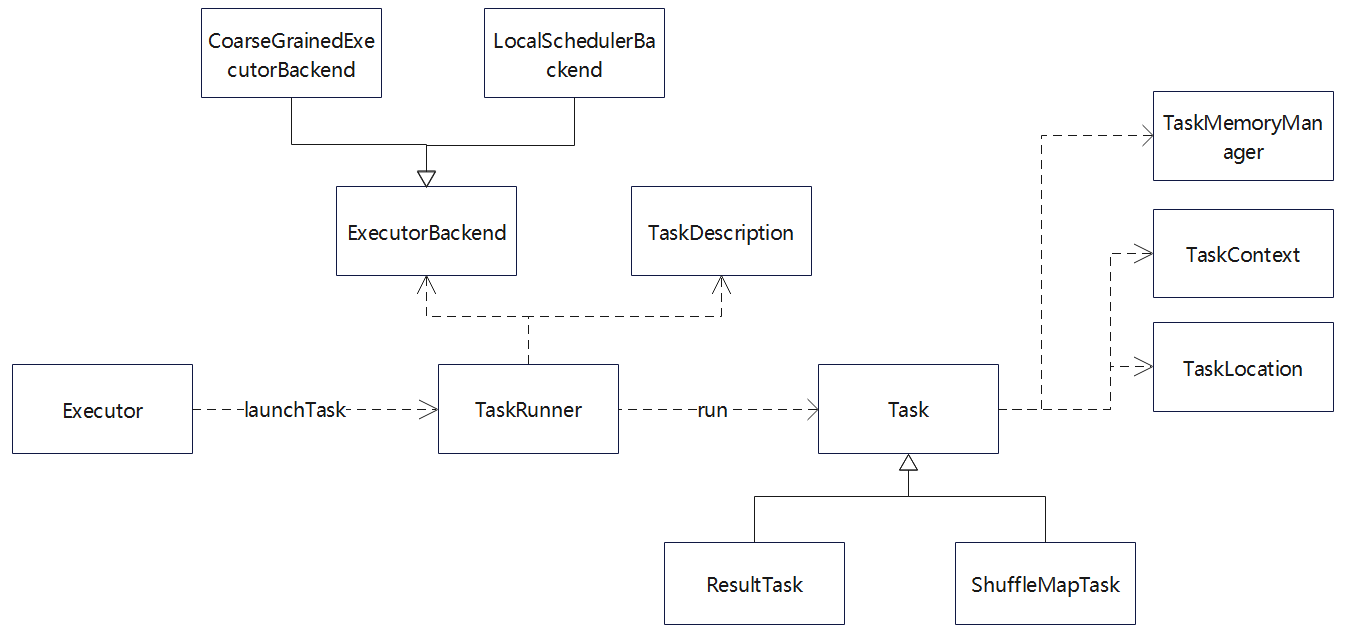
Task 分析
Task抽象类
- ShuffleMapTask
- ResultTask
TaskContext 抽象类
- BarrierTaskContext
- TaskContextImpl
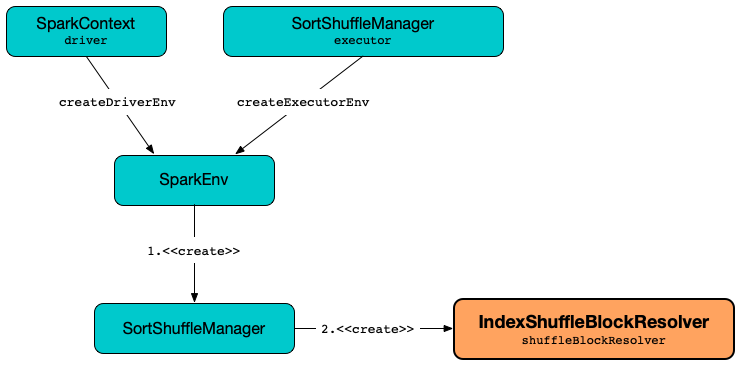
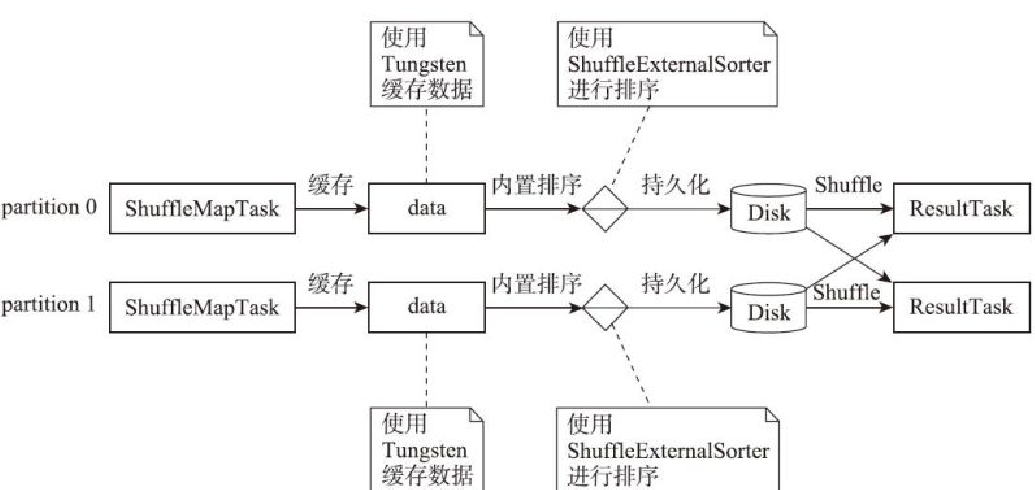
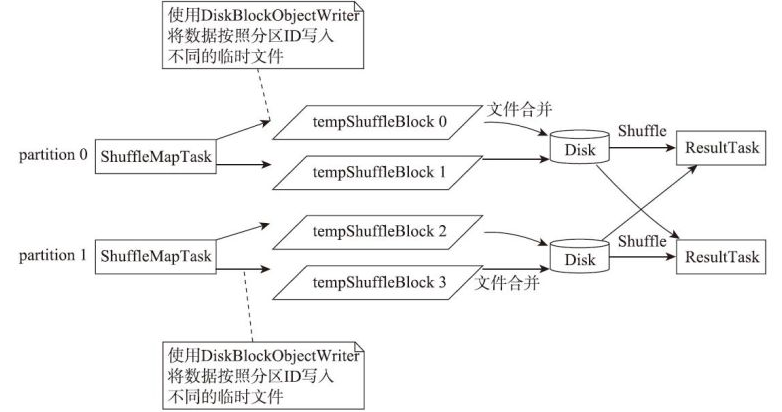
Shuffle
IndexShuffleBlockResolver 作用
- Resolves Shuffle Blocks: It translates logical shuffle block identifiers into physical storage locations on disk.
- Manages Shuffle Index Files: It creates and maintains index files that map shuffle block IDs to their corresponding disk locations. These index files facilitate efficient data retrieval during the shuffle read phase.
- Ensures Fault Tolerance: By maintaining index files and data blocks, it helps Spark recover shuffle data in case of executor failures.
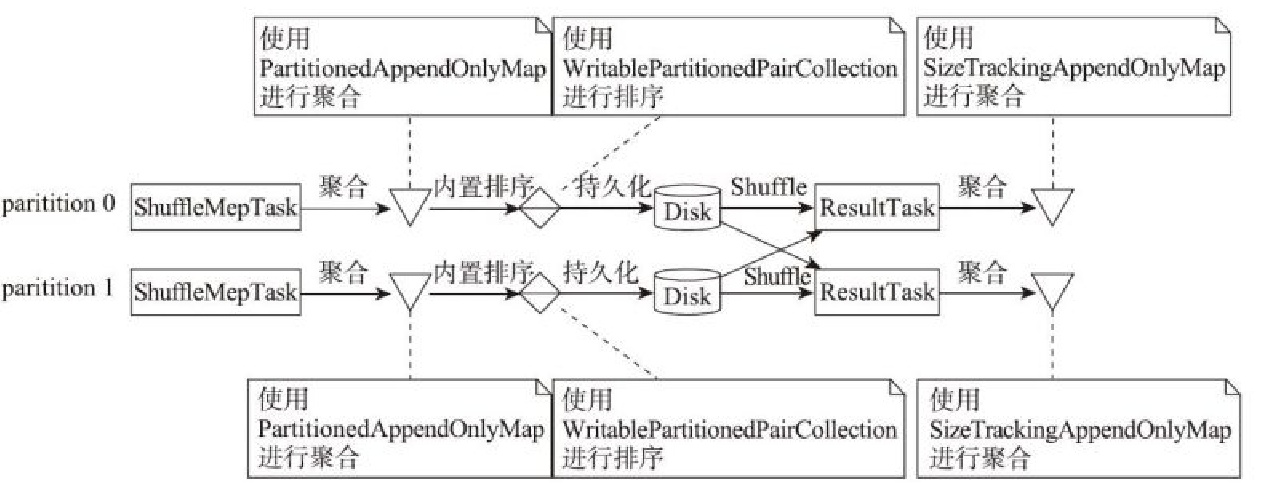
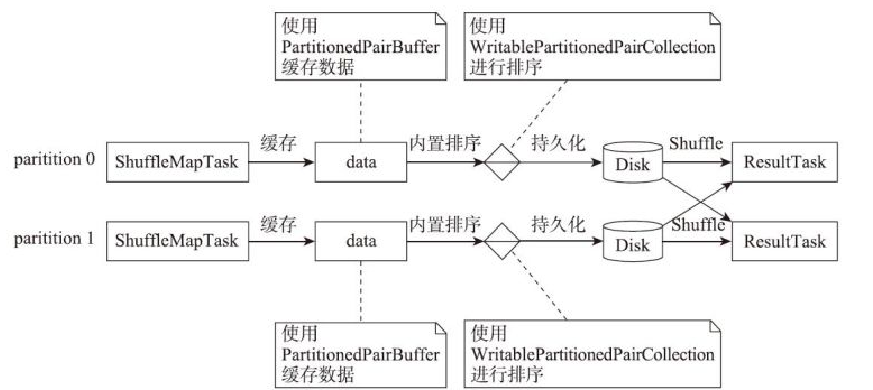
收集数据集评估
- 抽象类 SizeTracker
- PartitionedAppendOnlyMap
- PartitionedPairBuffer
- SizeTrackingAppendOnlyMap
- SizeTrackingVector
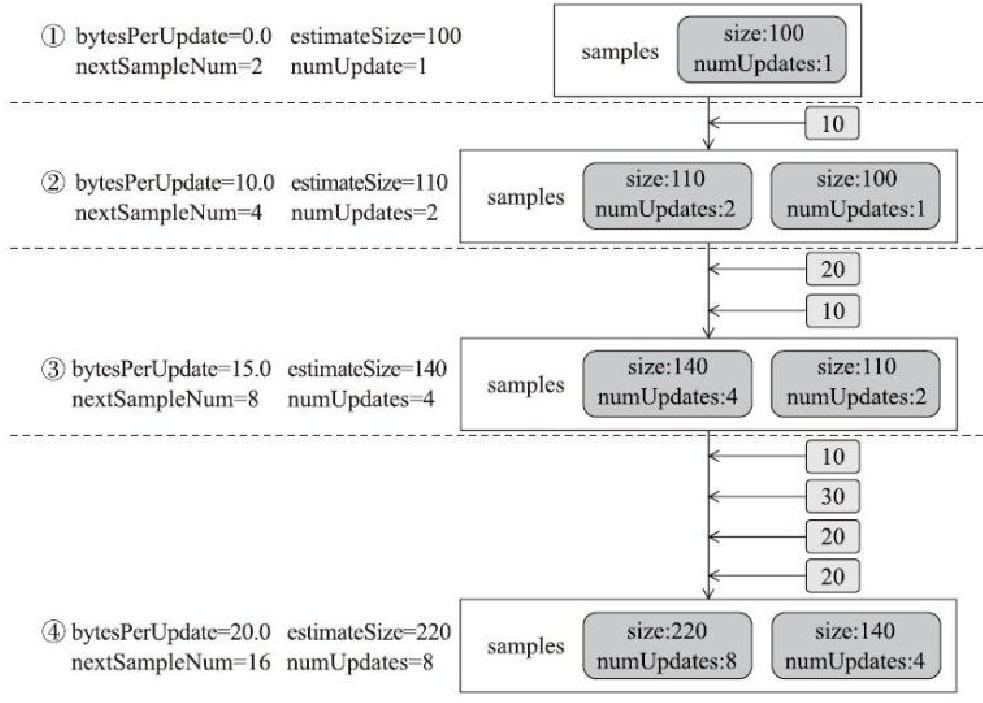
SizeTracker的工作原理
WritablePartitionedPairCollection
- PartitionedAppendOnlyMap,又继承了 AppendOnlyMap
- PartitionedPairBuffer
AppendOnlyMap
- Efficient Memory Usage:AppendOnlyMap is optimized for scenarios where data grows incrementally without requiring costly operations like deletion or resizing.
- Open Addressing for Hash Collisions:Uses open addressing to resolve hash collisions, minimizing memory usage compared to structures like Java’s HashMap which rely on linked lists for collisions.
- Custom Growth Mechanism:The map dynamically resizes its internal array when the load factor exceeds a threshold, maintaining performance as data grows.
- Specialized for Spark Use Cases: Focused on Spark’s data aggregation needs where intermediate results (e.g., during shuffle or reduce operations) accumulate but do not need to be removed.
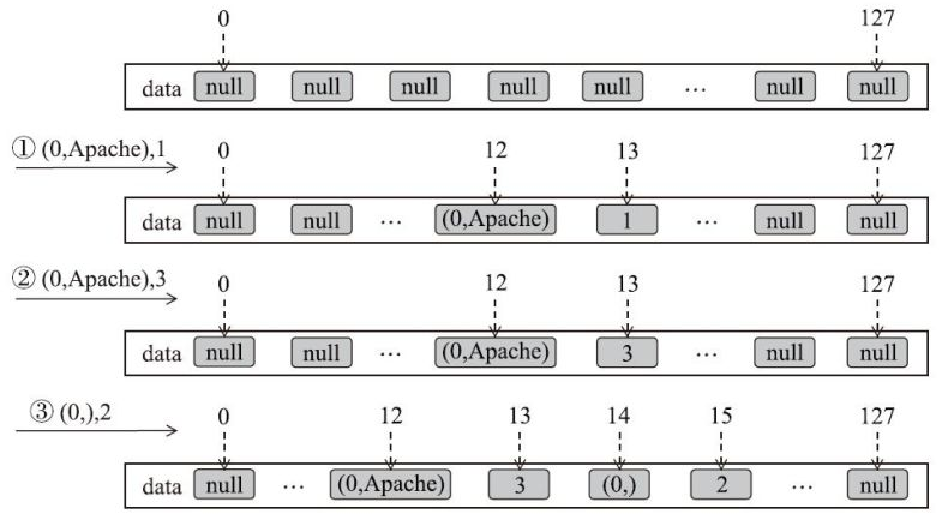
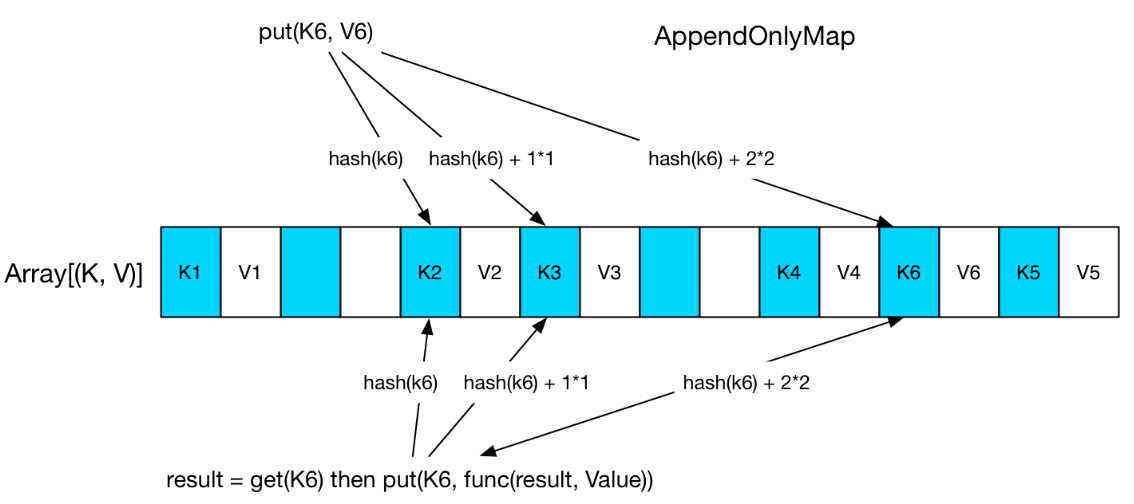
- 传入的key为(0,Apache),value为1,计算得到pos为6,由于2×6=12的索引位置没有元素,因此将(0,Apache)放入data数组索引为12的位置,将1放入索引为2×6+1=13的位置
- key为(0,Apache),value为3,计算得到pos为6,由于2×6=12的索引位置的元素与(0,Apache)一样,因此将3更新到索引为2×6+1=13的位置
- 传入的key为(0,),value为2,计算得到pos为6,由于2×6=12的索引位置已经放入了(0,Apache),因此向后寻找新的位置。pos为7时,由于2×7=14的索引位置没有元素,因此将(0,)放入data数组索引为14的位置,将2放入索引为2×7+1=15的位置
AppendOnlyMap
基于开放地址的 hashmap,根据阈值做 翻倍增长
如下 AppendOnlyMap,经过三次探测找到了合适的位置
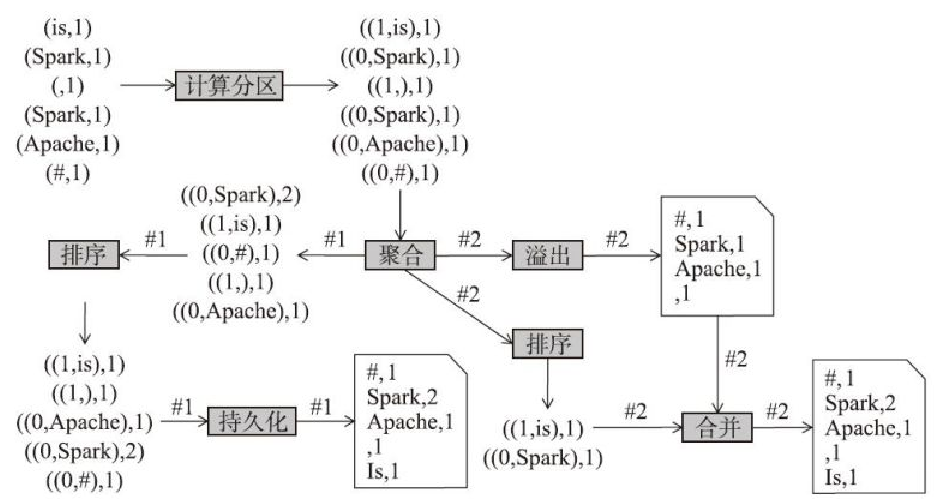
几个排序、溢出类的类图
- 这几个类都是继承了 MemoryConsumer或者其子类 Spillable
- ExternalSorter、ExternalAppendOnlyMap 差不多,有 spill,merge,插入
- 这两个类都是调用DiskBlockObjectWriter 完成磁盘写入
- ShuffleExternalSorter、UnsafeExternalSorter 基于shuffle写入和off-heap 排序,都有spill
- ShuffleExternalSorter 调用了 DiskBlockObjectWriter,UnsafeExternalSorter有自己的磁盘写入
- 和几个类都是调用 iterator,迭代遍历写入磁盘

| Feature | ExternalSorter | ExternalAppendOnlyMap | UnsafeExternalSorter | ShuffleExternalSorter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use Case | Sorting and optional aggregation | Key-value aggregation | Sorting binary row data | Sorting and shuffling intermediate data |
| Data Format | Key-value pairs | Key-value pairs | Binary-encoded rows | Binary-encoded rows |
| Aggregation Support | Optional (via combining comparator) | Yes (custom aggregation functions) | No | No |
| Spill Mechanism | Sorts and spills sorted chunks | Spills serialized key-value pairs | Spills binary data | Spills binary data |
| Final Merge | Merges sorted chunks | Merges aggregated chunks | Merges binary data | Optimized merge for shuffle output |
| Memory Efficiency | Standard object-based memory management | Standard object-based memory management | Off-heap memory, avoids GC overhead | Off-heap memory, avoids GC overhead |
| Performance | Optimized for sorting and aggregation | Optimized for key-value aggregation | Highly optimized for sorting binary data | Optimized for shuffle performance |
Shuffle读写
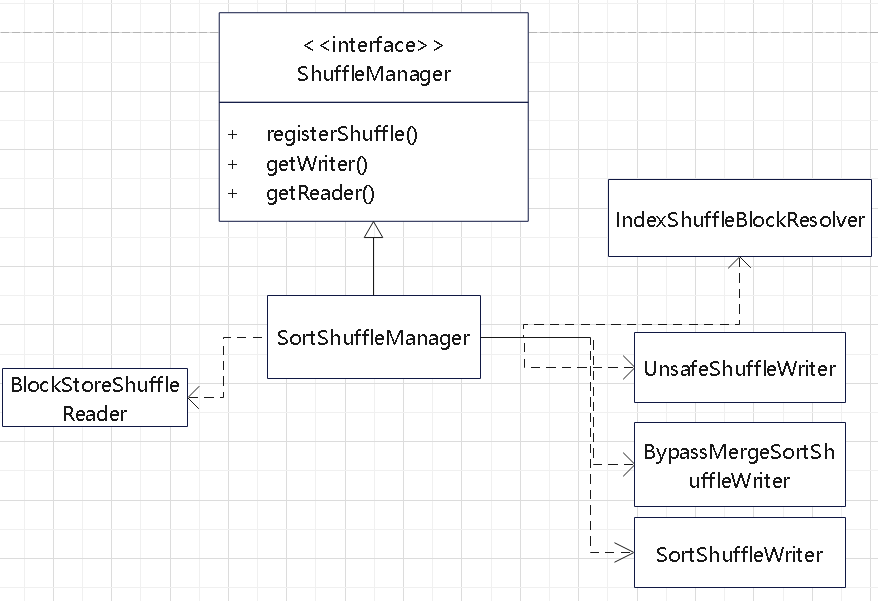
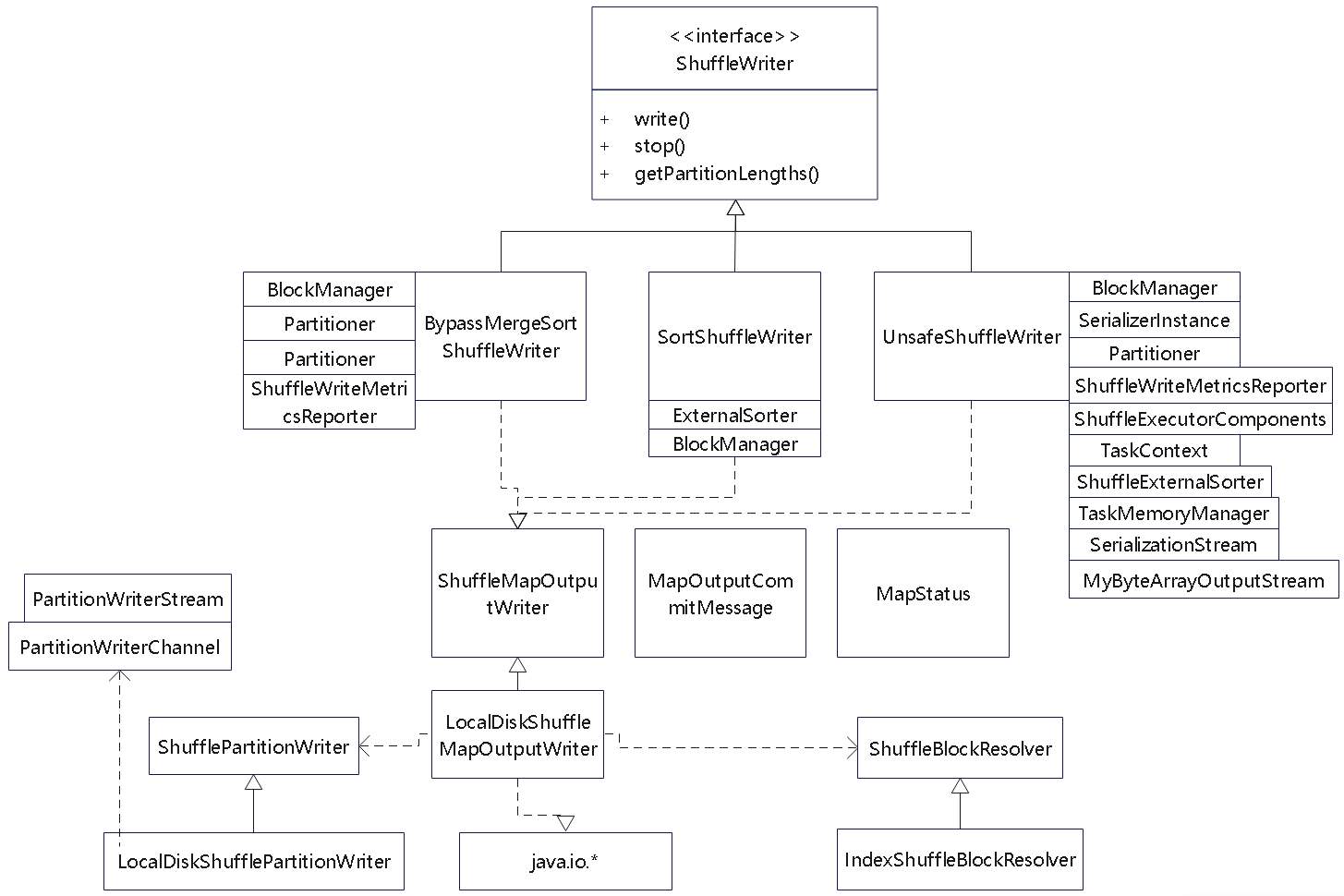
几个shuffle 的类图结构
- 父类都是 ShuffleWriter
- 三个子类:BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter、SortShuffleWriter、UnsafeShuffleWriter
- 这三个类都用了 ShuffleMapOutputWriter 完成 map 端的写磁盘操作
- 它只有一个实现类 LocalDiskShuffleMapOutputWriter
- 又关联了ShufflePartitionWriter、ShuffleBlockResolver,并使用 java.io 类完成最终写入
- map端不需要在持久化数据之前进行聚合、排序等操作。可以用:BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter
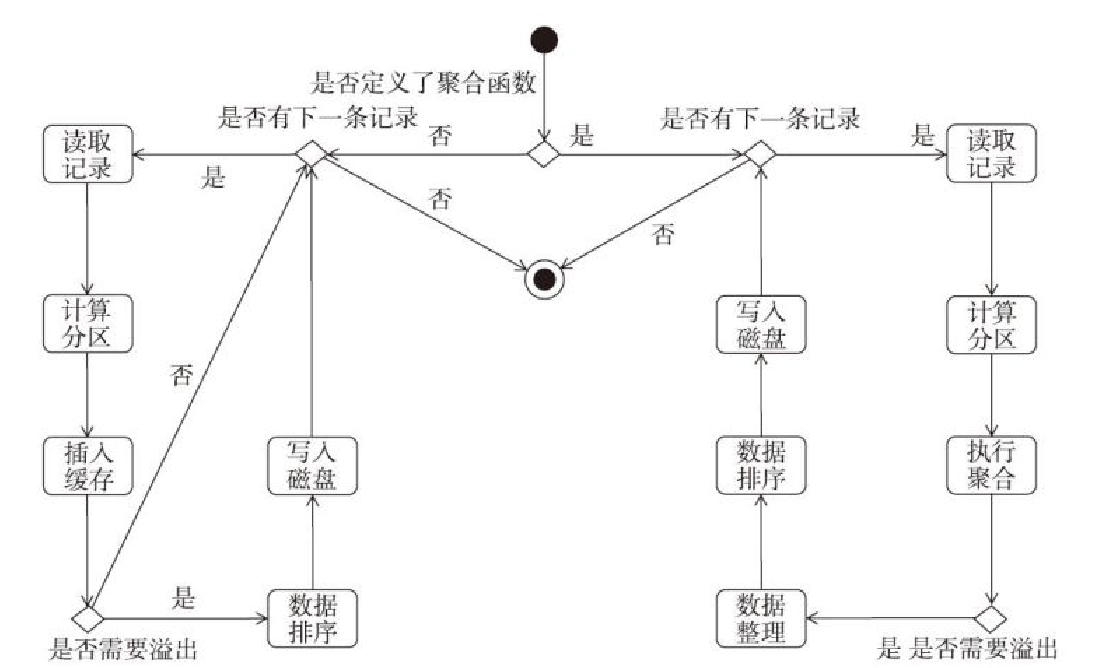
SortShuffleWriter在map端聚合的执行流程,也可以不在 map 端聚合
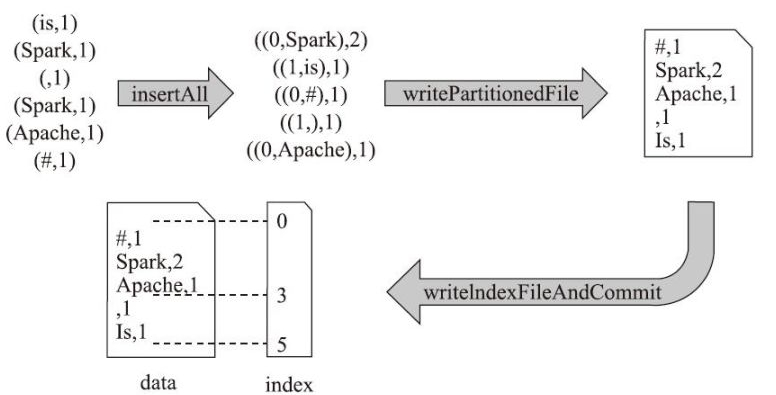
BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter的write方法的执行流程
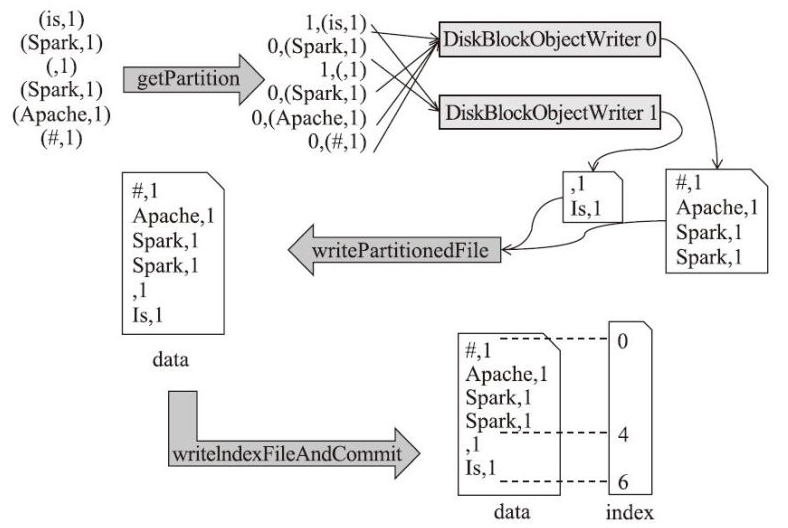
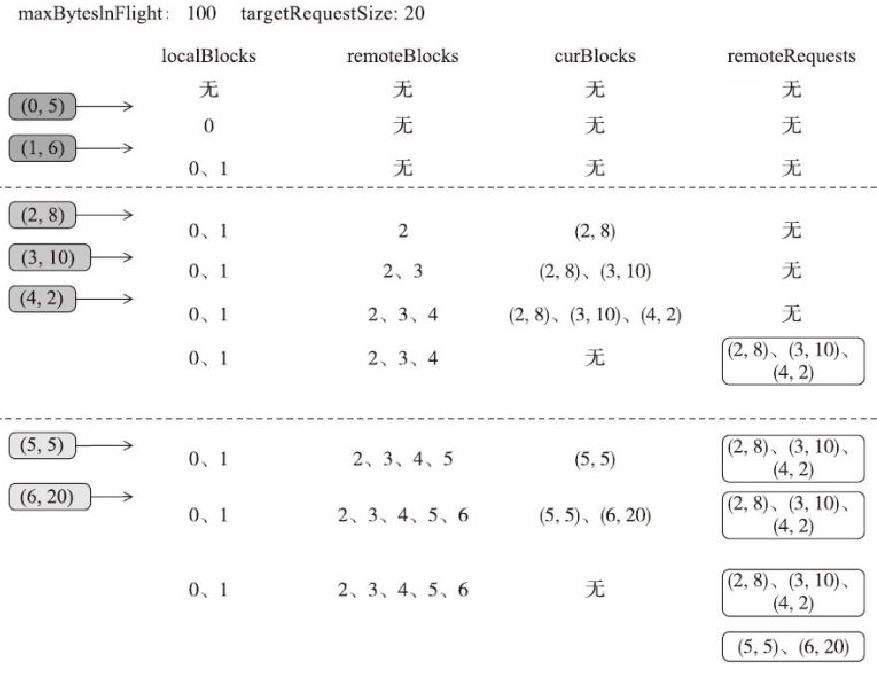
shuffle read 相关的类
- 核心是委托给 ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator 完成的
- 这里会不断 fetch 拿到 block块
- 可能从远端获取,也可能从 本地获取
- 根据 FetchResult 的结果,有不同的 case 判断
- BlockStoreShuffleReader表示reducer从其他Block文件中读取 起始、结束指定范围内的数据
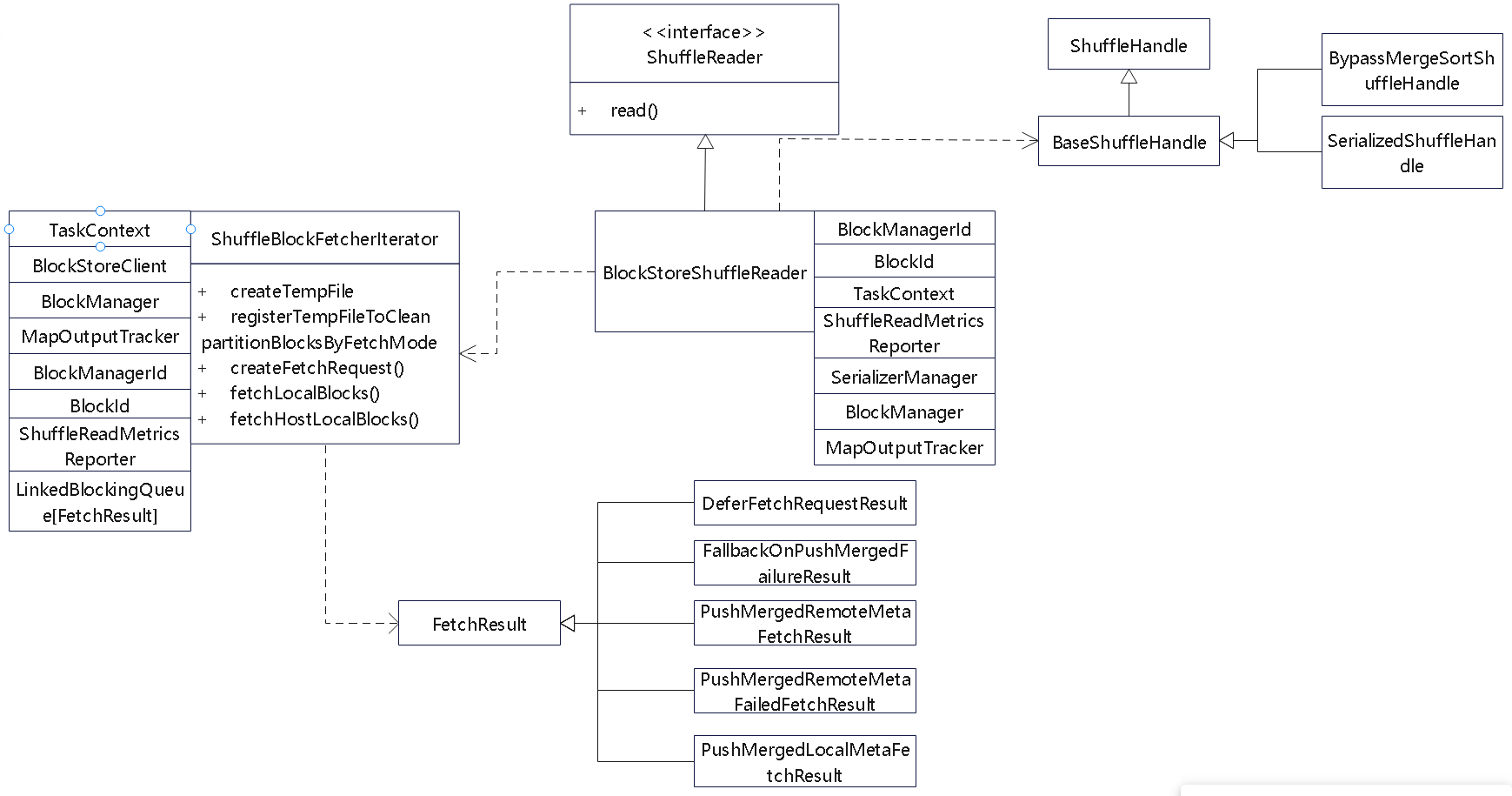
此外还有一个 ShuffleManager 抽象类
|
|
部署模式
Task
Task 相关的类图
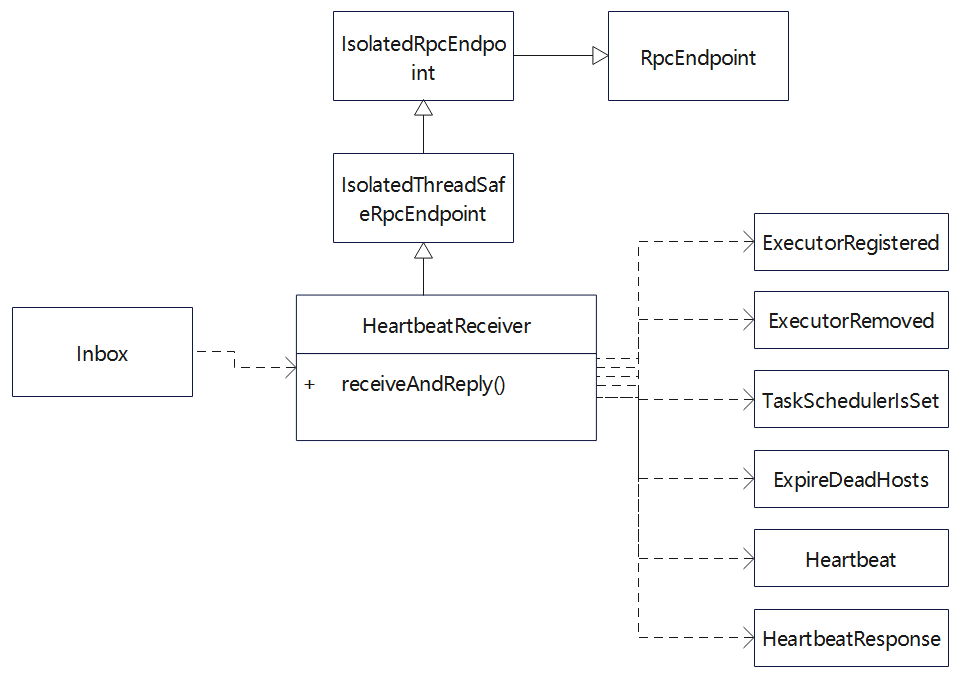
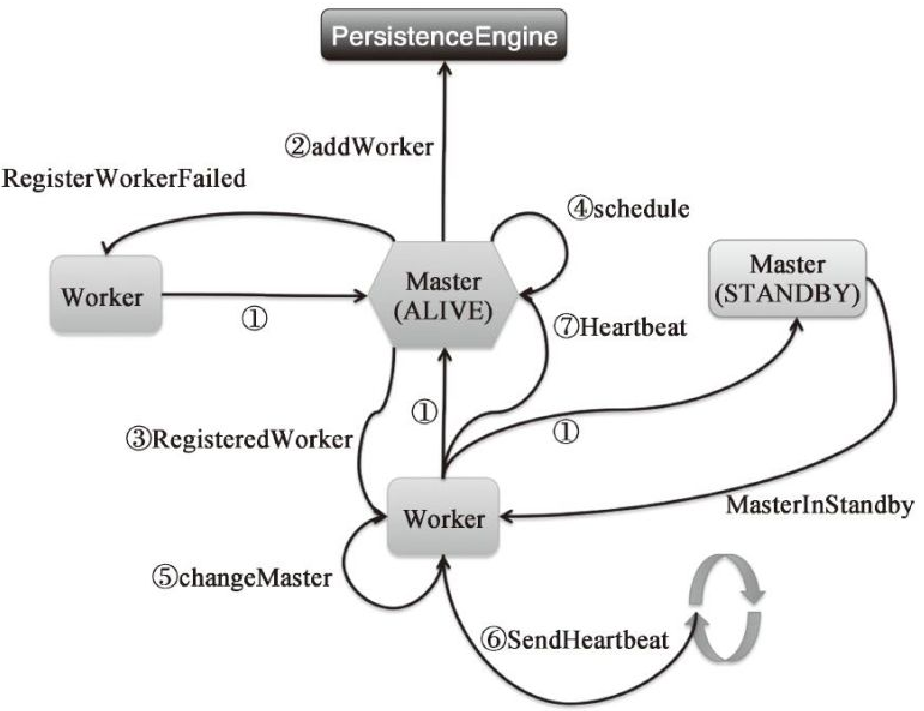
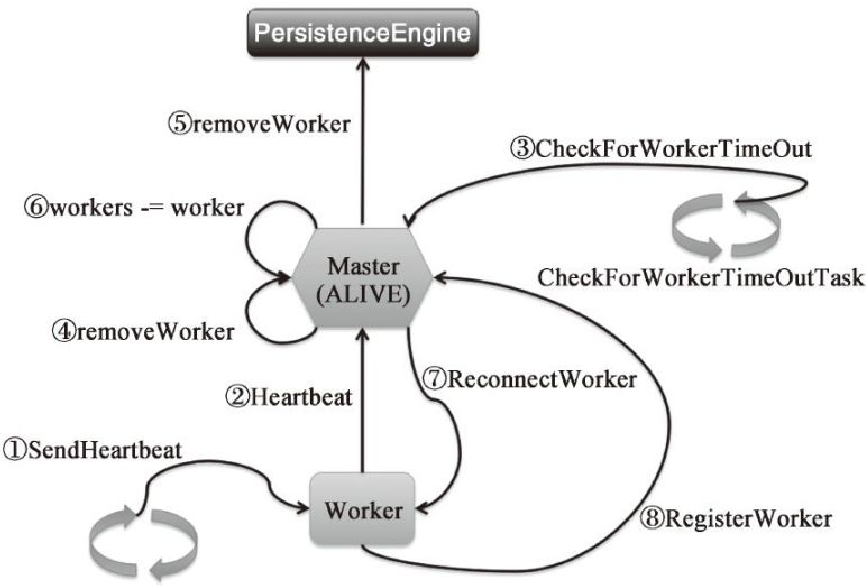
心跳相关类图
Master
当 master 故障后,选举出新的 master
- 抽象类:PersistenceEngine
- BlackHolePersistenceEngine
- FileSystemPersistenceEngine
- ZooKeeperPersistenceEngine
LeaderElectionAgent 抽象类
- MonarchyLeaderAgent
- ZooKeeperLeaderElectionAgent
org.apache.spark.deploy.master.Master 的类图
- 继承了领导选举的类
- 关联了 worker,application、driver 等info 类
- 还有一些 metrics、web-ui 的类
- 以接收到数据后的一些 case 类,根据case 条件调用相应的判断
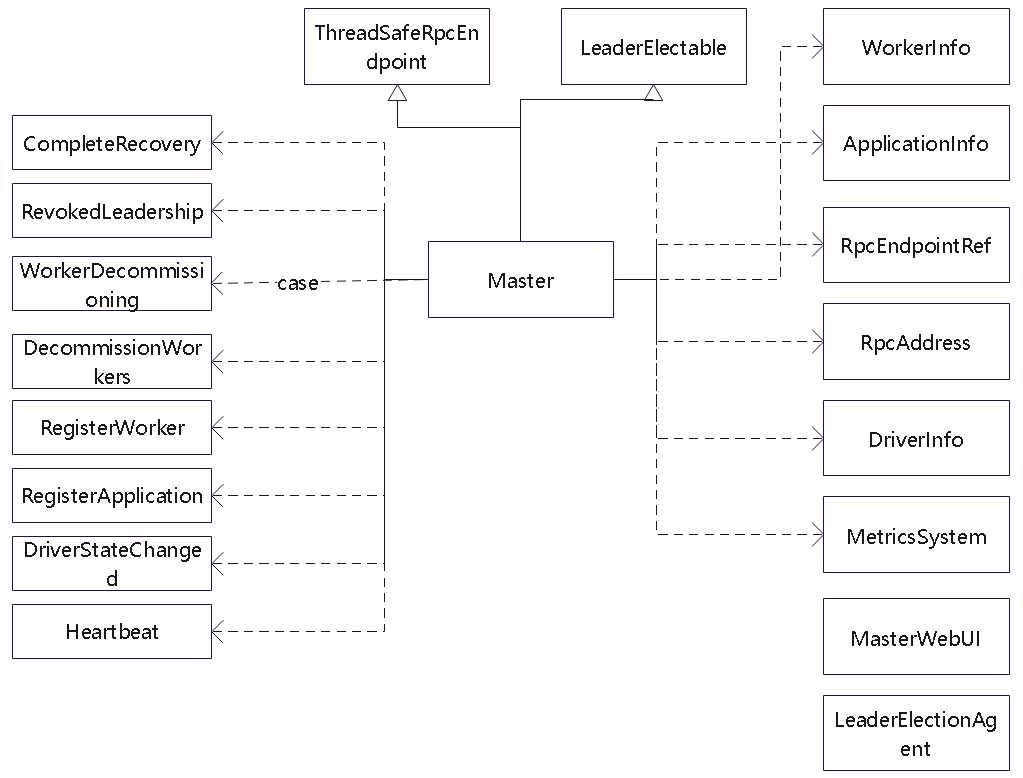
Master 包含的一些功能
- 启动
- 检查 worker 超时
- 被选举为领导时的处理
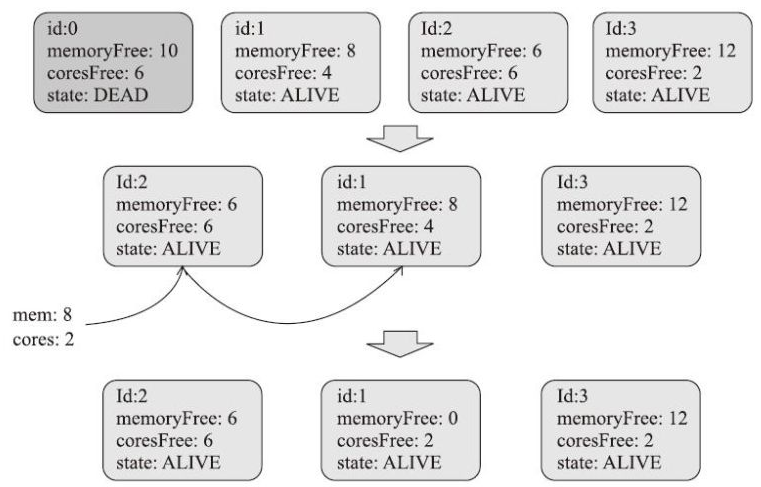
调度过程
- Driver 调度时,先对所有 worker 做shuffle,只调度活跃状态
- 然后挨个看是否满足条件
- 比如当前需要 2C8G,id-2 不满足,id-1 满足
- 调度到 id-1 后,同时修改 id-1 剩余的资源
- 之后发送 RPC 请求,运行 driver
executor 分配过程
假设
- 有 3 个 worker,每个 4C,20G,启动 3个 executor,每个 2C10G
- 第一个 worker 分配一个 executor,剩余 2C10G
- 第二个 worker 分配一个 executor, 剩余 2C10G
- 第三个 worker 分配一个 executor,剩余 2C10G
- 如果是 spreadOutApps为 false
- 第一个 worker 会分配 2 个executor,剩余 2C,0G
其他的一些情况
- 注册 worker
- 启动 worker
- 更新 worker 状态
- 处理Worker的心跳
- 注册Application
- 处理Executor的申请
- 处理Executor的状态变化
Worker
相关类图
- 跟Master 类似,这里的 reciver 函数,接收到消息后
- 根据 case 处理不同的事件
- 它会关联一个 ExternalShuffleService类
- 这个类用来接收 reducer的读取shuffle数据,元信息回存储在 roacksDB或者 levelDB中
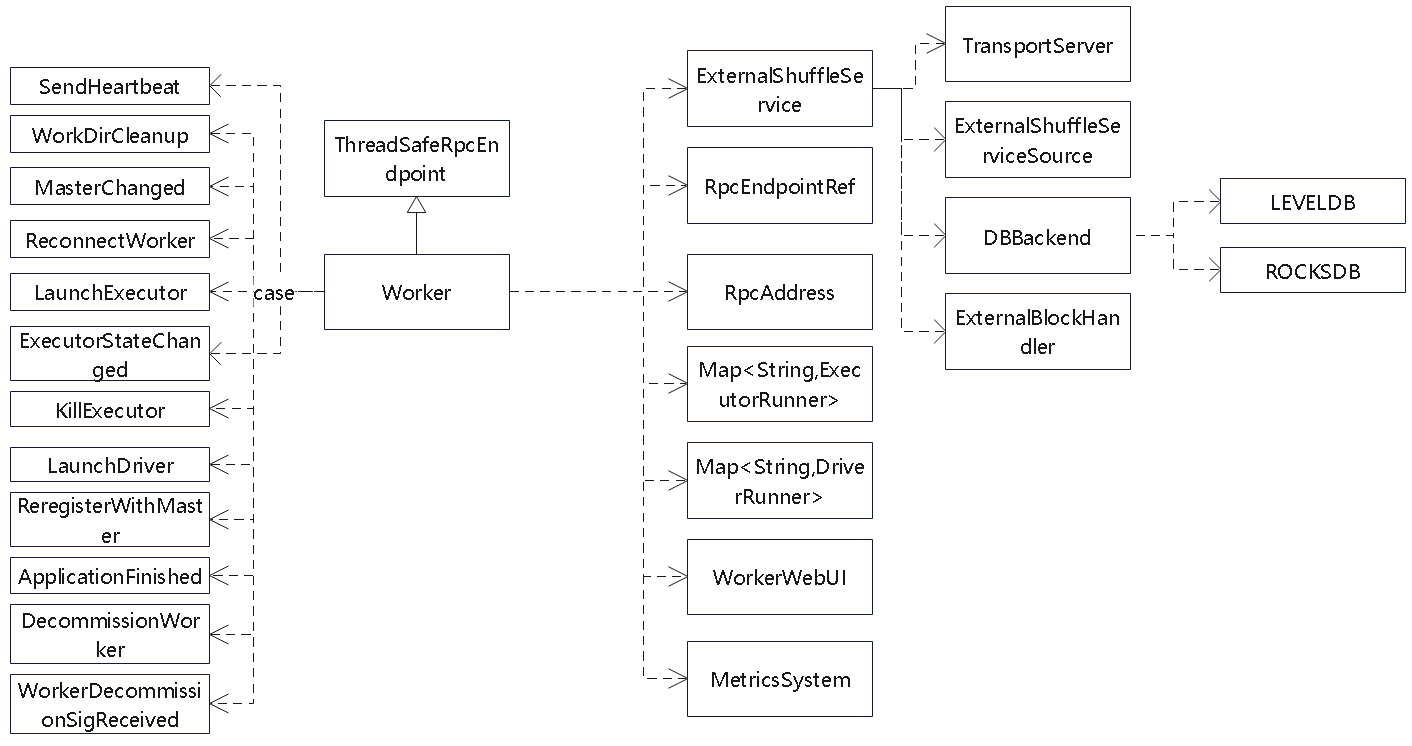
启动过程
- 创建 临时目录
- 创建 ExternalShuffleService,如果设置为true
- 创建 woker 资源
- 启动 web-ui
- 注册 metrics
worker 中包含了 main,可以作为新的 java 进程方式启动
同时也会解析传入的参数,作为新进程的参数来启动
其他的一些行为
- 向Master注册Worker
- 向Master发送心跳
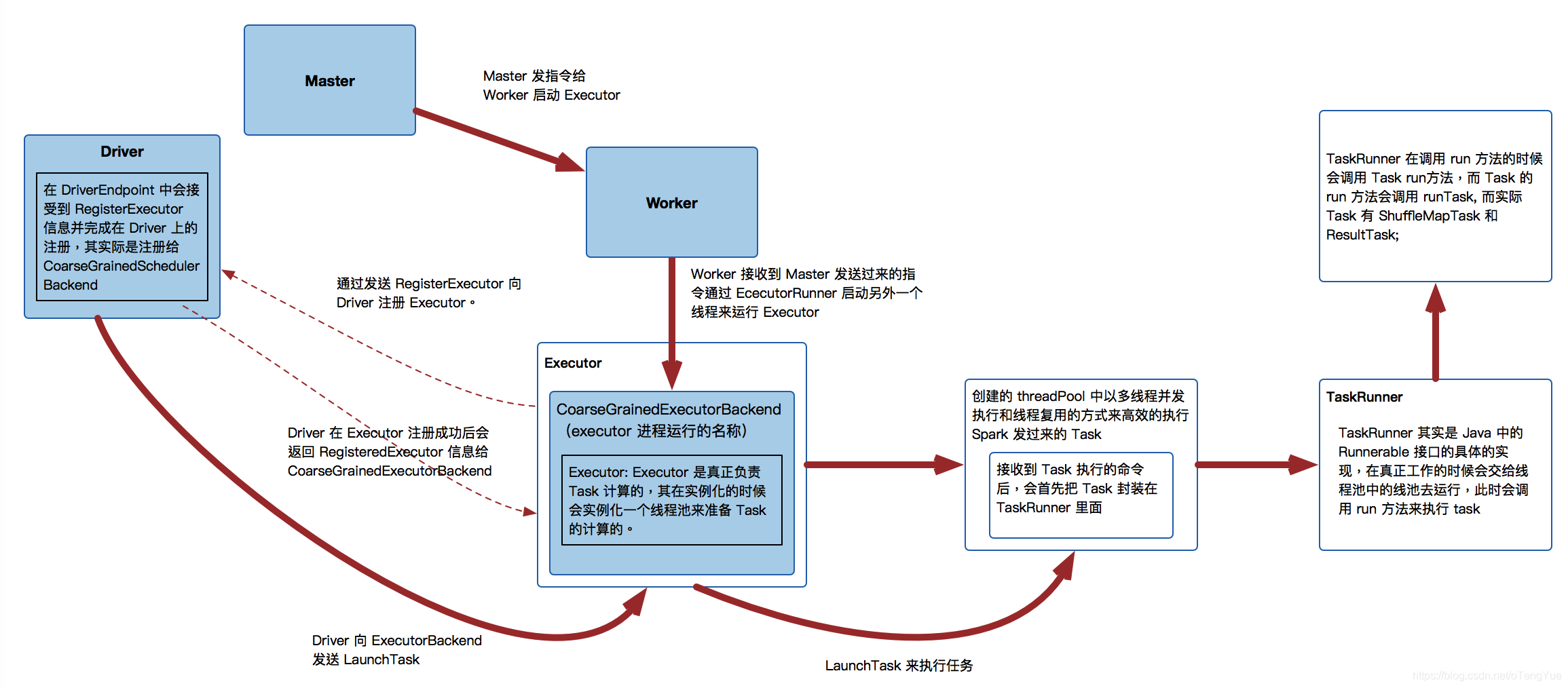
Executor 启动
- 通过 ExecutorRunner 启动的
- 这个类的 start()函数中,创建新线程来启动 executor
- fetchAndRunExecutor 中获取资源信息,然后封装出 ProcessBuilder
- 之后启动新进程,传入命令行参数,启动 executor
- 再封装 executor 的输出、错误信息,将日志写到 指定文件中
- worker 还负责接受 executor 退出信息,并发送 executor 状态变更通知
Executor 停止
- 启动时会保存 java.lang.Process
- 通过 Process 类来关闭进程
- 同时关闭对应的日志文件
StandaloneAppClient
- 应用程序和 spark standalone 模式的交互客户端
- 负责创建、停止
- 创建会向 master注册
- 接收各种 case 类的事件
- ApplicationRemoved
- ExecutorAdded
- ExecutorUpdated
- WorkerRemoved
- MasterChanged
Executor
CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 主要功能
- Task Execution:
- Receives tasks from the driver via the TaskScheduler and executes them on the executor.
- Manages the lifecycle of tasks and reports the status (success/failure) back to the driver.
- Communication with Driver:
- Communicates with the driver using the CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend via RPC (Remote Procedure Call).
- Registers itself with the driver when it starts (registerExecutor).
- Resource Management:
- Allocates CPU and memory resources for tasks on the executor.
- Manages task threads using a thread pool.
- Data Processing:
- Reads shuffle data, processes RDD partitions, and performs transformations/actions.
CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend 主要功能
- Resource Management:
- Allocates resources (CPU, memory) for executors on the cluster.
- Manages executor registration and lifecycle (e.g., launching, removing executors).
- Task Scheduling:
- Works with the TaskScheduler to assign tasks to executors.
- Sends LaunchTask messages to executors via CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend.
- Fault Tolerance:
- Detects failed executors and nodes, and handles retries or rescheduling of tasks.
- Cluster Communication:
- Communicates with the cluster manager (e.g., YARN, Kubernetes, Mesos) to request resources.
- Tracks executor state and resource availability.
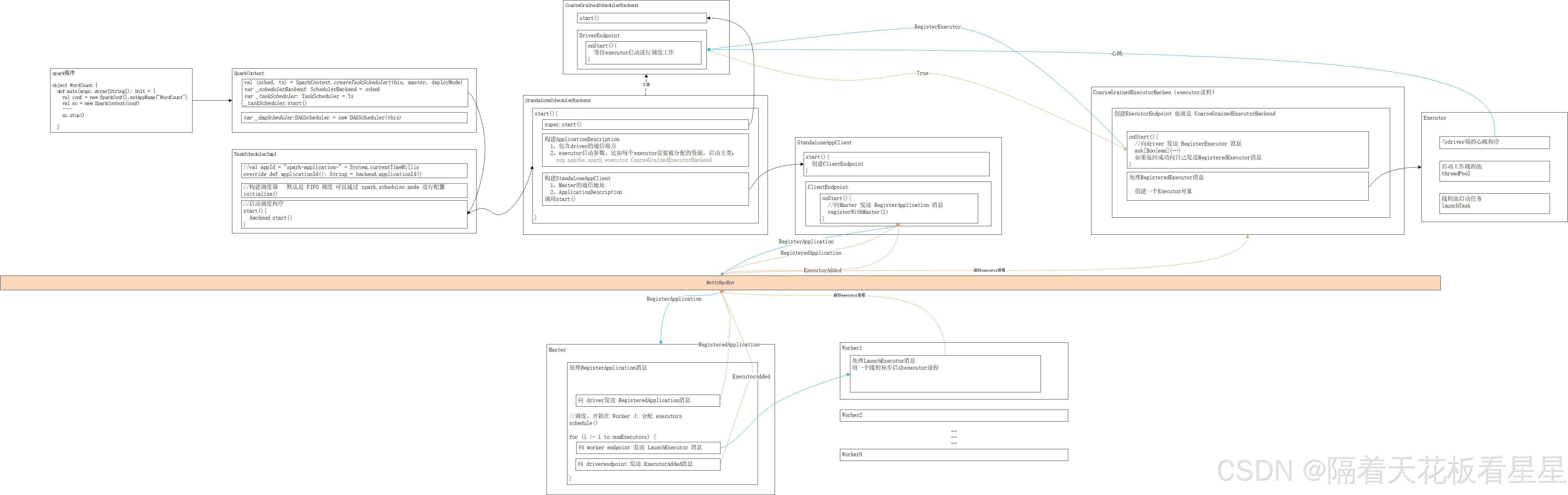
Local 集群部署方式
local-cluster部署模式的启动过程
- 由 LocalSparkCluster启动 Master
- 这里还会注册选举,不过只有一个Master,它就是活跃的
- 之后 LocalSparkCluster 创建 Woker,Woker 向 Master注册
- 在创建出 StandloneSchedulerBackend,并由它创建出 StandaloneAppClient
- StandaloneAppClient 会向 Master注册

local-cluster部署模式下的Executor资源分配过程
- master 向 worker 触发 启动 executor 命令
- 委托 ExecutorRunner,创建新进程
- CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 会向 Driver注册 executor 信息
- CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 会启动 Executor
- CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 和 Executor 在各种模式下都是一个 JVM内的
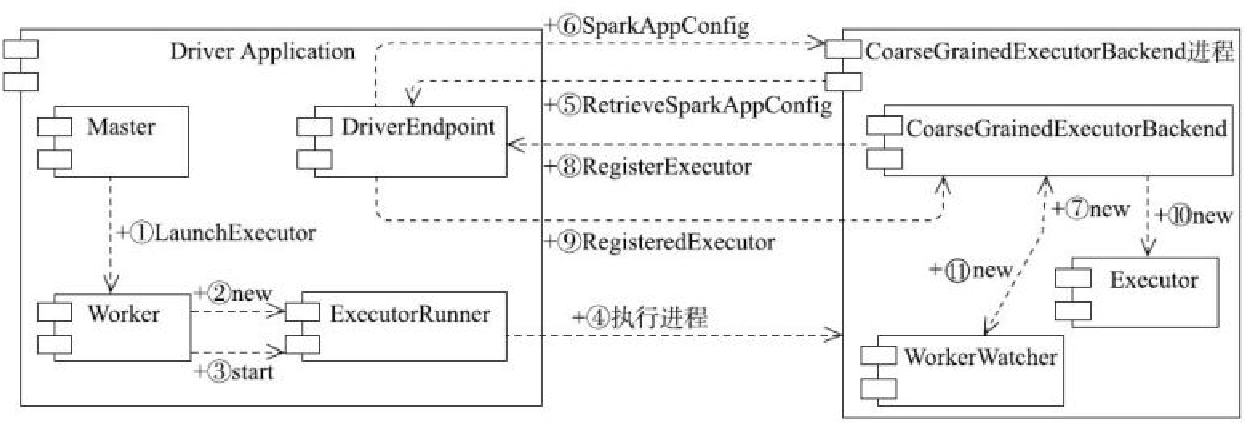
local-cluster部署模式下的任提交过程
- TaskSchedulerImpl 提交 Task 任务,之后发送给 Driver
- Driver 调用 TaskSchedulerImpl获取资源分配情况
- Driver 发送给 CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 进程,launchTask
- CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 启动 Executor,,并调用Executor#launchTask 启动 Task
- Executor 会不断更新 Task状态,并同步给 Driver
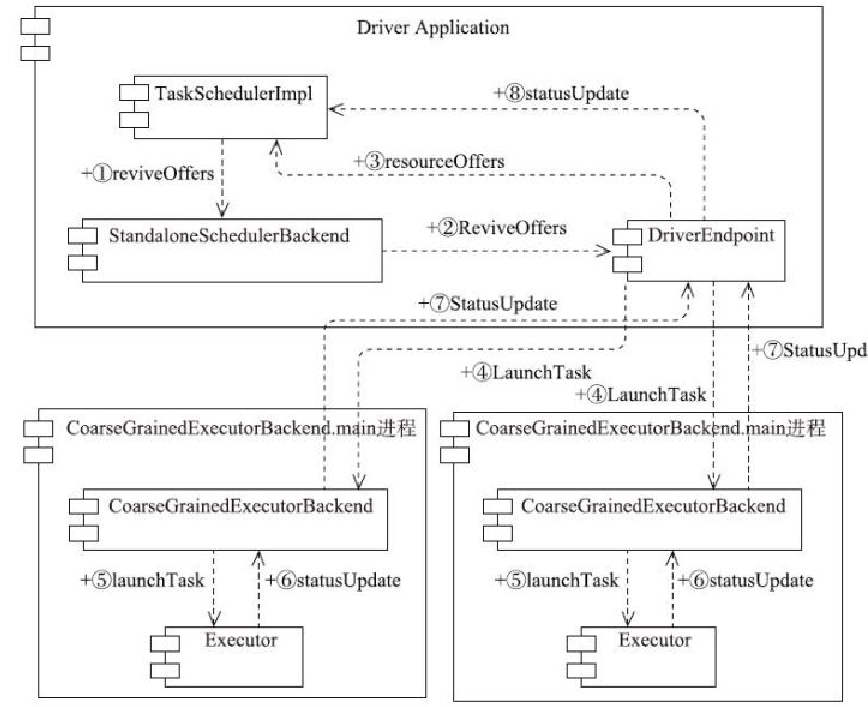
集群部署
Standalone部署模式的启动过程
- Standalone模式下会有多个 Master,每个Master都会向 ZK 注册选举
- Worker 会向 Master注册信息
- 启动 Dirver,TaskSchedulerImpl会调用 StandaloneSchedulerBackend,再启动 StandaloneAppClinet
- 之后Driver 向 Master 注册
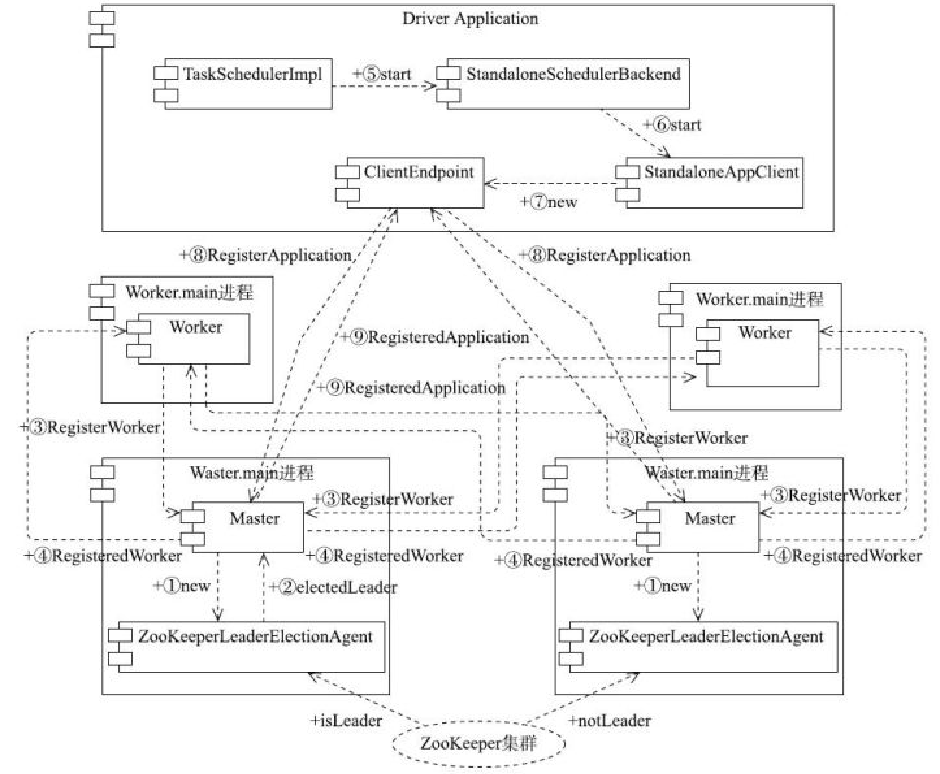
Standalone部署模式下的Executor资源分配过程
- master发送启动 executor 的命令
- worker 接收到后,创建ExecutorRunner,后者负责启动新进程
- 通过 ProcessBuilder 方式启动新进程,也就是CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend
- CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend会向 Dirver 注册
- 启动 executor 并向 driver 注册
- CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend会向创建 WorkerWatcher,后者负责跟Worker通讯
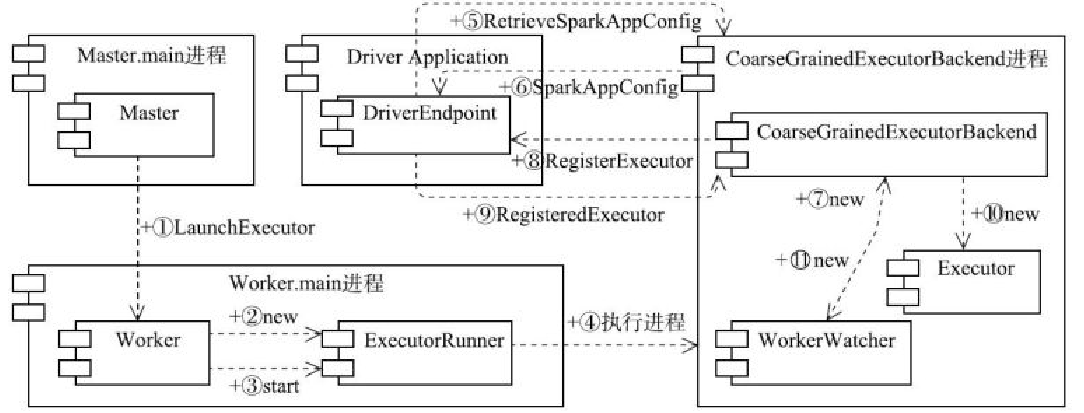
Application 退出
- 由于会保持 netty的网络通讯
- 当 application 正常或者异常退出,都会触发到 master
- master会调用响应机制,回收资源
Executor异常退出的容错处理
- worker 会持有 executor 的 java.lang.Processor 句柄
- 当 executor 正常或者异常退出时,worker都会感知到
- worker会转交给master
- mater将 driver发送 launchExecutor 命令
- 启动 executor并将driver 注册

Worker异常退出的容错处理
- worker退出后,master的心跳超时
- 正常情况下,当 executor 被杀死、退出时候会通知 worker
- worker再通知master,当超时后
- master会向driver发送 executor状态更新的消息
- driver 会发送启动 executor 的消息
- master向其他 worker节点发送 launchExecutor 的消息

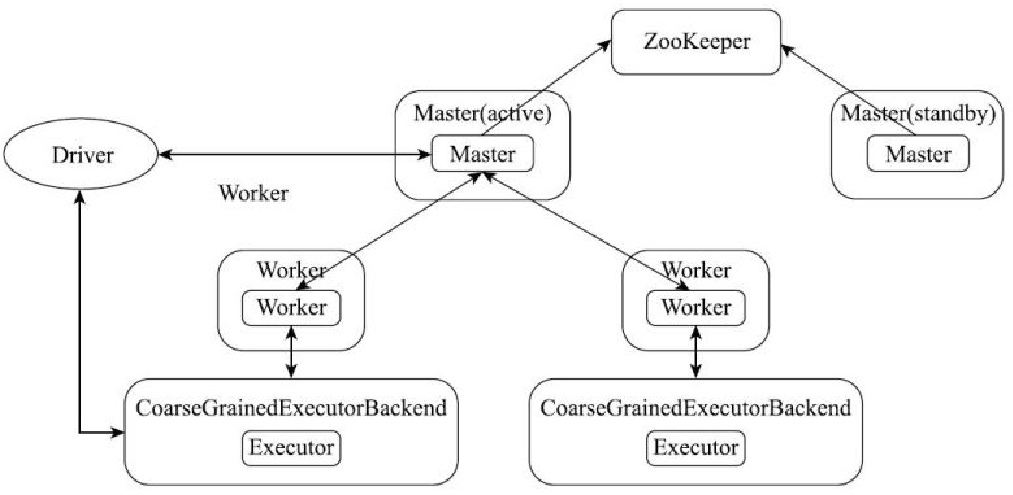
ZooKeeper热备和选举示意图
- 只有一个maser时,当master挂了,driver和executor都可以正常运行
- 当executor异常退出时,driver的新任务无法提交,executor占用资源无法被释放(master没了)
- 如果worker退出,则driver无法提交任务
- 新的driver 也无法提交任务
- 新master选举后会重新跟worker、driver通讯
Key Components
- Master: The central coordinator in Standalone mode responsible for managing workers and resources.
- Worker: A node that hosts executors to perform task execution.
- Driver: The client-side process responsible for submitting applications, scheduling tasks, and orchestrating execution.
- Executor: A distributed process responsible for executing tasks and storing data.
- CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend: Driver-side scheduler for managing executors.
- CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend: Executor-side component for task execution and communication with the driver.
Deployment Modes and Relationships
| Mode | Master Process | Worker Process | Driver Process | Executor Process | Component Relationship |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local-Cluster | Single JVM | Simulated as threads in JVM | Same JVM | Same JVM (threads simulate executors) | All components run in the same JVM. CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend and Executor in the same thread. |
| Standalone Cluster | Separate JVM | Separate JVM | Separate JVM | Separate JVM per executor | Master manages Workers. Each Worker launches executors. CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend and Executor in the same executor process. |
| YARN/Kubernetes | N/A | N/A | Separate JVM | Separate JVM per executor | Cluster manager launches executors. CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend and Executor in the same executor process. |
YARN模式
YARN的架构
- ResourceManager(RM):全局资源管理器,负责整个集群的资源管理与分配
- ApplicationMaster(AM)与RM通信获取资源,将作业划分为更细粒度的任务,与NodeManager(NM)通信启动或停止任务,监控失败任务
- NodeManager(NM):单个节点上的资源与任务管理器,它负责向RM定时汇报本节点的资源使用情况及各个Container的状态
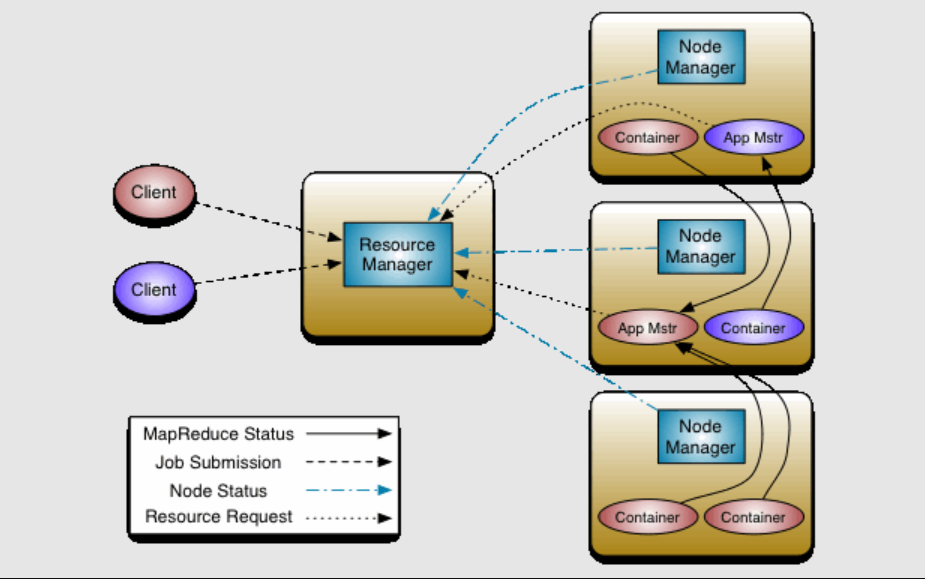
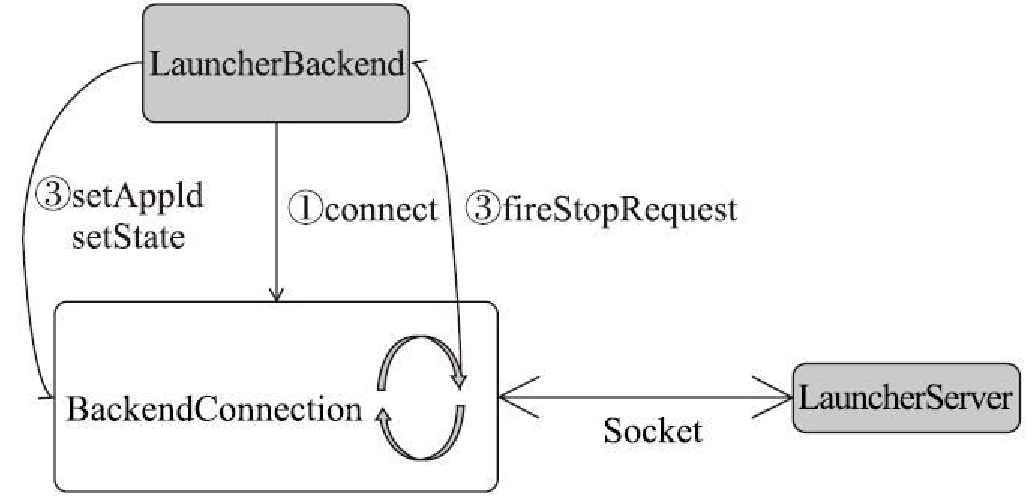
cluster 模式下,spark整合YARN
client 模式下
cluster模式、client模式对比
| Aspect | YARN Client Mode | YARN Cluster Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Driver Location | Runs on the client machine. | Runs inside the YARN cluster. |
| Fault Tolerance | Less fault-tolerant (client failures affect execution). | More fault-tolerant (driver managed by YARN). |
| Network Latency | Higher latency due to driver-executor communication over WAN. | Lower latency as driver and executors are co-located. |
| Use Case | Interactive applications (e.g., Spark Shell). | Batch or production jobs with no user interaction. |
| Resource Allocation | Client handles driver resources, YARN manages executors. | YARN manages both driver and executor resources. |
| Client Dependency | The client must remain active for the driver. | The client can disconnect after submission. |